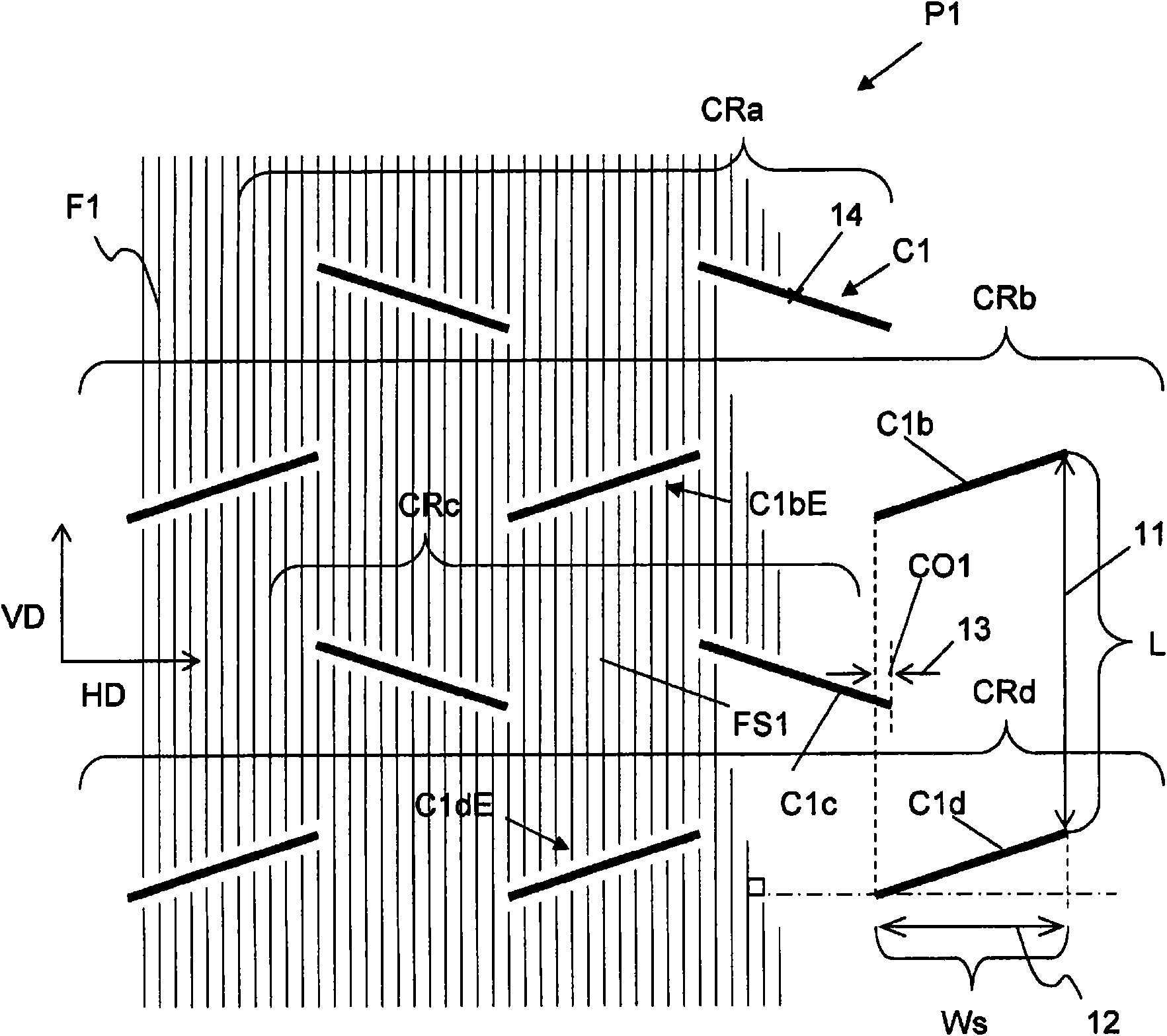
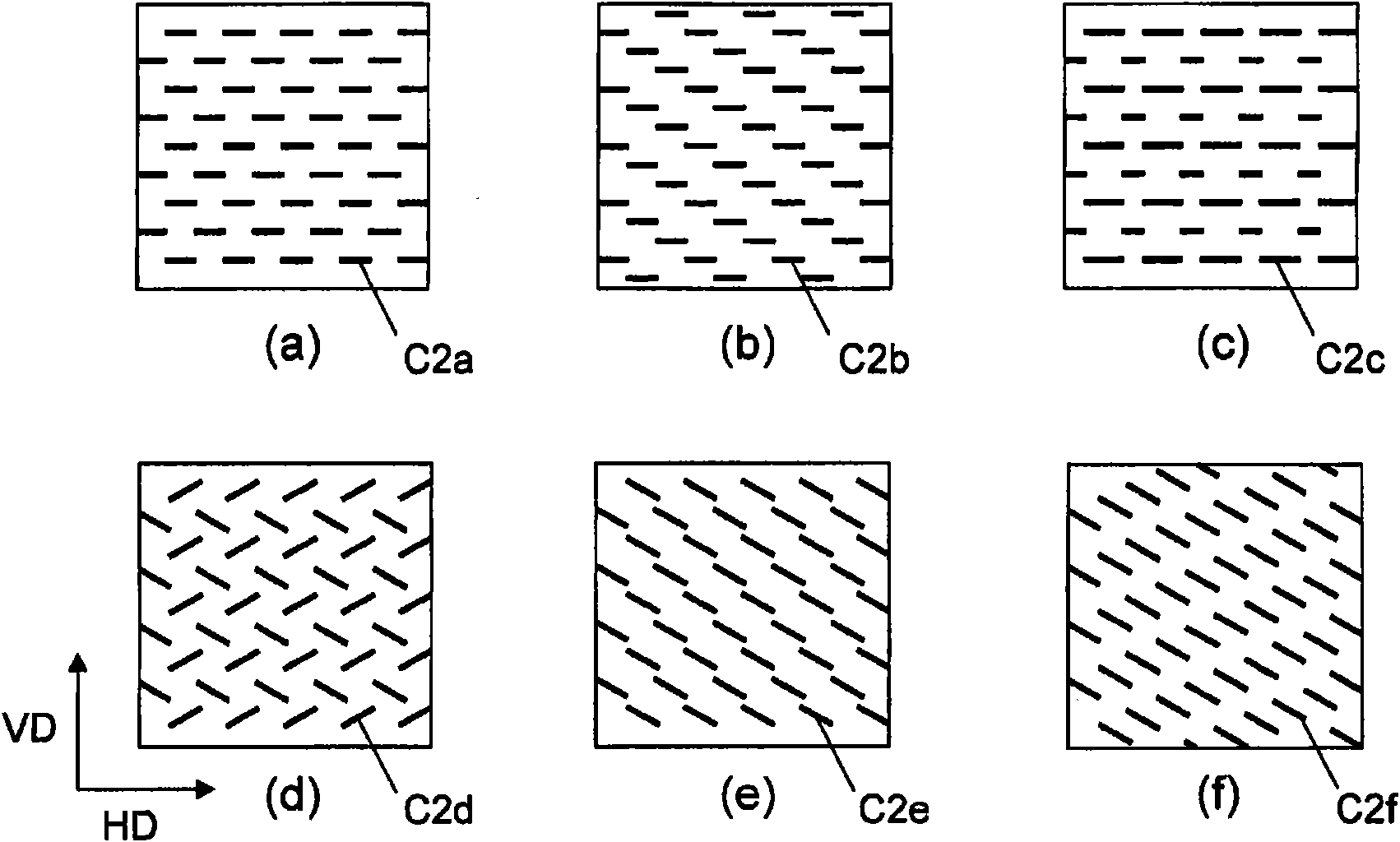
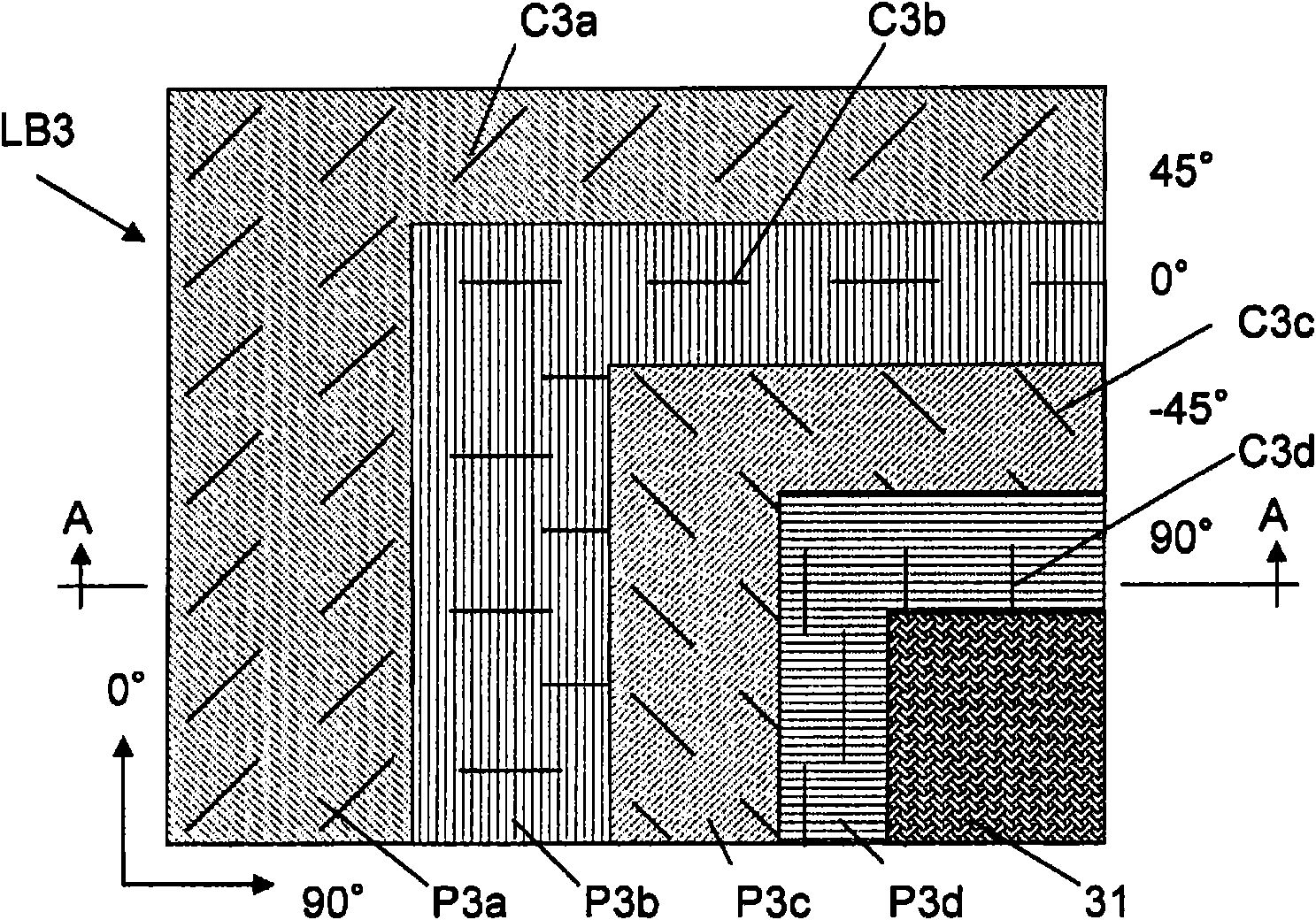
Prepreg base material, layered base material, fiber-reinforced plastic, process for producing prepreg base material, and process for producing fiber-reinforced plastic
A technology of prepreg and laminated substrates, which is applied in the field of laminated substrates, fiber reinforced plastics, and fiber reinforced plastics, and can solve the problem of reduced tensile strength, tensile fatigue strength, and unevenness of moldings , can not be considered to have problems such as strength, to achieve the effect of excellent mechanical properties, small unevenness, and excellent dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0290] Epoxy resin ("Epicoat (registered trademark)" manufactured by Japan Epoxy Resin Co., Ltd. 828: 30 parts by weight, "Epicoat (registered trademark)" 1001: 35 parts by weight, "Epicoat (registered trademark)" 154 parts by weight using a kneader : 35 parts by weight) and heated and kneaded 5 parts by weight of thermoplastic resin polyvinyl formal ("Vinylec (registered trademark)" K) manufactured by Chisso Co., Ltd. to dissolve the polyvinyl formal uniformly, and then kneaded Refining 3.5 parts