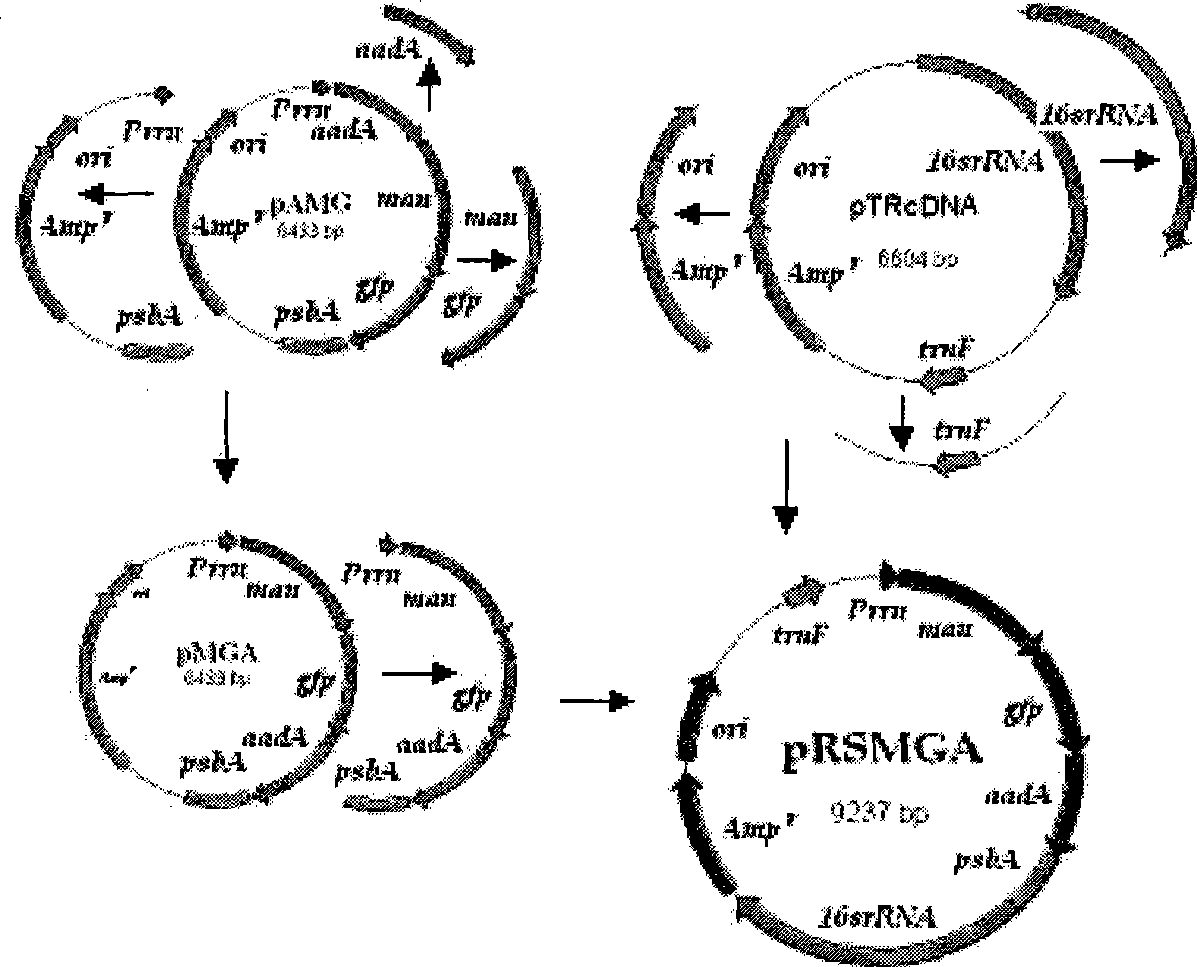
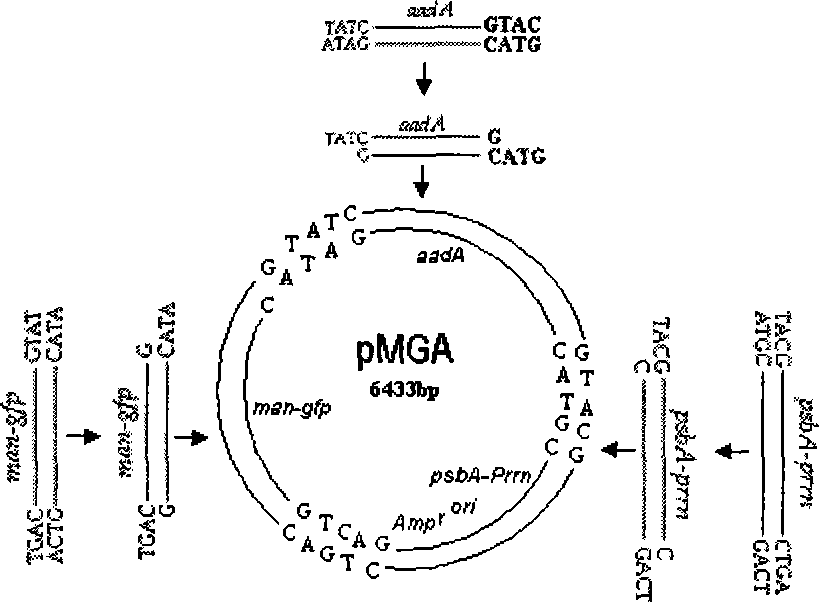
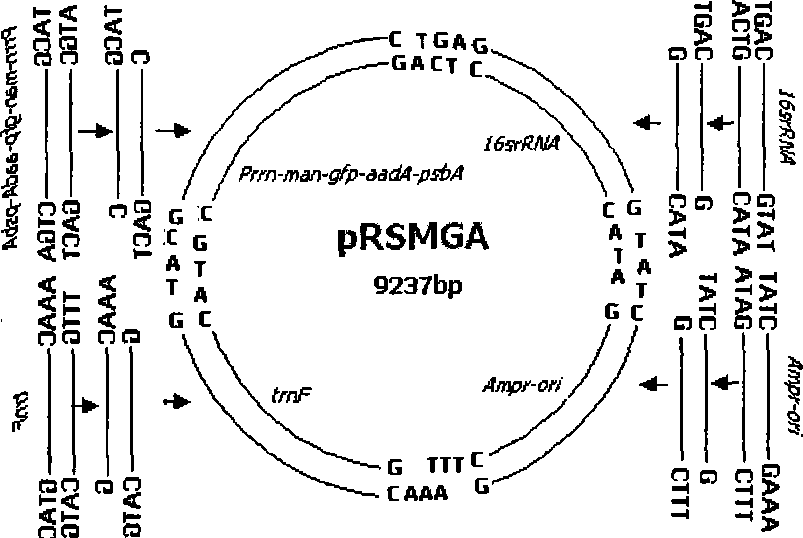
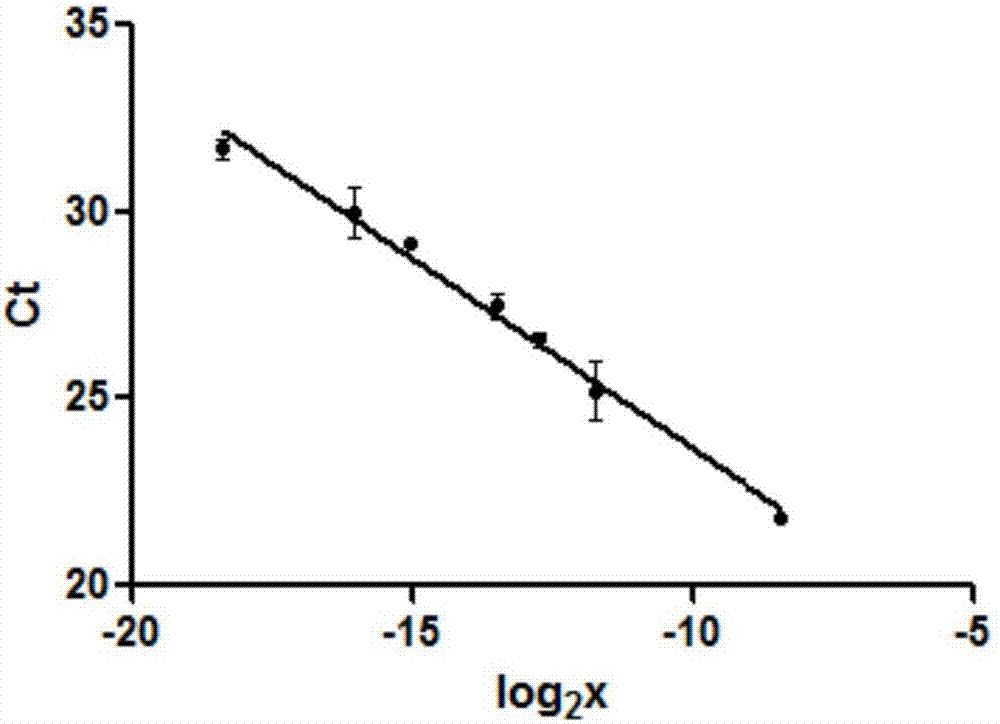
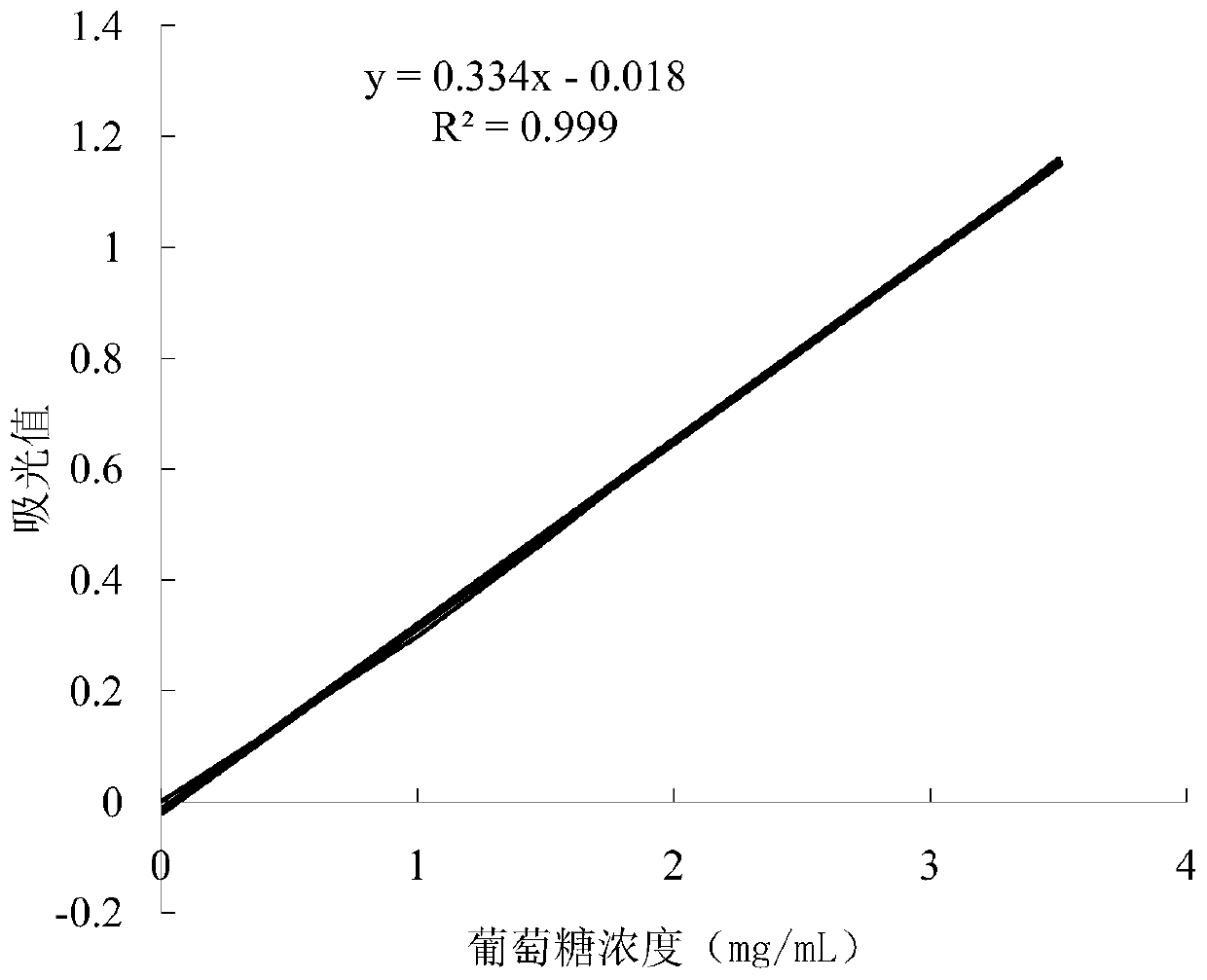
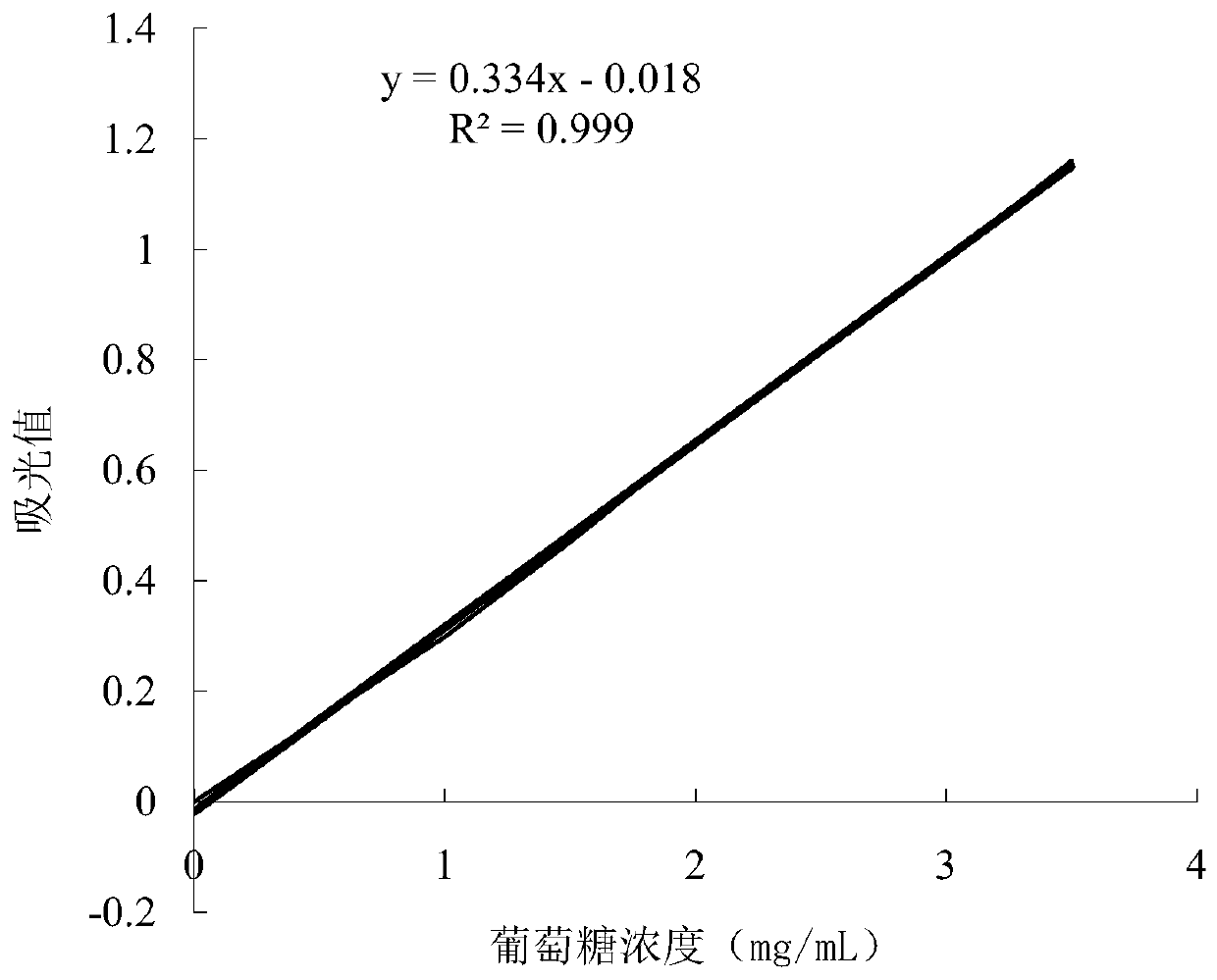
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Exochitinase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of