Memory cell having improved mechanical stability and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of storage unit and storage element, which is applied in the direction of information storage, static memory, digital memory information, etc., and can solve the problems of electrode poor adhesion, bottom electrode falling off, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0119] The following description of the invention refers to specific structural embodiments and methods. It is to be understood that the scope of the invention is not limited to the specific disclosed embodiments and that the invention can be practiced with other features, elements, methods and embodiments. The preferred embodiments are described to understand the present invention, but not to limit the scope of the present invention, which is defined by the claims. Those skilled in the art can understand equivalent changes of the present invention according to the subsequent description. Similar elements in various embodiments will be designated with similar reference numerals.
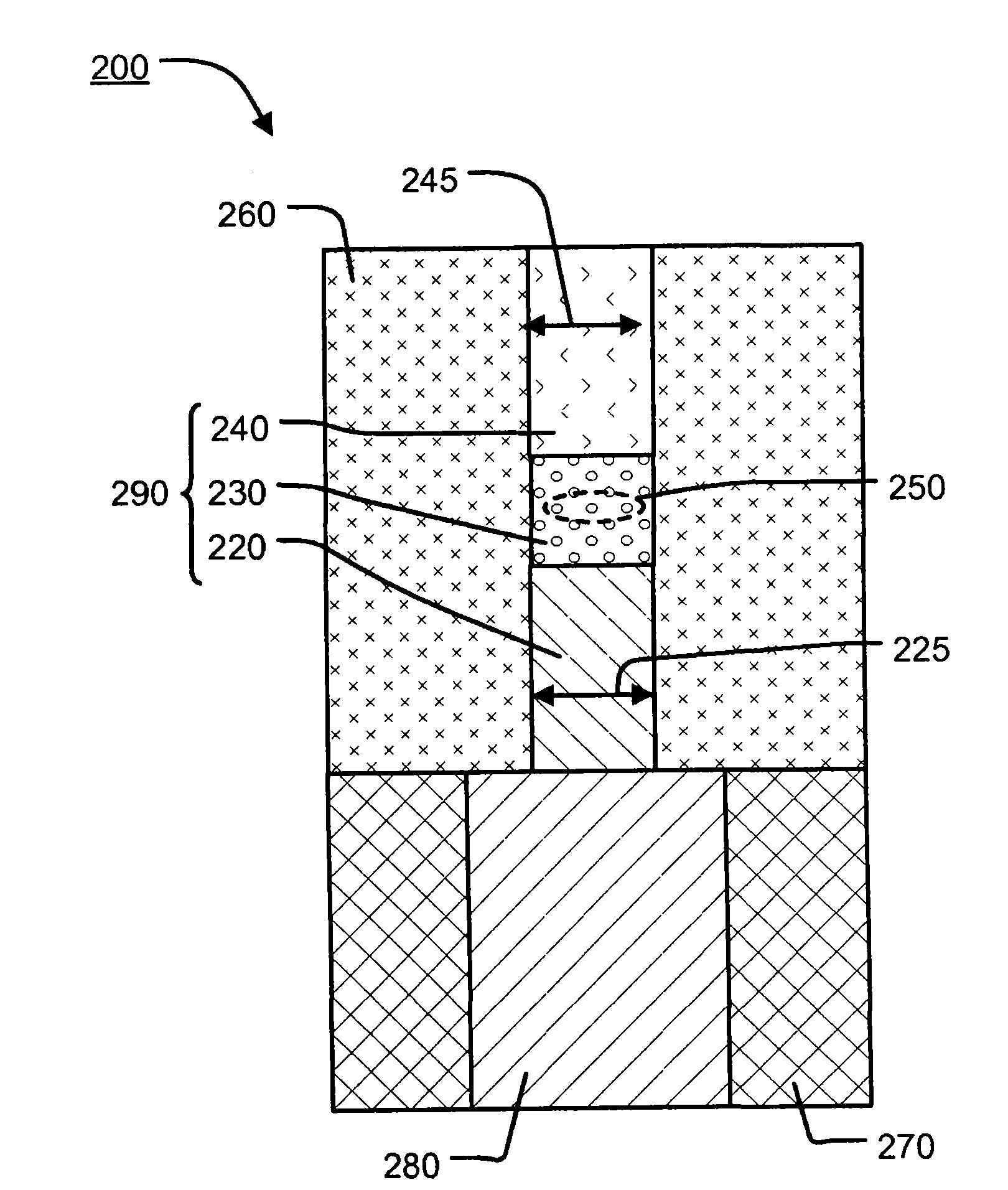
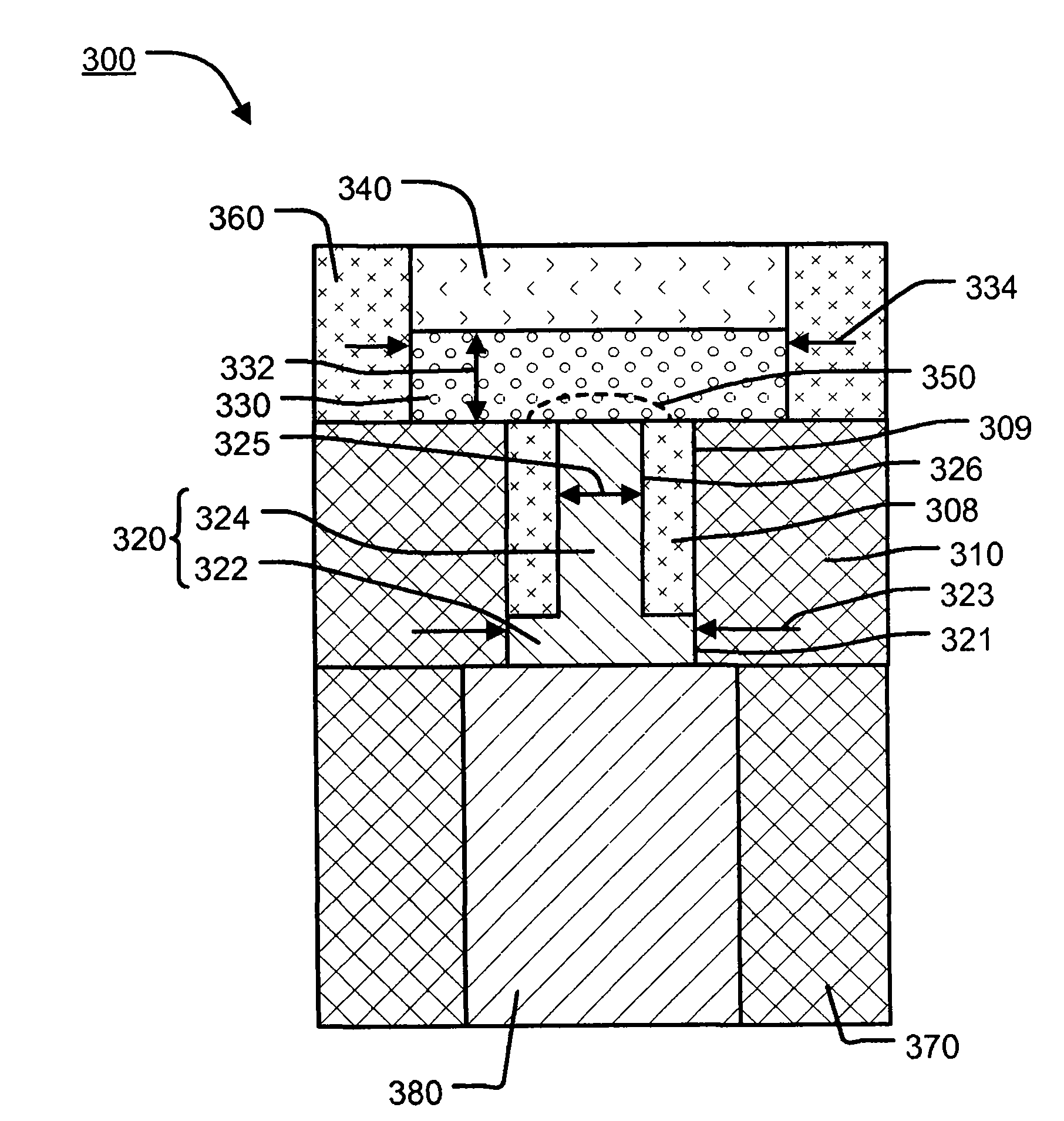
[0120] Subsequent descriptions of the invention will refer to Figure 1 to Figure 21 .