by weight of curing agent dicyandiamide (Japan Epoxy Resin (Co., Ltd.) system DICY7), 4 parts by weight of curing accelerator 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (protected DCMU99 manufactured by Tsuchiya Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.) prepared an uncured epoxy resin composition. This epoxy resin composition was coated on silicon-coated release paper with a thickness of 100 μm using a reverse roll coater to prepare a resin film.
[0291] Then, a resin film is laminated on both sid...
Embodiment 2
[0302] Except that the curing accelerator was changed to 5 parts by weight of 2,4-toluene bis(dimethylurea) ("Omicure (registered trademark)" 24 manufactured by PTI Japan Co., Ltd.), it was performed in the same manner as in Example 1 to produce A notched prepreg base material, and a laminated base material using the base material. A fiber-reinforced plastic was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the pressing time (curing time) of the obtained laminated base material was changed to only 3 minutes with a heat-type press molding machine. Although the pressing time was 1 / 10 of that of Example 1, it showed substantially the same glass transition temperature, and it was found that the epoxy resin composition used had excellent rapid curing properties.
[0303] The resulting fiber-reinforced plastic has no fiber undulations and the fibers flow equally to their ends. In addition, there was no warpage, and it had good appearance quality and smoothness. The tens...
Embodiment 3
[0305] Except that the curing accelerator was changed to 7 parts by weight of 4,4-methylene bis(phenyl dimethyl urea) ("Omicure (registered trademark)" 52 manufactured by PTI Japan Co., Ltd.), the same method as in Example 2 was used. Methods to obtain fiber reinforced plastics. Although the pressing time was 1 / 10 of that of Example 1, it showed substantially the same glass transition temperature, and it was found that the epoxy resin composition used had excellent rapid curing properties.
[0306] The resulting fiber-reinforced plastic has no fiber undulations and the fibers flow equally to their ends. In addition, there was no warpage, and it had good appearance quality and smoothness. The tensile elastic modulus was 44 GPa, and the tensile strength was 430 MPa, showing high values. The coefficient of variation (CV value) of the tensile strength was 5%, showing a low value. The above values are not inferior to those of Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com