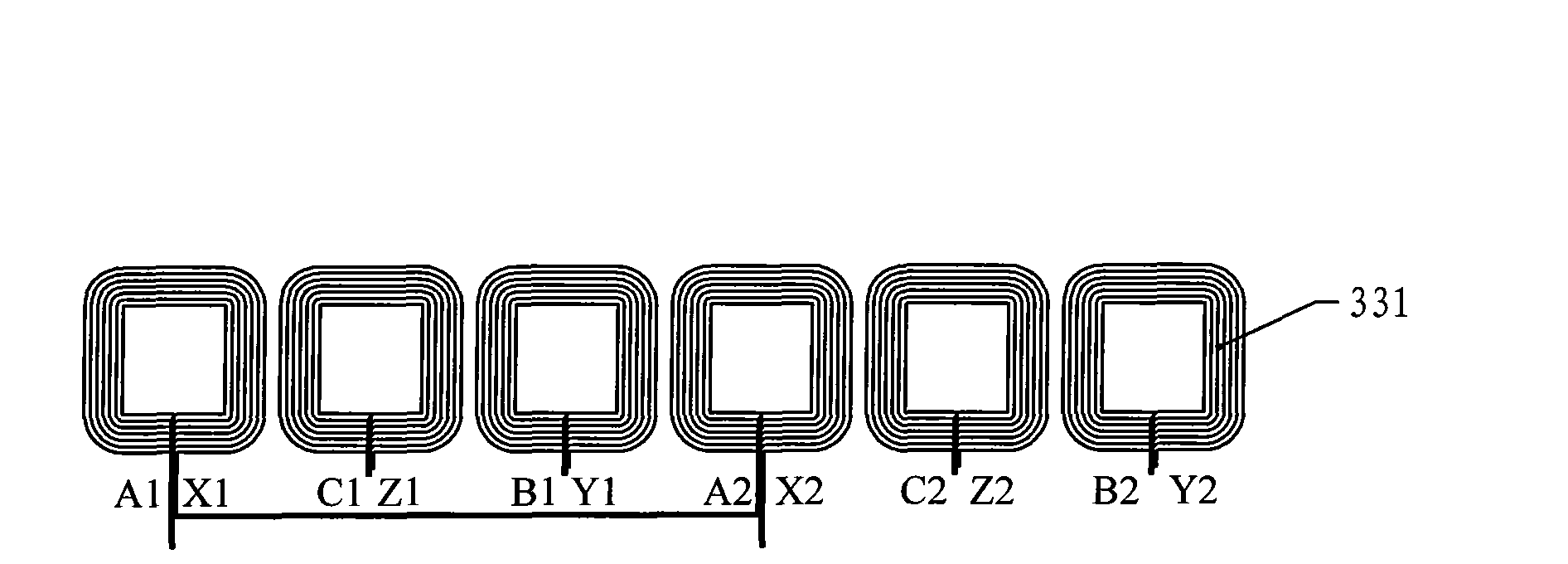Flywheel motor adopting no-cross one-range winding
A flywheel motor and single-plane technology, applied in the field of motors, can solve problems such as poor torque stability, large power consumption, and complex structure, and achieve the effects of stable operation, low loss, and small size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
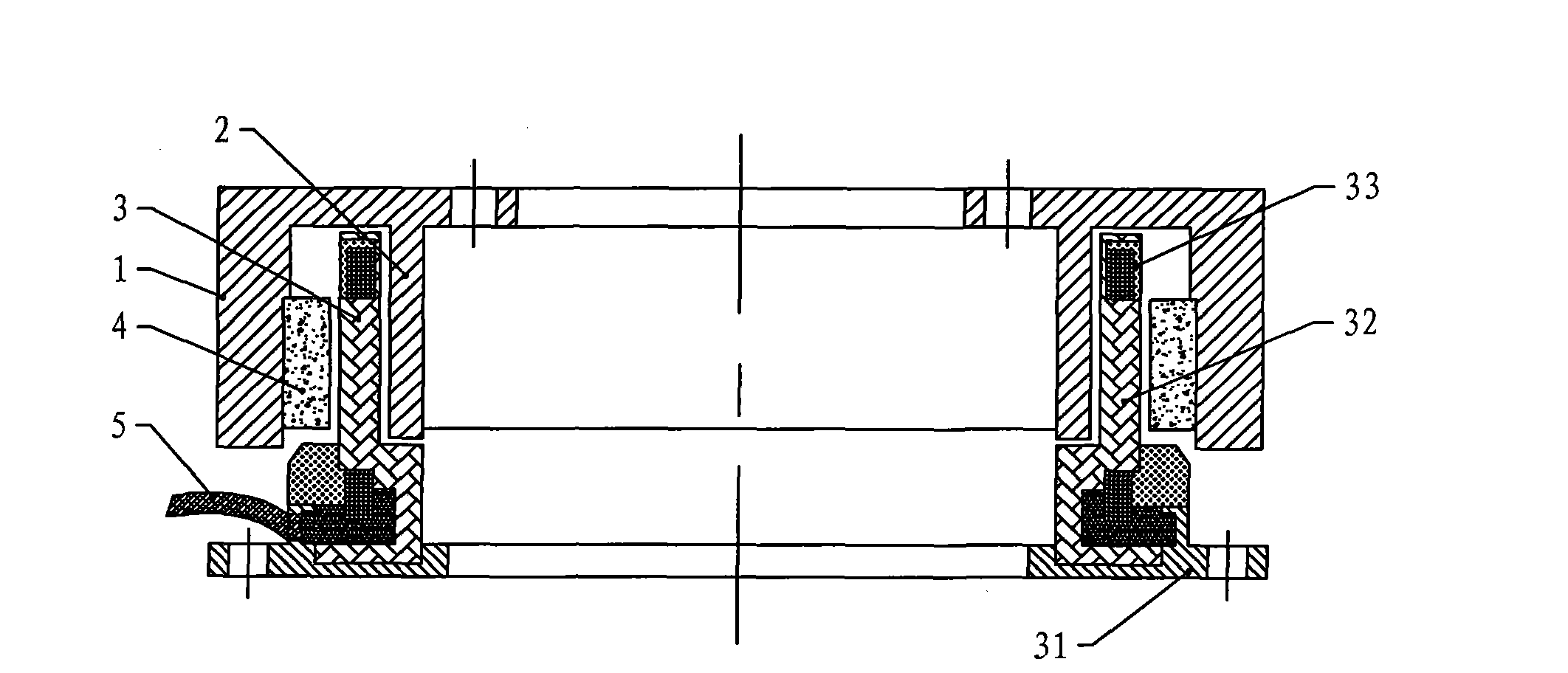
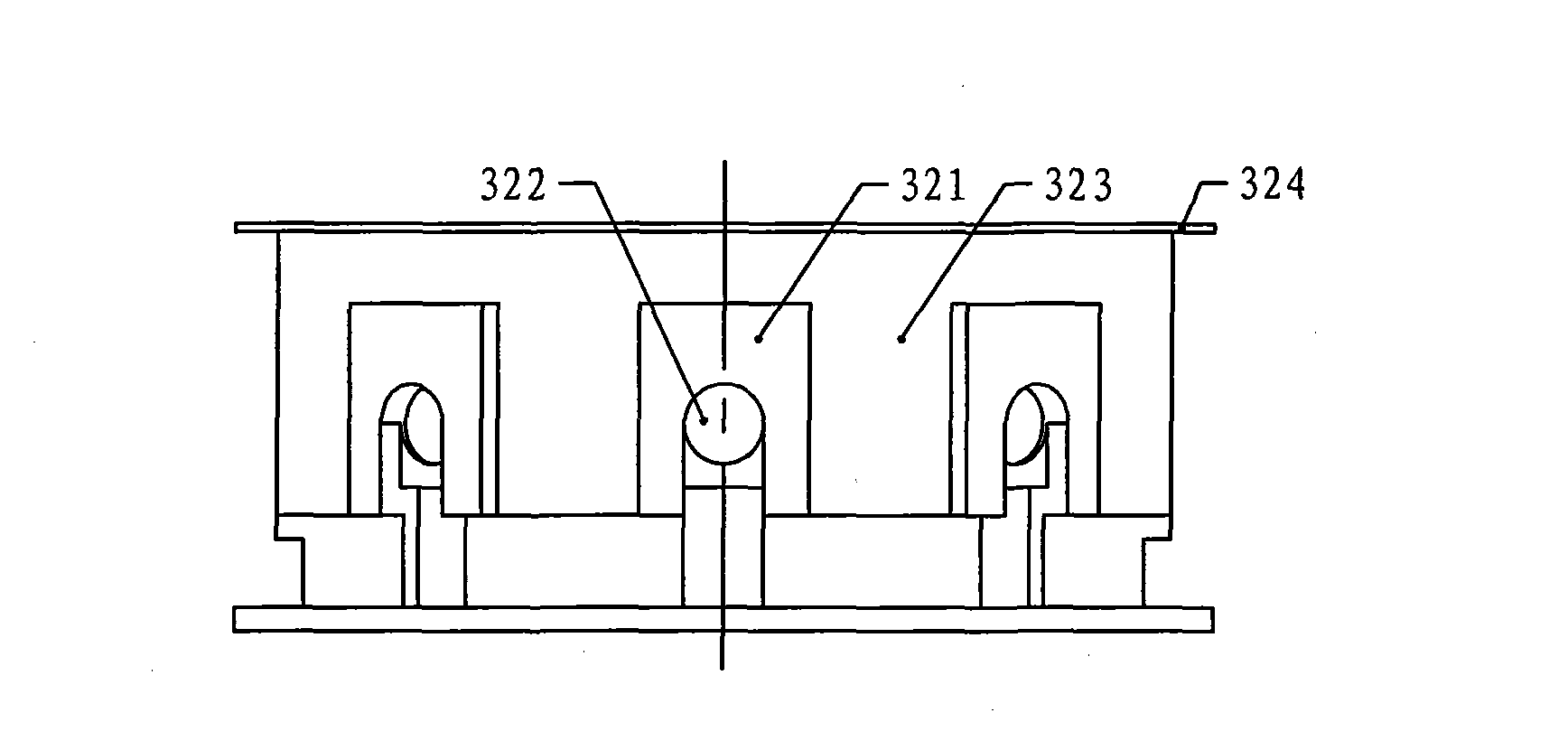
[0017] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 This embodiment will be described. The flywheel motor using non-crossing single-plane windings described in this embodiment is composed of a rotor, a coreless skeleton stator 3, a permanent magnet 4 and three position sensors. The rotor is composed of an outer rotor core 1 and an inner rotor core 2. The inner rotor core 2 and the outer rotor core 1 are fixedly connected on the torque output shaft, and the coreless skeleton stator 3 is fixed between the inner rotor core 2 and the outer rotor core 1, and is connected with the inner rotor core 2 and the outer rotor core. There is an air gap between the rotor cores 1, and the permanent magnet 4 is fixed on the inner rotor core 2 or the outer rotor core 1 on the side wall opposite to the coreless frame stator 3, and the coreless frame stator 3 is composed of a winding 33 , a skeleton 32 and a stator base 31, the skeleton 32 is fixed on the stator base 31, the winding 33 is a th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0037] Specific Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the flywheel motor without intersecting single-plane winding described in Specific Embodiment 1 is that the inner rotor core 2 and the outer rotor core 1 are split structures, and the inner rotor core 2 and one end of the outer rotor core 1 are connected by a beam 21 and fixed with screws.
[0038] In this embodiment, the inner rotor core 2 and the outer rotor core 1 adopt a split structure, which makes the installation of the permanent magnet 4 more flexible and facilitates production.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the flywheel motor without intersecting single-plane winding described in Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the permanent magnet 4 is fixed on the outer wall of the inner rotor core 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com