Steel material for thermal cutting with oxygen
A technology of thermal cutting and steel materials, which is applied in laser welding equipment, manufacturing tools, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of short life of consumables, and achieve the effect of high-speed and stable thermal cutting operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
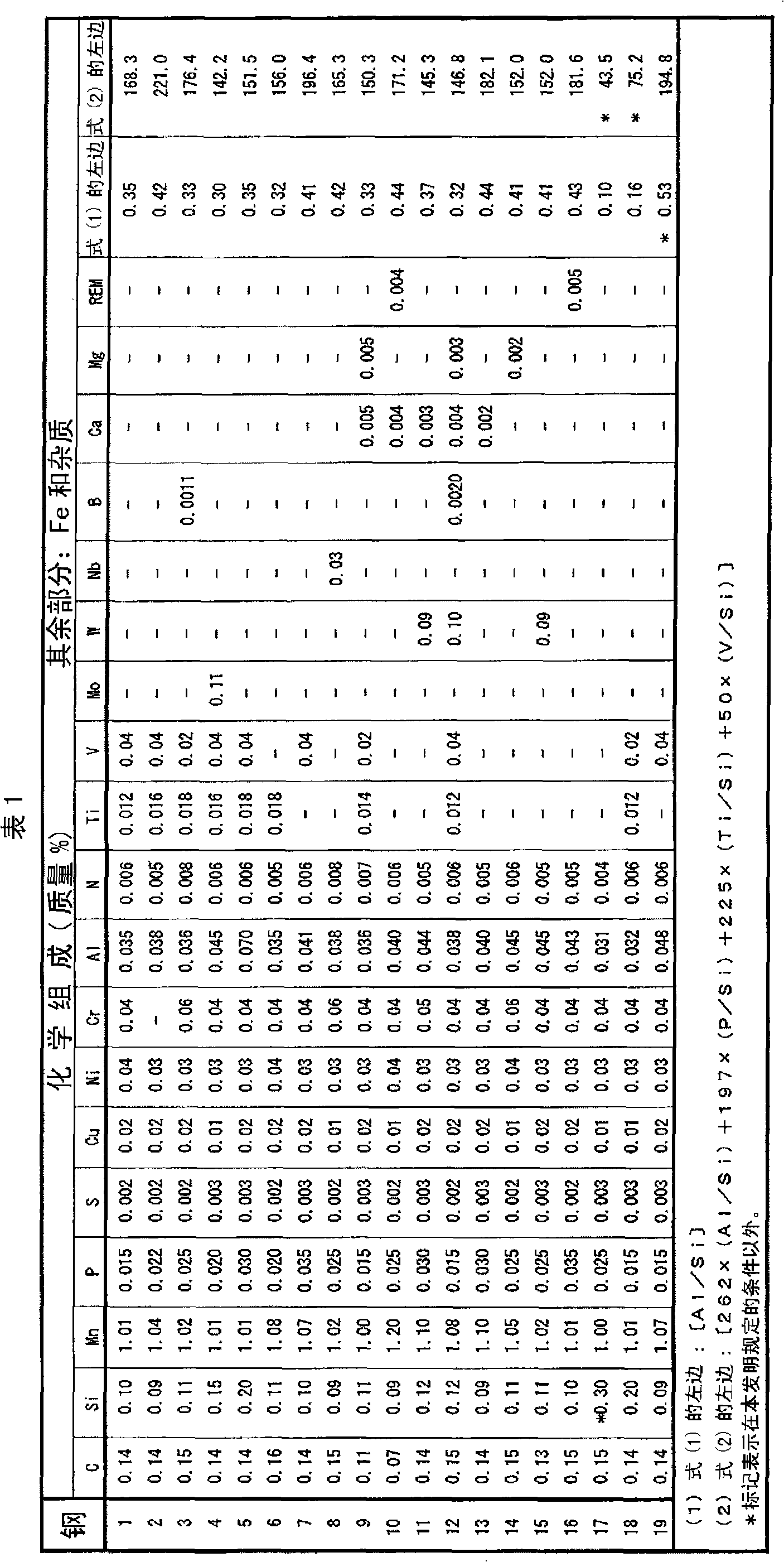
[0152] Steels 1 to 19 having the chemical compositions shown in Table 1 were melted in the laboratory, and then hot-rolled to produce two types of steel materials with a width of 250 mm, a length of 500 mm, and a thickness of 16 mm and 23 mm, respectively.
[0153] In addition, steels 1 to 16 in Table 1 are steels of the examples of the present invention whose chemical compositions are within the prescribed range of the present invention. On the other hand, steels 17 to 19 are steels of comparative examples whose chemical compositions are outside the conditions specified in the present invention.
[0154]
[0155] Next, the surface of the rolled steel material is shot blasted to remove the rolled scale. In addition, the 10-point average roughness (RzJIS) of the surface of any of the steel materials after shot blasting was 49.6 μm.