terminal 1,4-beta-linkages of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) polymers of chitin and chitodextrins. Typically, exochitinases progressively cleave off two subunits from the reducing or non-reducing ends of the chitin chain. [EC:3.2.1.-, GOC:bf, GOC:kah, GOC:pde, PMID:11468293, PMID:16298970, PMID:21390509]
Fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction solution and fluorescence quantitative PCR method
ActiveCN102465120ASolve the problem of low amplification efficiencyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBetaineFluorescence
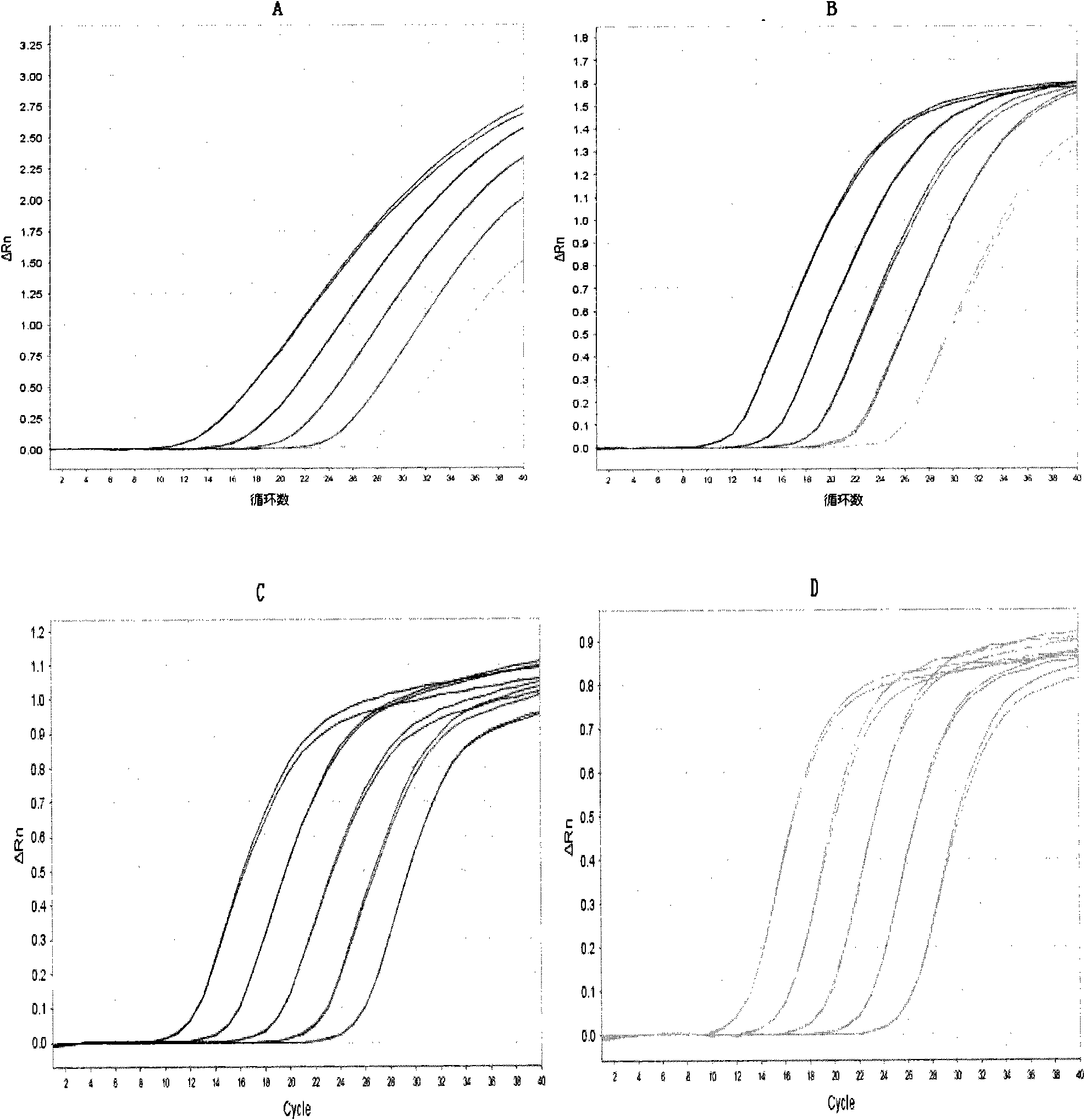
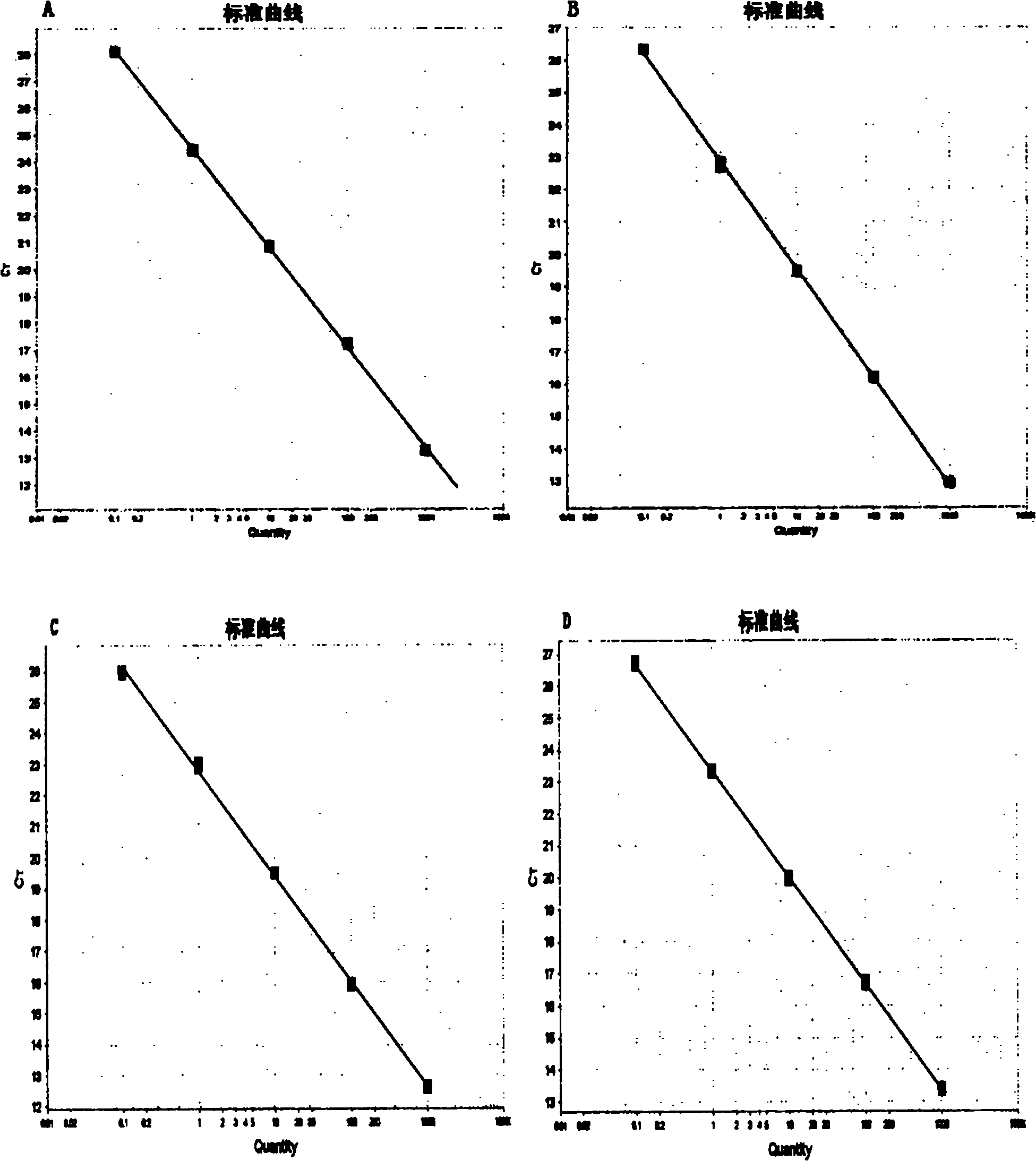
