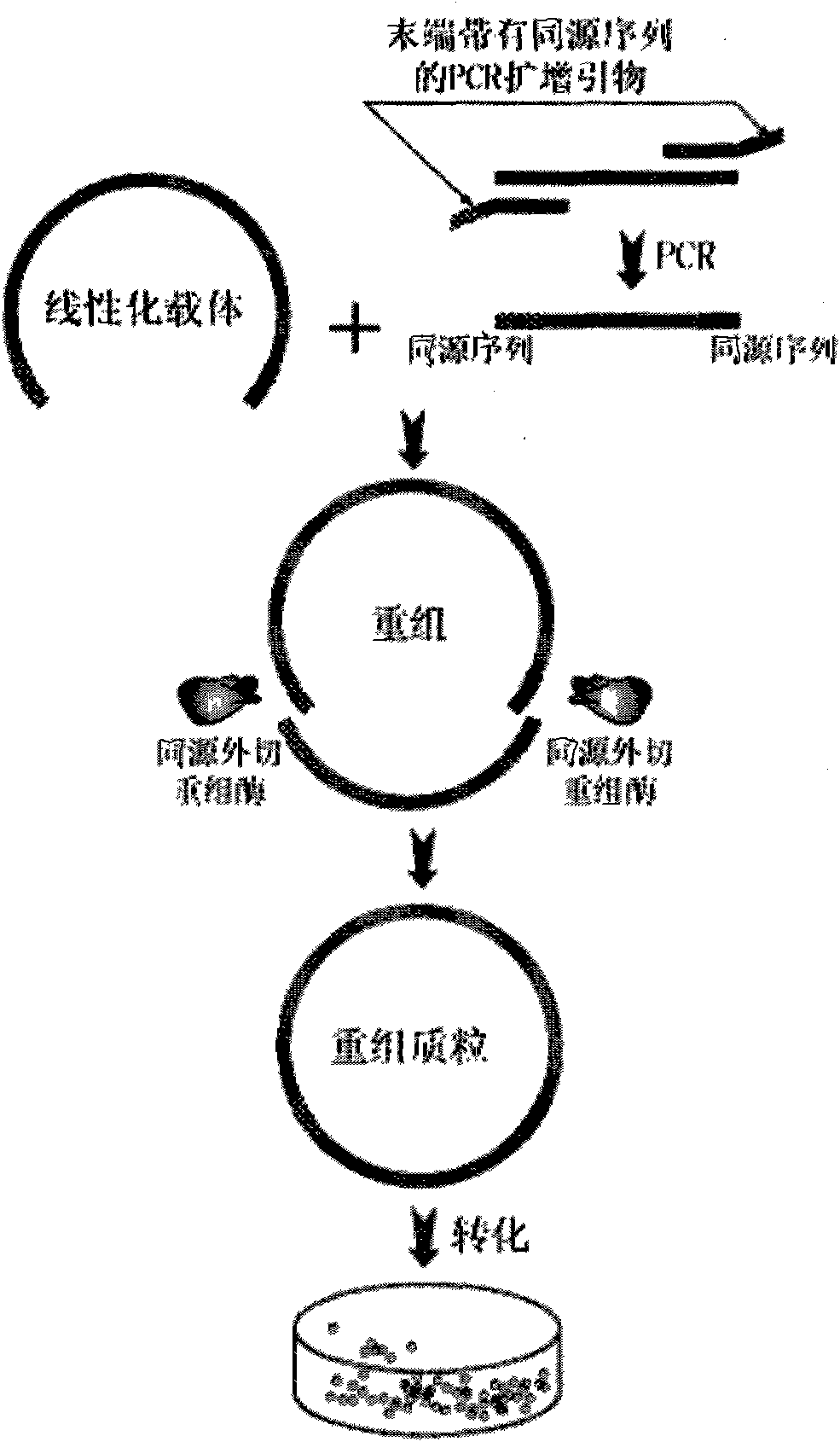
Method for inserting target DNA fragment into vector
A purpose and fragment technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, the use of vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc., can solve the problems of lack of flexibility, high price, harsh conditions, etc., and achieve the effect of wide application range, low cost and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1) Preparation of insert fragments
[0021] The sequences of the PCR primers are as follows:
[0022] Forward primer: TGCCGCGCGGCAGCC ATGAGCCATATTCAACGG;
[0023] Reverse primer: GTTAGCAGCCGGATC GAAAAACTCATCGAGCATCAAATG.
[0024] The underlined part is the exo-recombination homologous vector sequence, and the rest is the template sequence. Primers were synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
[0025] Using the plasmid pET28a (purchased from Novagen) as a template, the PCR reaction was carried out using the above primers. The PCR reaction was carried out using a PCR amplification kit from Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd. The PCR reaction system and reaction procedure are as follows.
[0026] PCR amplification system:
[0027] template DNA
1μl
10×PCR buffer
1.5μl
MgCl 2 (25nM)
1.5μl
dNTP (10mM)
0.3μl
Forward primer (10pM)
0.25μl
Reverse primer (10pM)
0.25μl
Taq e...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1) Preparation of insert fragments
[0051] The sequences of the PCR primers are as follows:
[0052] Forward primer: CCTGGTGCCGCGCGGCAGCC ATGAGCCATATTCAACGG;
[0053] Reverse primer: GCTTTGTTAGCAGCCGGATC GAAAAACTCATCGAGCATCAAATG.
[0054] 2) The preparation of the linear carrier is the same as in Example 1.
[0055] 3) The establishment of the homologous recombination reaction system is the same as in Example 1.
[0056] 4) conversion, with embodiment 1.
[0057] 5) Determination of recombinant identification and acquisition rate of effective clones
[0058] The number of clones on the petri dish was 136, and 16 single colonies were randomly selected for sequencing. The results showed that 15 were positive clones containing the target fragment, and 1 was empty vector.
Embodiment 3
[0060] 1) Preparation of insert fragments
[0061] The sequences of the PCR primers are as follows:
[0062] Forward primer: CAGCC ATGAGCCATATTCAACGG;
[0063] Reverse primer: GGATC CGAAAAAACTCATCGAGCATCAAAATG.
[0064] 2) The preparation of the linear carrier is the same as in Example 1.
[0065] 3) The establishment of the homologous recombination reaction system is the same as in Example 1.
[0066] 4) conversion, with embodiment 1.
[0067] 5) Determination of recombinant identification and acquisition rate of effective clones
[0068] The number of clones on the petri dish was 63, and 16 single colonies were randomly selected for sequencing. The results showed that 13 were positive clones containing the target fragment, and 3 were empty vectors.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com