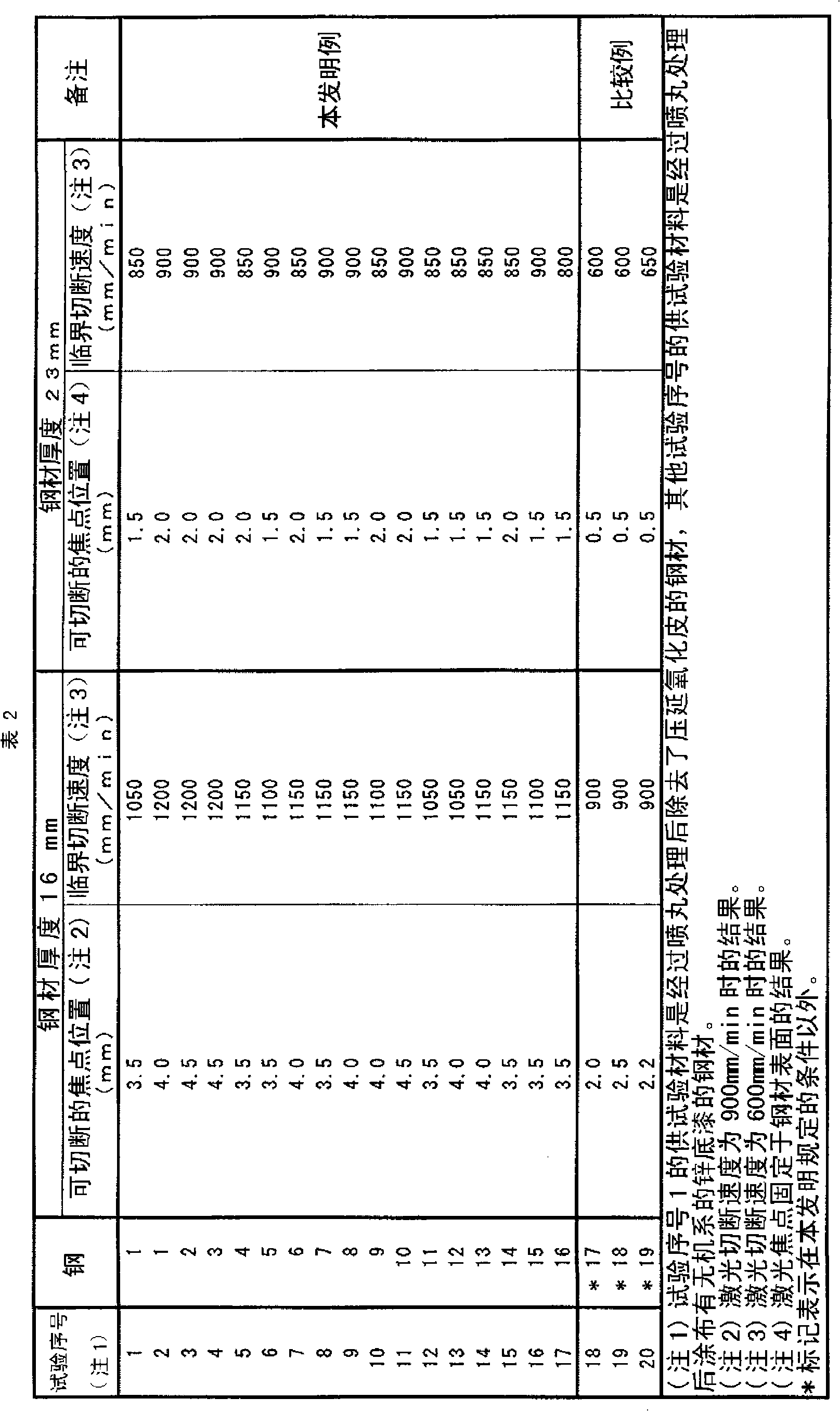
[0156] Then, adopt the method of air spraying, to each steel material except test serial number 1 in Table 2, i.e. to each steel material surf...