The invention belongs to the fields of molecular biotechnology and experimental methods and specifically relates to a fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction solution. The solution is characterized by comprising a PCR reaction reinforcing agent which is one or more selected from the group consisting of dimethyl sulfoxide, glycerin, bovine serum albumin, methanamide, polyethylene glycol 6000, spermidine, ammonium sulfate and betaine, e.g., dimethyl sulphoxide, bovine serum albumin and betaine. The fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction solution further comprises heatproof DNA polymerase having 5'-3' polymerase activity and 5'-3' exonuclease activity and preferably comprises heatproof DNA polymerase and hot-start heatproof DNA polymerase, both of which having 3'-5' exonuclease activity. The invention also relates to a kit containing the reaction solution and a method of applying the reaction solution in fluorescence quantitative PCR.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
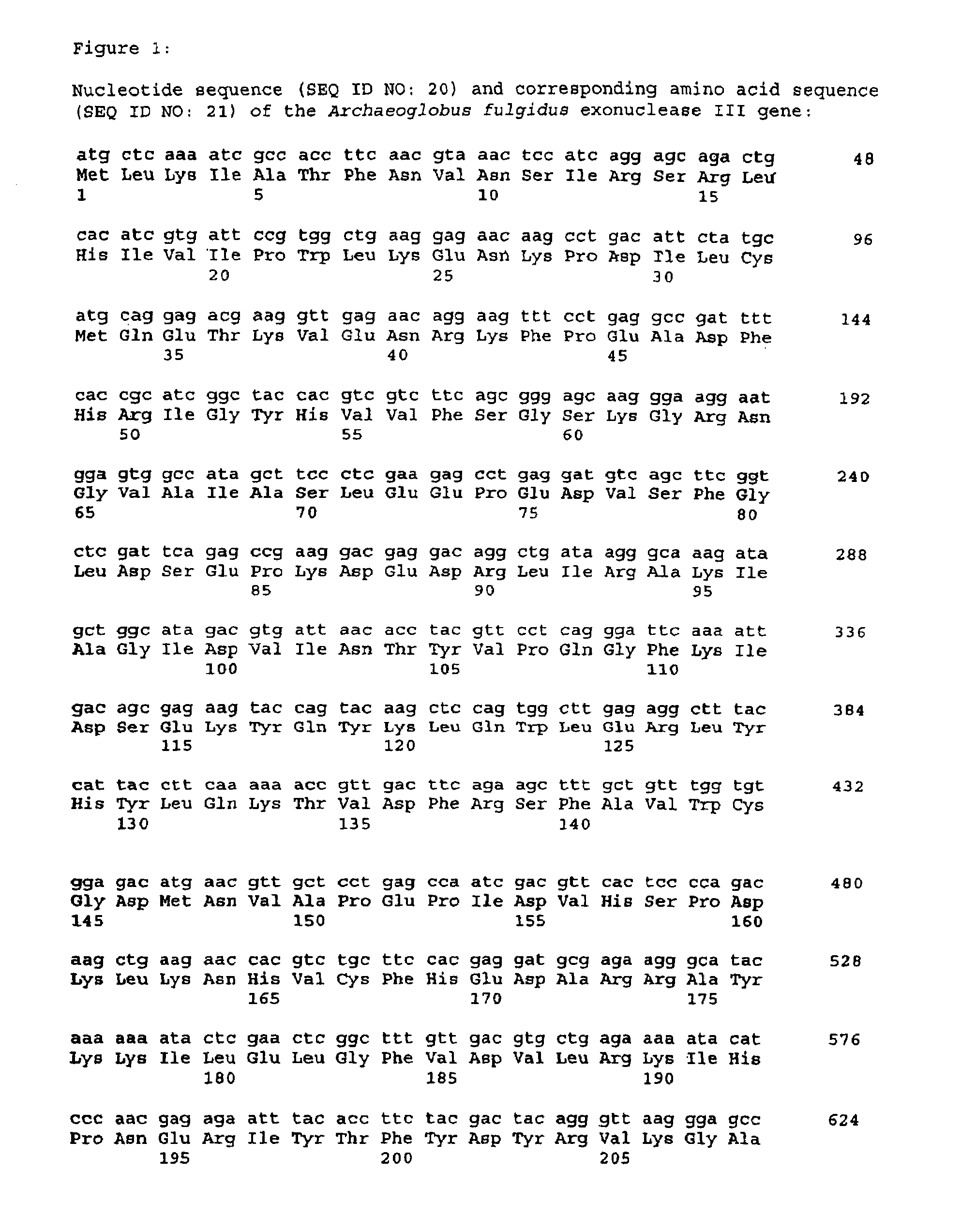
