Method for evaluating cooperative transformation of asphalt pavement material and optical fiber grating sensor
A fiber grating and asphalt pavement technology, applied to instruments, optical devices, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problem that the data cannot be directly used to evaluate the stress state of the asphalt pavement structure, and achieve the effect of simple force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
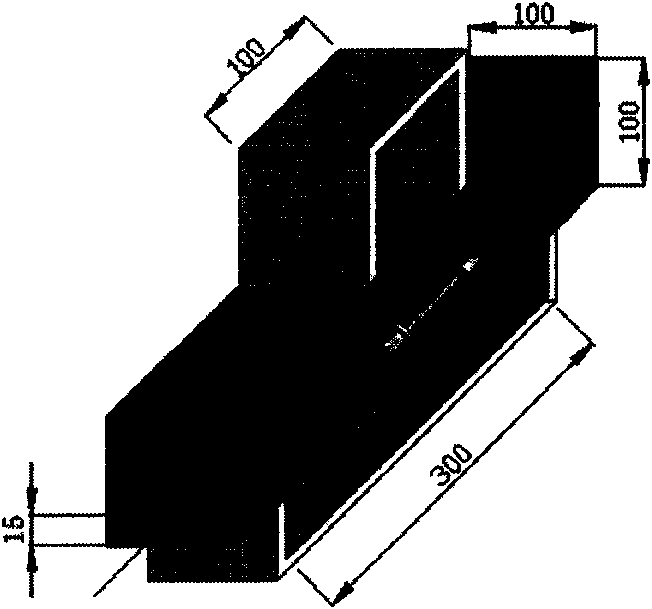
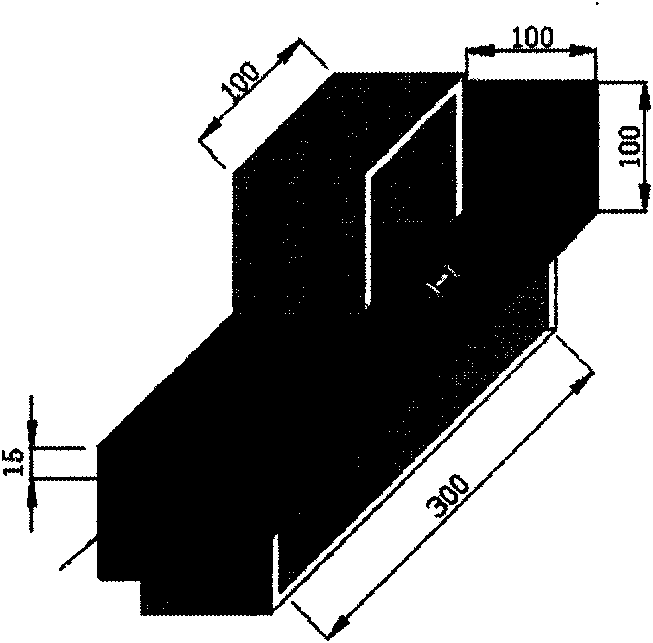
[0015] Specific implementation mode one: see Figure 1~3 , the method for evaluating the cooperative deformation of the asphalt pavement material and the fiber grating sensor described in the present embodiment is realized according to the following steps:
[0016] Step 1. Implant the sensor into a cuboid mold with asphalt mixture, which is called a beam specimen; design the beam specimen implanted with the sensor as a four-point bending wide beam stress model; compact The asphalt mixture in the cuboid mold makes it truly simulate the asphalt pavement to be tested; the sensor is located at the upper or lower part of the neutral plane of the beam specimen; the corresponding position of the bottom end surface of the beam specimen is equipped with an LVDT displacement sensor; the test conditions The temperature is fixed.