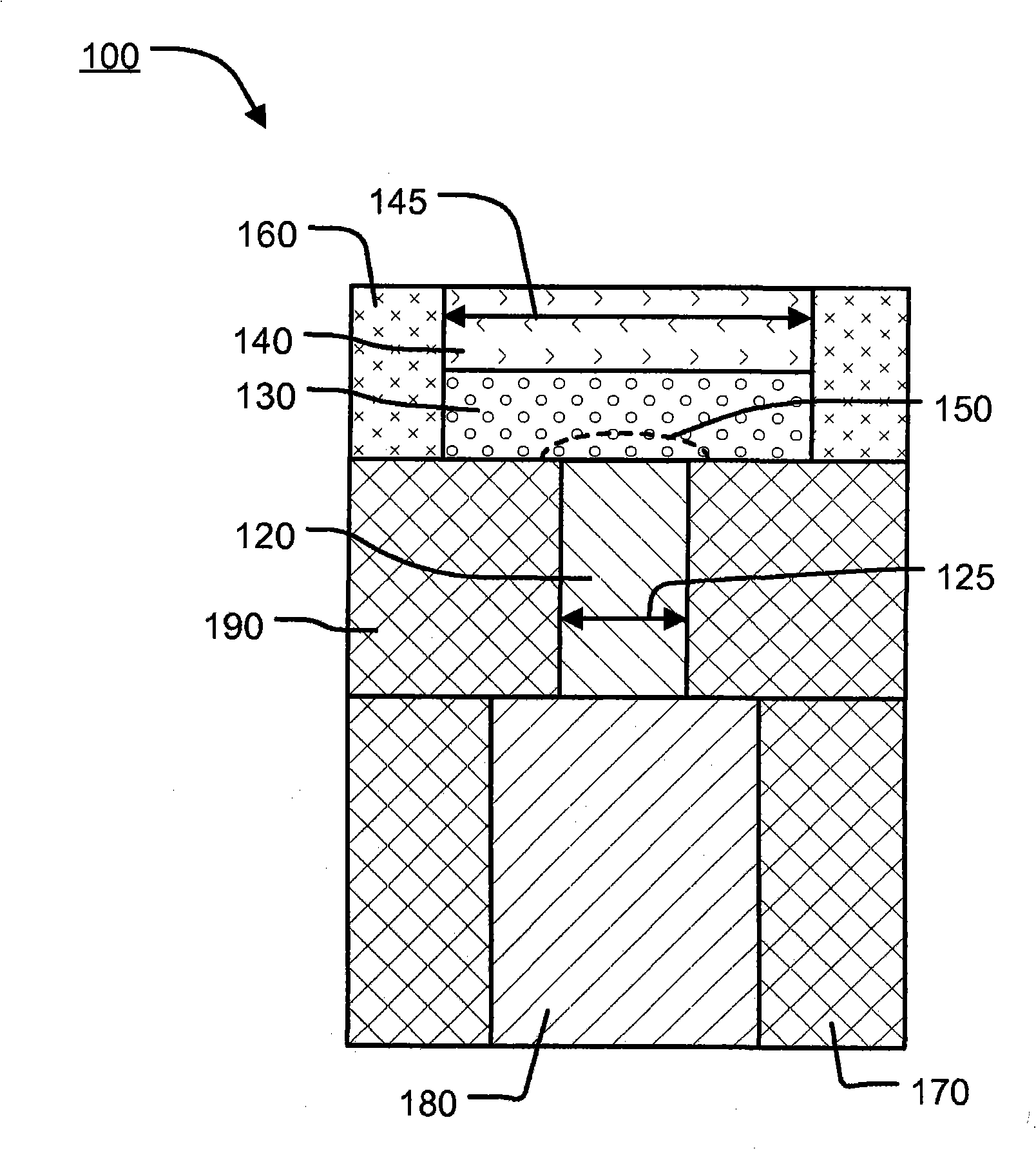
[0121] figure 1 A cross-sectional view of the prior art is shown with an "umbrella" memory cell 100 having a memory material layer 130 between a bottom electrode 120 and a top electrode 140 . A conductive pl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com