artificial nasolacrimal duct
A nasolacrimal duct and artificial technology, which is applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of increased surgical failure rate, inability to treat lacrimal canaliculus blockage, inability to use guided pull-in surgery, etc., to improve safety factor, service life, and indications Broad and positive curative effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
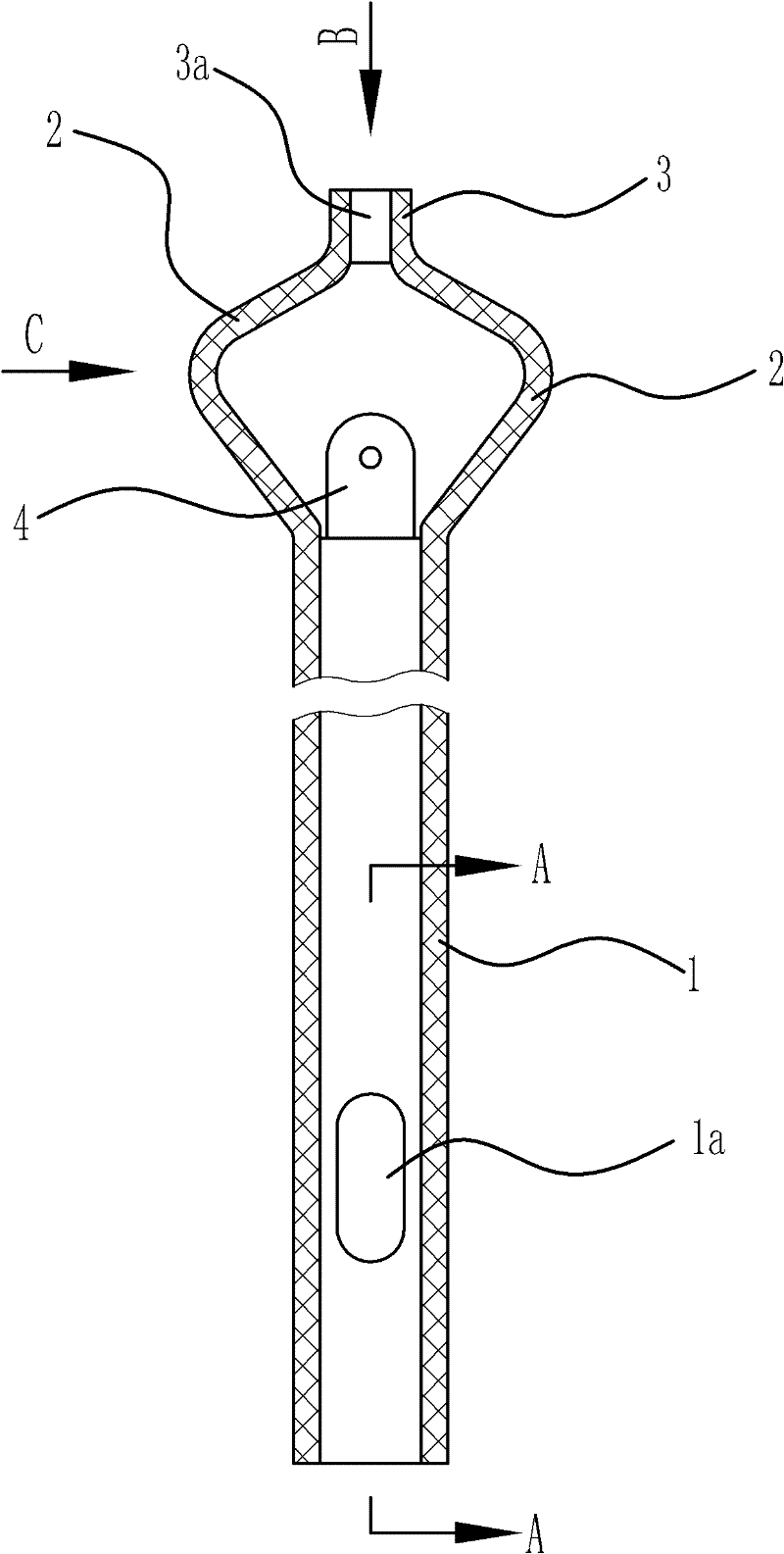
[0036] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 4 As shown, the artificial nasolacrimal duct includes a drainage main tube 1, a fixed valve 2, a fixed cap 3, and a drainage branch tube 4.