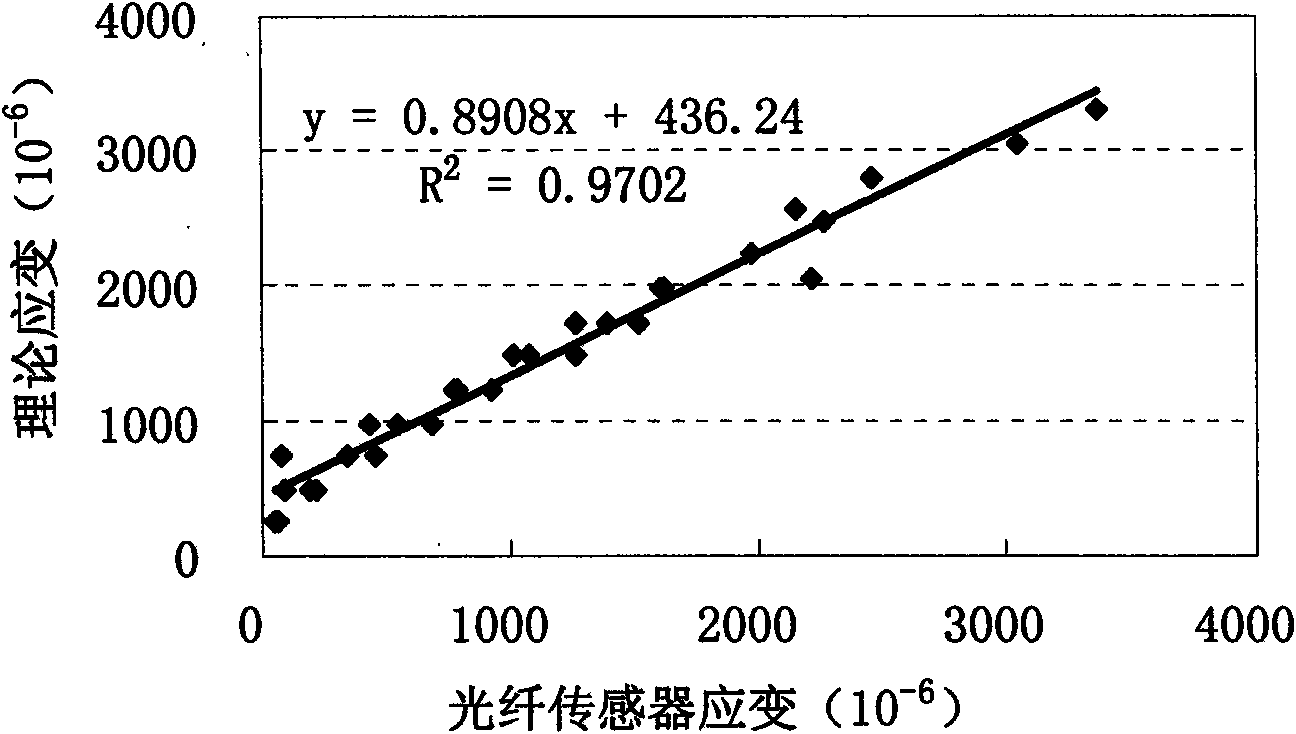
[0017] Step 2. Applying static load step by step on the upper end surface of the beam test piece at the corresponding position of the implanted sensor at inte...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific embodiment 2: In step 1 of this embodiment, the temperatures used in the test are respectively 4°C, 15°C, 25°C, 40°C or 55°C. Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Embodiment 3: In step 1 of this embodiment, two LVDT displacement sensors are evenly distributed at corresponding positions on the bottom end surface of the beam specimen, and the collected array value is the average value of the two LVDT displacement sensors. This setting makes the measured results more accurate. Other steps are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0026] Examples (see Figure 1~3 ):
[0027] Step 1. Design principle and design form
[0028] a. The design principle, considering that the beam-type specimen is subjected to a load perpendicular to the axial direction, and when the beam body is subjected to bending deformation due to the bending moment generated by an external force, the stress state is simple, and the compression zone at the top of the beam and the tension zone at the bottom are both Obviously, it can better simulate the state of compression and tension in the actual road surface. For this reason, a four-point bending wide beam test ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com