Thermostable enzyme promoting the fidelity of thermostable DNA polymerases-for improvement of nucleic acid synthesis and amplification in vitro
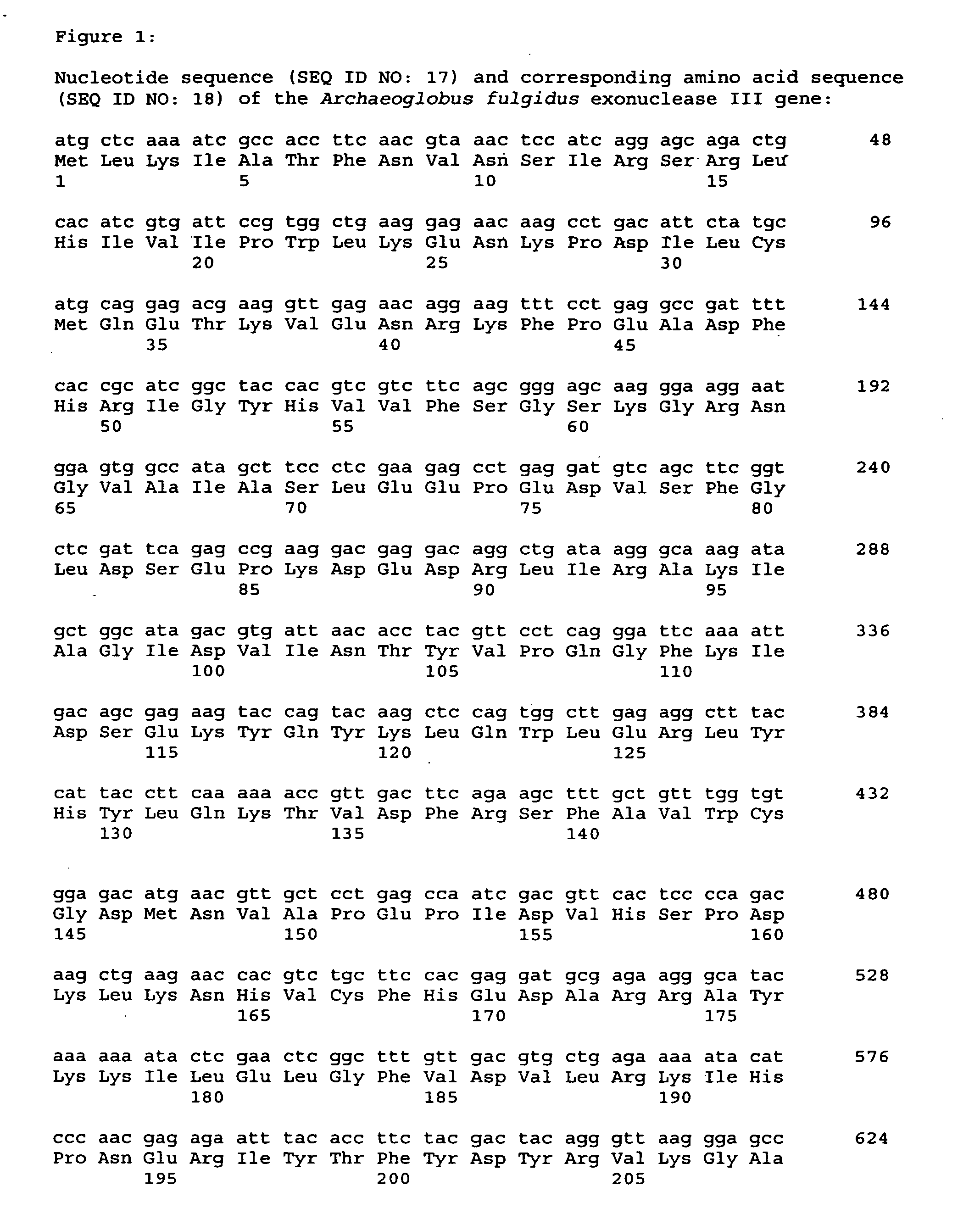
A purified thermostable enzyme is derived form the thermophilic archaebacterium Archaeoglobus fulgidus. The enzyme can be native or recombinant, is stable under PCR conditions and exhibits double strand specific exonuclease