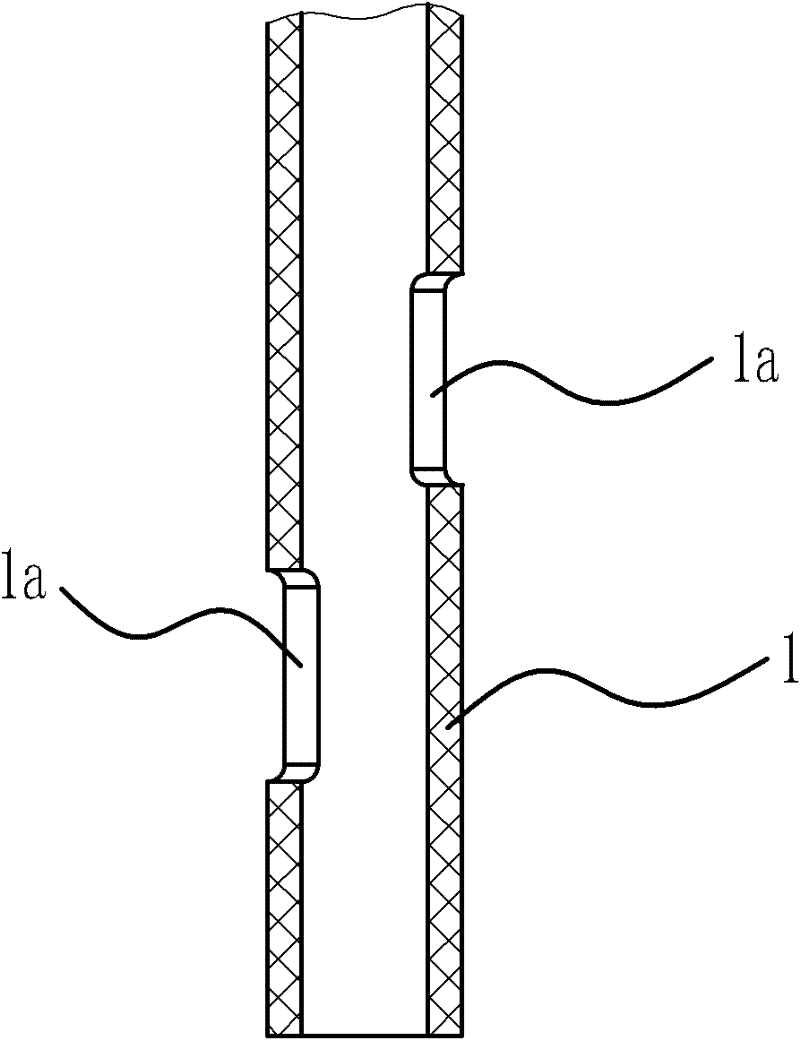
[0037] Specifically, such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the drainage main pipe 1 has a circular tube shape, and a positioning hole 1a is opened at the lower part thereof. The position of the positioning hole 1a relative to the drainage branch tube 4 is determined. Therefore, it is only necessary to determine the position relationship of the positioning hole 1a relative to the nasal passage during the operation, that is, the drainage branch tube 4 can be accurately introduced into the lacrimal canaliculus. If the artificial nasolacrimal duct fails to reach the designated position accurately after introduction, the guidewire hook can be used to hook the artificial nasolacrimal duct at the positioning hole 1a to pull out the artificial nasolacrimal duct. Therefore, the positioning hole 1a can make the...
Embodiment 2
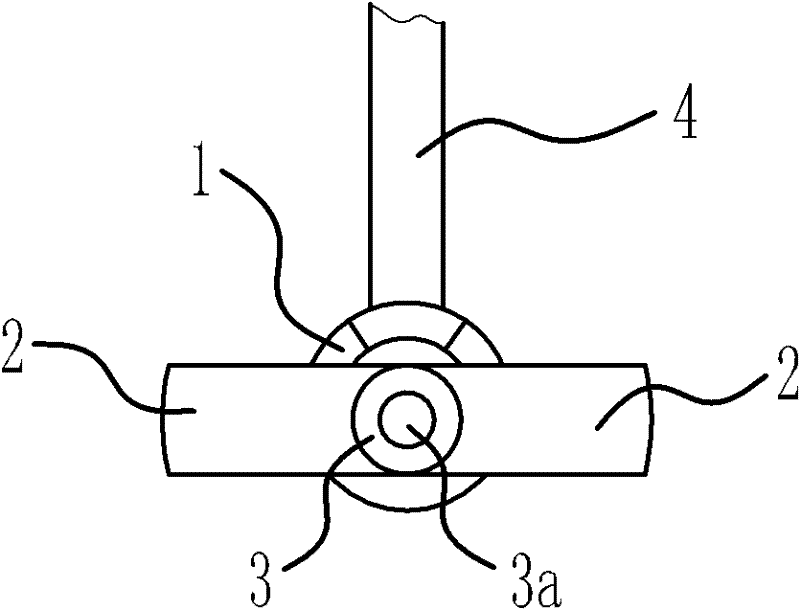
[0046] Such as Figure 5 with Figure 7 As shown, the structure and principle of this embodiment are basically the same as those of the first embodiment. The difference is that according to the physiological structure of the human nasolacrimal duct, when the fixed flap 2 is located in the lacrimal sac, the extension line of the upper lacrimal canaliculus is located in the fixed 2 petals and 3 close to the fixed cap. Therefore, in order to enable the above-mentioned drainage branch tube 4 to penetrate the upper lacrimal canaliculus, and at the same time, after the drainage branch tube 4 is penetrated, the upper lacrimal canaliculus is not deformed and the position of the drainage branch tube 4 relative to the fixed cap 3 does not change, then the drainage branch tube 4 The rear end is fixedly connected to the lower end surface of the fixing cap 3. The junction of the drainage branch tube 4 and the fixed cap 3 is located at one of the gaps between the two fixed flaps 2, but only ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Such as Image 6 with Figure 8 As shown, the structure and principle of this embodiment are basically the same as those of the first embodiment. The difference lies in: two tubular drainage branches that can penetrate into the lacrimal canaliculus are provided at one of the gaps between the two fixed flaps 2 4, namely, drainage branch pipe one 41 and drainage branch pipe two 42.
[0051] The lacrimal canaliculus includes the upper canaliculus and the small canaliculus; according to the physiological structure of the human nasolacrimal duct, when the fixed valve 2 is located in the lacrimal sac, the extension line of the lower canaliculus is located at the fixed valve 2 and close to the drainage main pipe 1. The extension of the tubule is located at the fixed valve 2 and close to the fixed valve 2. Therefore, in order to allow the above-mentioned drainage branch tube 41 to penetrate into the lower lacrimal canaliculus, drainage branch tube 2 42 can penetrate into the upper...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com