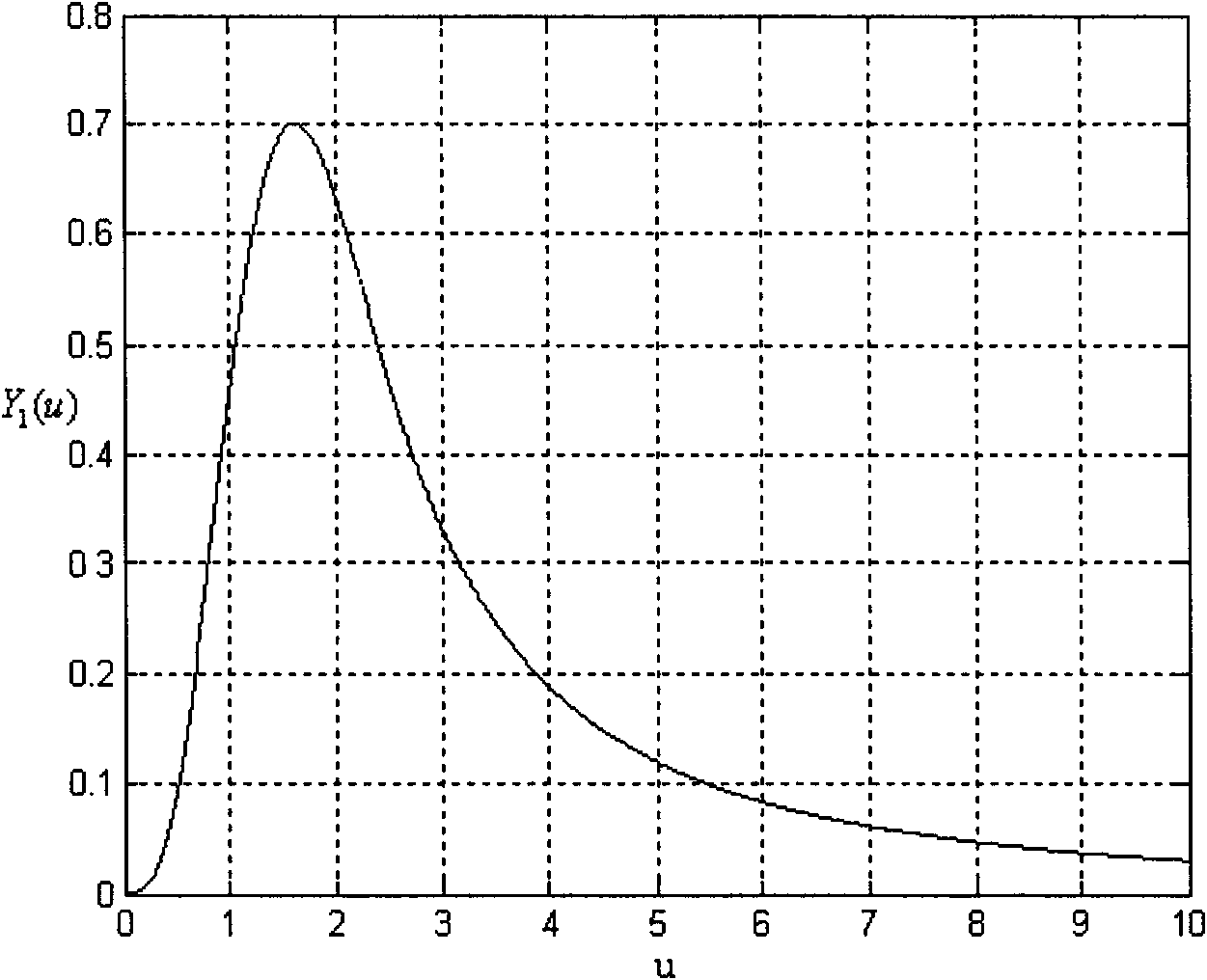
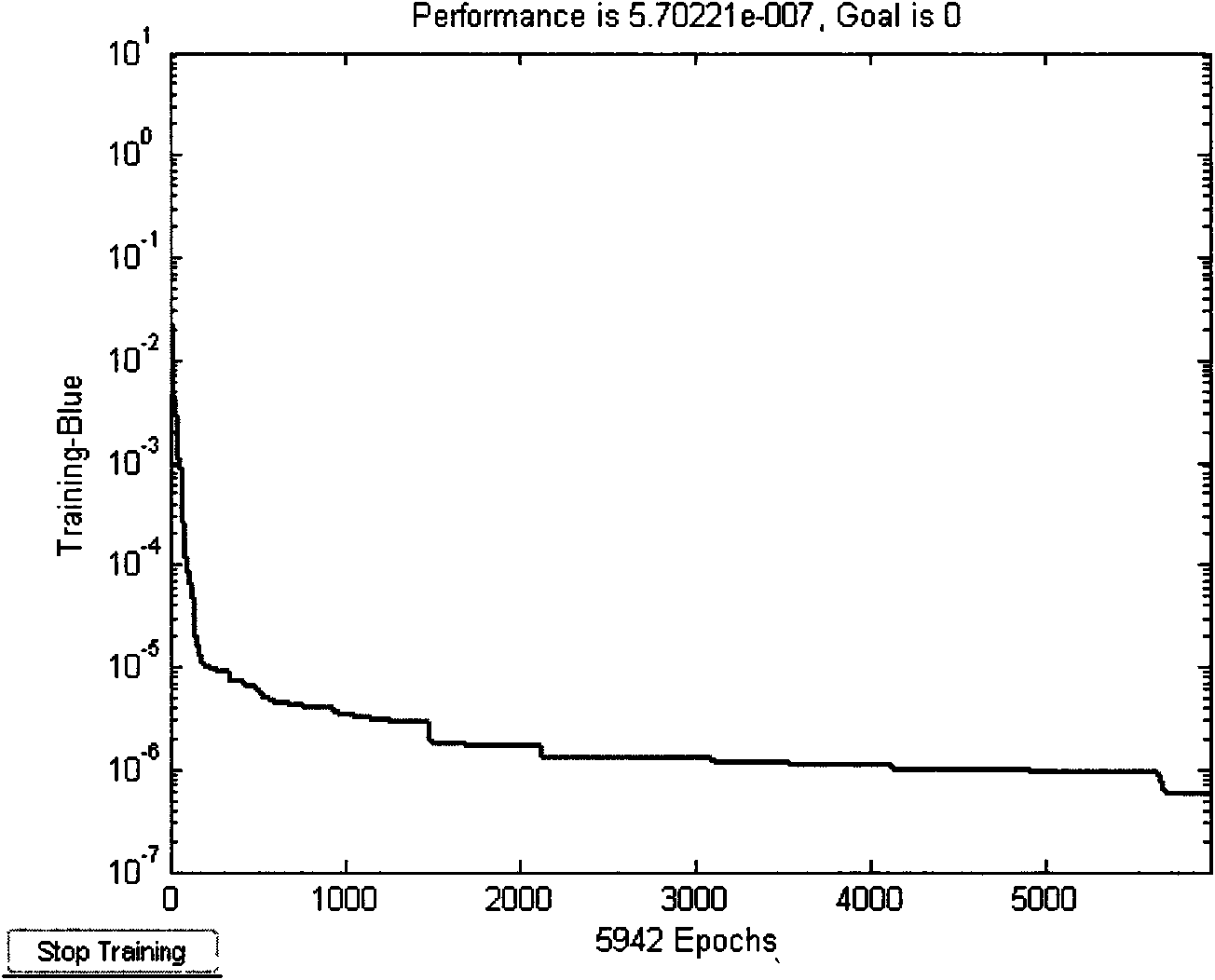
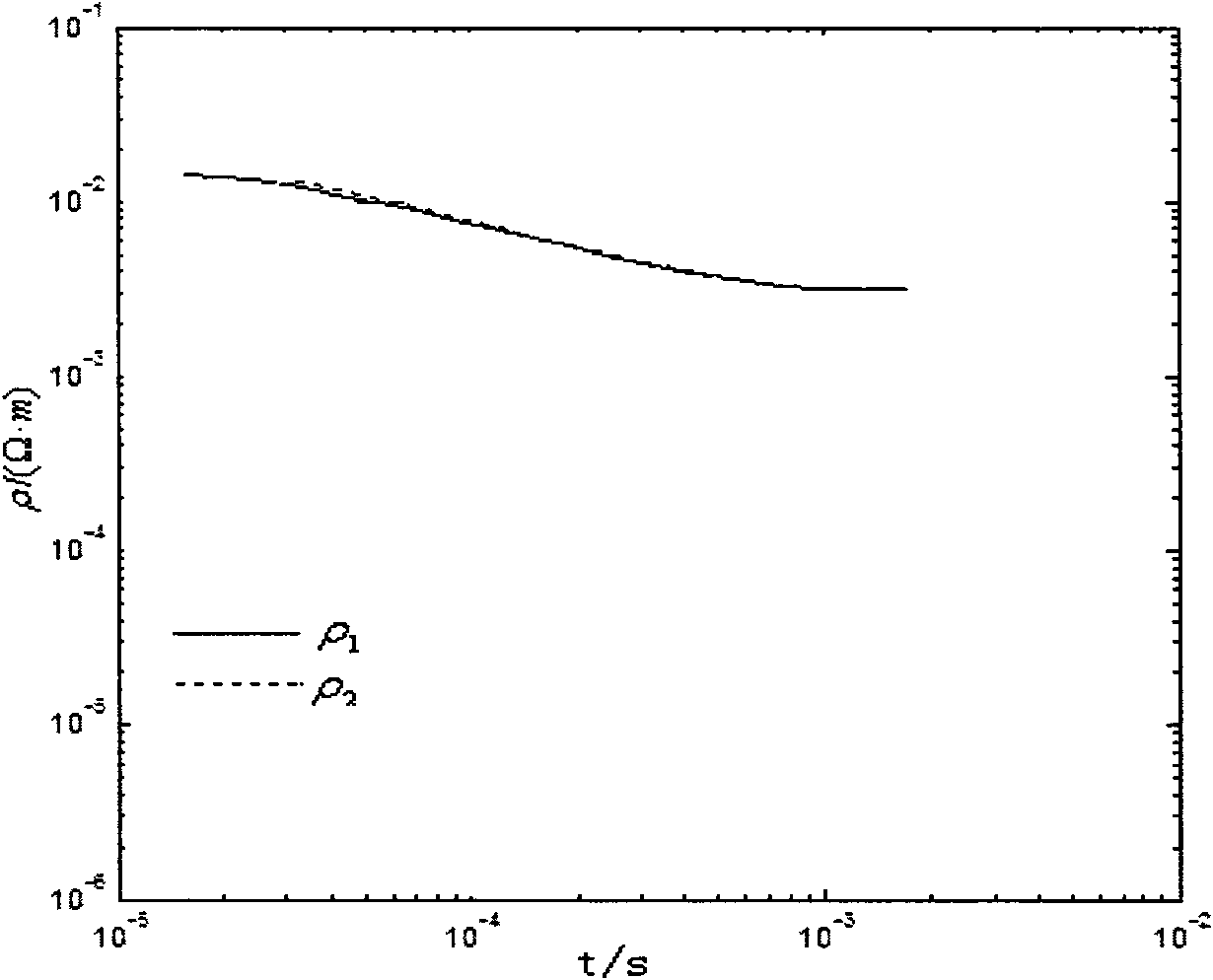
Back-propagation network calculating method of apparent resistivity
A technology of backpropagation network and apparent resistivity, which is applied in electric/magnetic exploration, acoustic wave reradiation, radio wave measurement system, etc. It can solve the problems of calculation process dependence, calculation process instability, large error, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The present invention will be further described in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and the following four schedules;
[0054] Table 1 is a list of Matlab functions selected when training the network
[0055] training method
Call functions
features
Remark
ladder with momentum
descending method
trangdm
Adding the momentum phase is equivalent to the damping term, which reduces the learning process
The oscillation trend in the process improves the convergence term
Incremental momentum
one-step secant method
trainos
The stacking speed is faster
save memory
conjugate ladder
descending method
Traincgf
Traincgp
Traincgb
Automatically adjust the learning rate, increase stability, and increase speed
Accuracy and Accuracy
add one
dimension search
Quasi-Newton Algorithm
trainbfg
The q...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com