Closed-loop driving circuit for micromechanical resonance structure
A technology of resonant structure and driving circuit, applied in the direction of electrical components, impedance network, etc., can solve the problems of unstable resonance of resonant structure, difficult debugging, small dynamic range of circuit signal, etc., to avoid coupling influence, facilitate debugging, and expand linearity. The effect of the working area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
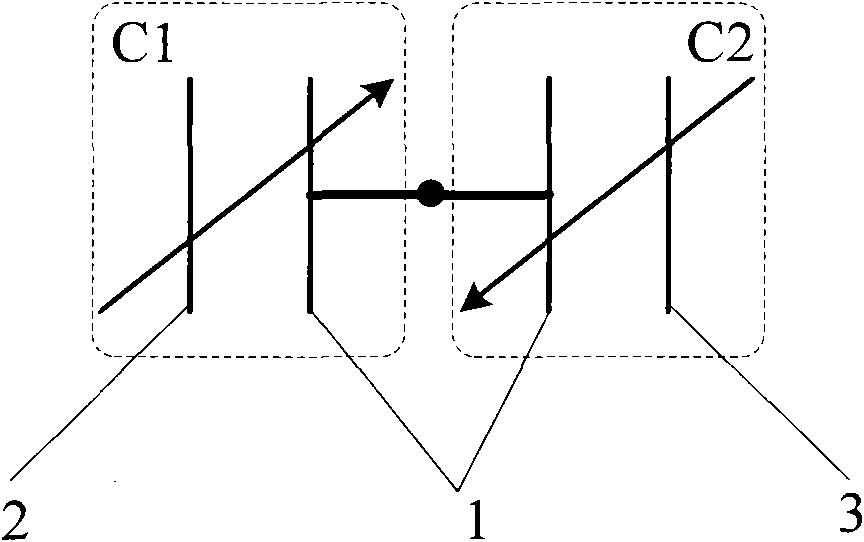
[0025] The first type of closed-loop drive circuit for a micromechanical resonant structure. The specific structure corresponding to the micromechanical resonant structure 4 in this embodiment is Figure 6 The shown comb-driven micromechanical resonant structure with the stationary teeth disconnected, Figure 8 The structure is abstracted as a micromechanical resonant structure-14, and its specific implementation is as follows:
[0026] refer to Figure 8 , the present embodiment is directed to a micromechanical resonant structure 14, which belongs to a structure in which the fixed electrodes on both sides of the common electrode 1 are disconnected. The micromechanical resonant structure 14, corresponding to figure 1 In the electrical model shown, the fixed electrode I2 is disconnected into two electrodes, the sensitive electrode AI15 and the driving electrode AI17; the fixed electrode II3 is disconnected into two electrodes, the sensitive electrode AII16 and the driving ele...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The second type of closed-loop drive circuit for micromechanical resonant structures. The specific structure corresponding to the micromechanical resonant structure 4 in this embodiment is Figure 6 The comb-driven micromechanical resonant structure with the stationary teeth disconnected is shown, Figure 9 The structure is abstracted as a micromechanical resonant structure-14, and its specific implementation is as follows:
[0032] refer to Figure 9 , the present embodiment is directed to a micromechanical resonant structure 14, which belongs to a structure in which the fixed electrodes on both sides of the common electrode 1 are disconnected. The micromechanical resonant structure 14, corresponding to figure 1 In the electrical model shown, the fixed electrode I2 is disconnected into two electrodes, the sensitive electrode AI15 and the driving electrode AI17; the fixed electrode II3 is disconnected into two electrodes, the sensitive electrode AII16 and the driving ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The third type of closed-loop drive circuit for micromechanical resonant structures. The specific structure corresponding to the micromechanical resonant structure 4 in this embodiment can be Figure 2 to Figure 5 Either structure shown, Figure 10 The structure is abstracted as a micromechanical resonant structure 227, and its specific implementation is as follows:
[0037] refer to Figure 10 , this implementation is aimed at the micromechanical resonant structure 27, which belongs to the structure in which the fixed electrodes on both sides of the common electrode are connected. The MEMS resonant structure II 27, corresponds to figure 1 In the electrical model shown, the fixed electrode I2 is integrated, and the fixed electrode II3 is also integrated. In this embodiment, the fixed electrode I2 and the fixed electrode II3 are embodied as a sensitive electrode B24 and a driving electrode B25 respectively.
[0038] First, the common electrode 1 of the second microme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com