Driving limited-slip differential
A limited-slip differential, limited-slip technology, applied in differential transmission, transmission, belt/chain/gear, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of improving driving stability and safety, ensuring steering flexibility and stability, and easy electronic control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with drawings and embodiments.
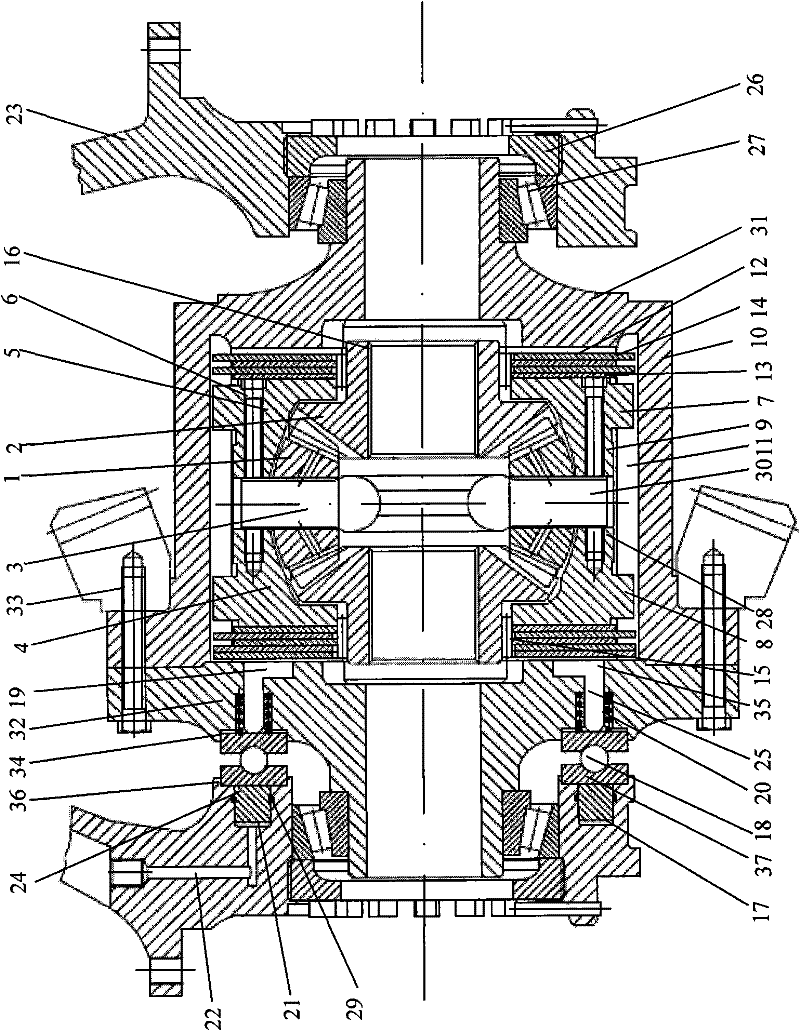
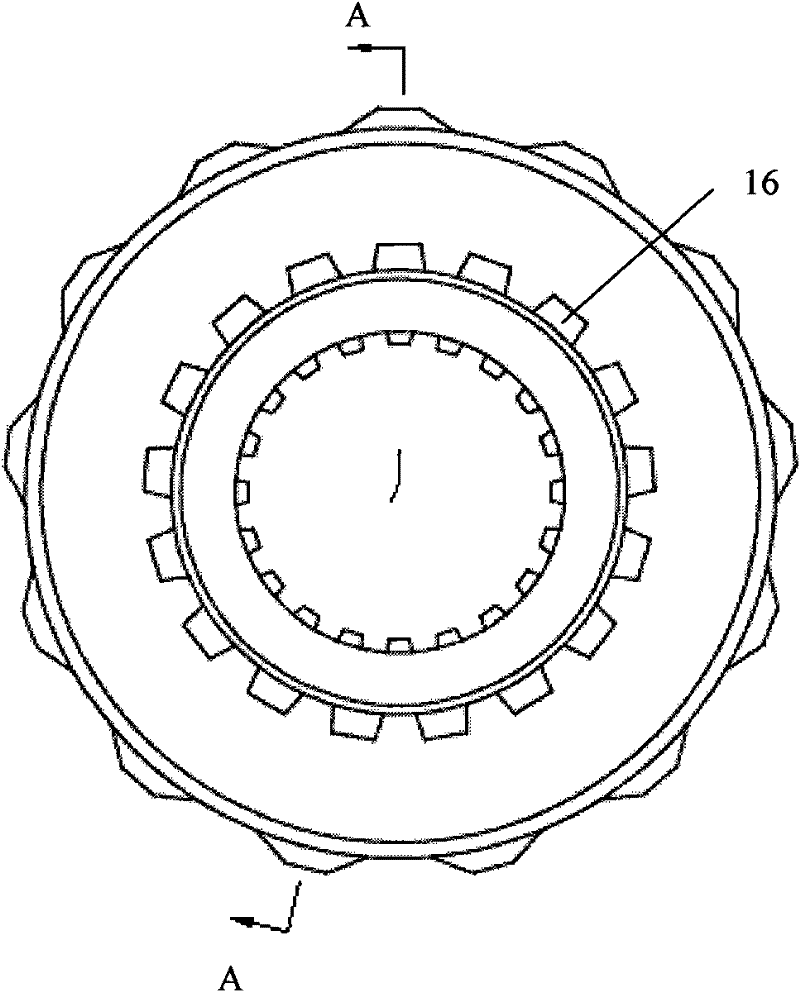
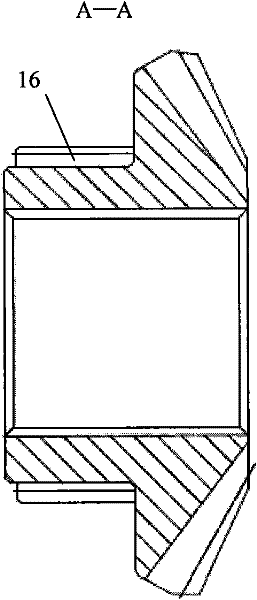
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the differential gear of the present invention is made up of planetary gear train, limited-slip friction pair, outer casing, inner casing and hydraulic thrust mechanism etc. Among them, the planetary gear train is composed of planetary gear 1, side gear 2 and cross shaft 3. The four planetary gears 1 are installed on the four shafts of the cross shaft 3, and the two side gears 3 are placed on both sides of the cross shaft 3 and meshed with the four planetary gears 1 to form a planetary gear train, which is placed inside Inside the casing, a differential mechanism is formed. Such as figure 1 As shown, the inner shell is composed of the left half shell 4 and the right half shell 5, the cross shaft 3, the left half shell 4 and the right half shell 5 of the inner shell are fixedly connected into one body through the inner shell bolt 6, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com