Embodiment 2
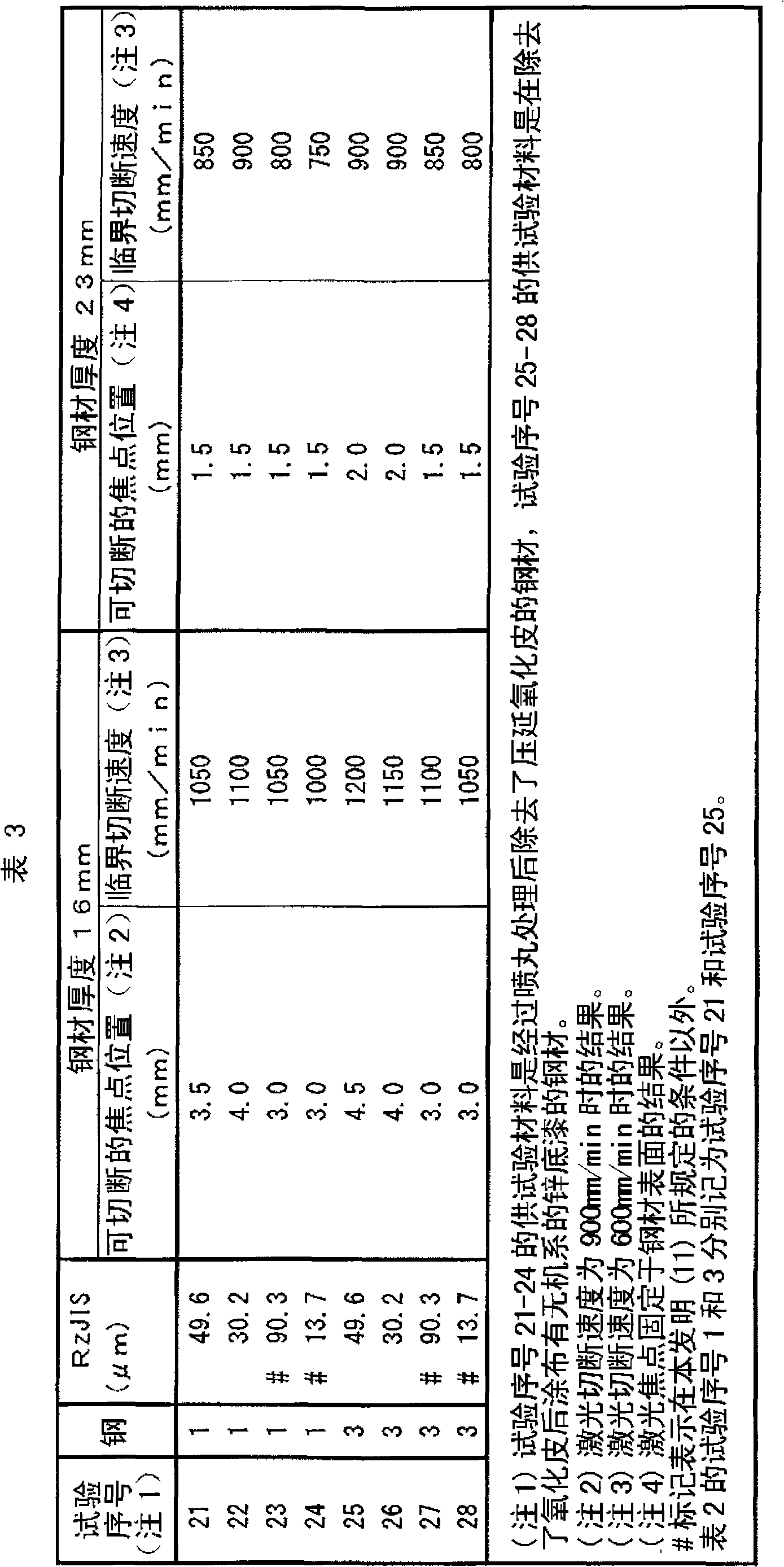
[0169] The same test as in Example 1 above was performed by changing the surface roughness of the steel material. More specifically, using steel 1 and steel 3 described in Table 1, the size of the balls in shot blasting was changed, and test pieces having different surface roughness RzJIS were produced, and the laser cutting properties were evaluated in the same manner as the steel materials shown in Example 1.
[0170] Table 3 shows the results of the investigation when the surface roughness was changed. In addition, in Table 3, the test materials of test numbers 21 to 24 are steel materials from which scale has been removed, and the test materials of test numbers 25 to 28 are steel materials coated with steel materials in the same manner as after descaling. Steel with zinc primer. In addition, the test number 1 and the test number 3 of are described as the test number 21 and the test number 25, respectively.
[0171]
[0172] It can be seen from Table 3 that, for test...
Embodiment 3
[0174] The remainder of the steel material used in , especially the steel material having a thickness of 23 mm, was subjected to plasma cutting to evaluate plasma cutting properties.
[0175] The plasma cutting machine used for the cutting was a plasma cutting machine (SUPER400) manufactured by Koike Sanso Co., Ltd., the cutting condition was an output current of 137.8 A, and oxygen was used as the plasma gas.
[0176] After piercing (piercing), cut out a 50 mm x 50 mm block from each steel material, check whether there is any defect in the cut surface at this time, and observe the presence of slag (that is, the attachment on the cut side of the molten steel containing oxides). Attachment status. The evaluation of the critical cutting speed is: increase the cutting speed of 1200mm / min at a speed of 120mm / min (10% speed of the initial cutting speed), and determine whether there is a chipping phenomenon, slag adhesion, and poor cutting caused by overburning. And the highest cut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mean roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com