activity. It is a 3′-5′ exonuclease and cleaves to produce 5′-mononucleotides. Thermostable exonucleases are useful in many recombinant DNA techniques, in combination with a thermostable DNA polymerase like Taq especially for nucleic acid amplification by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH +1
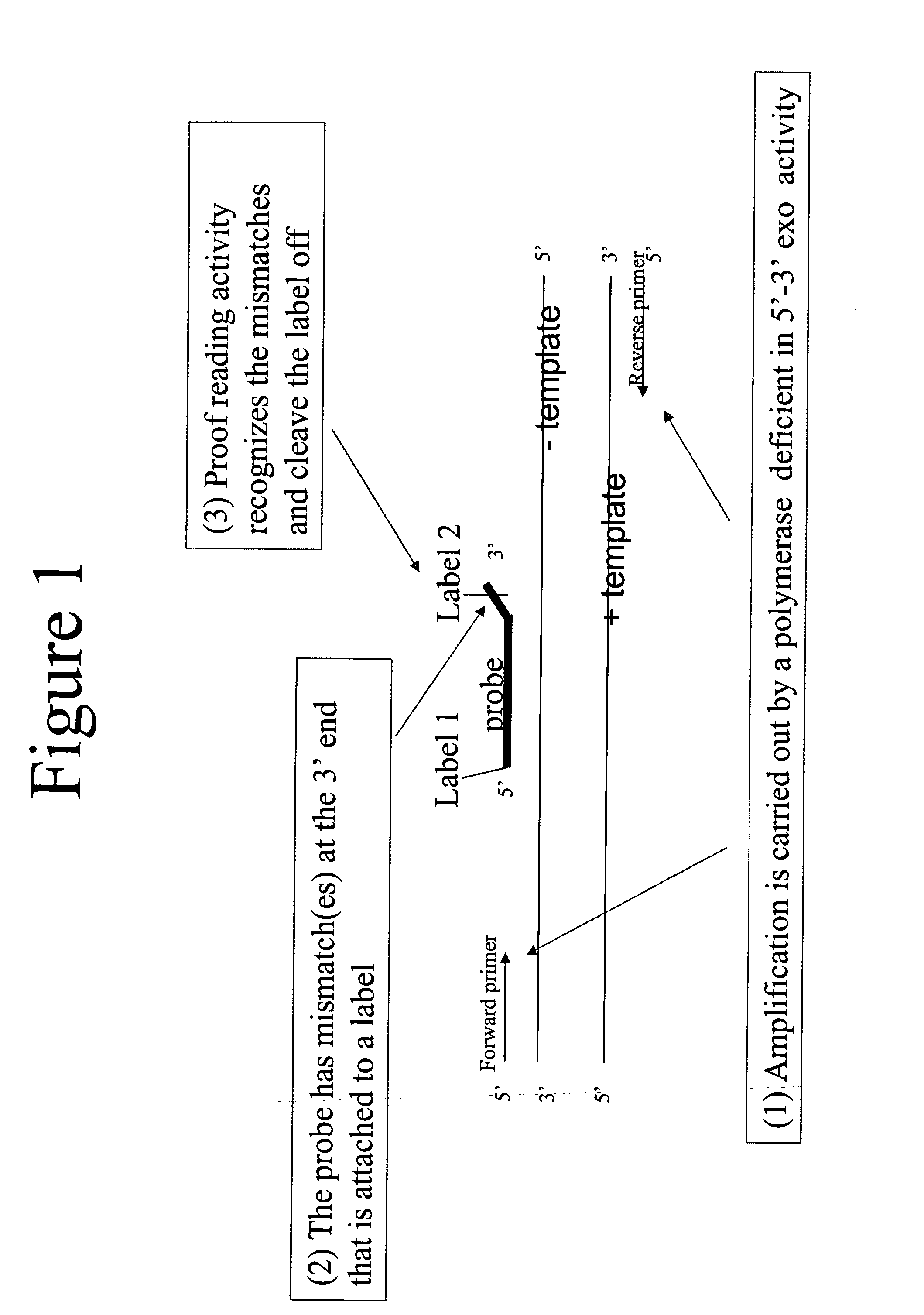
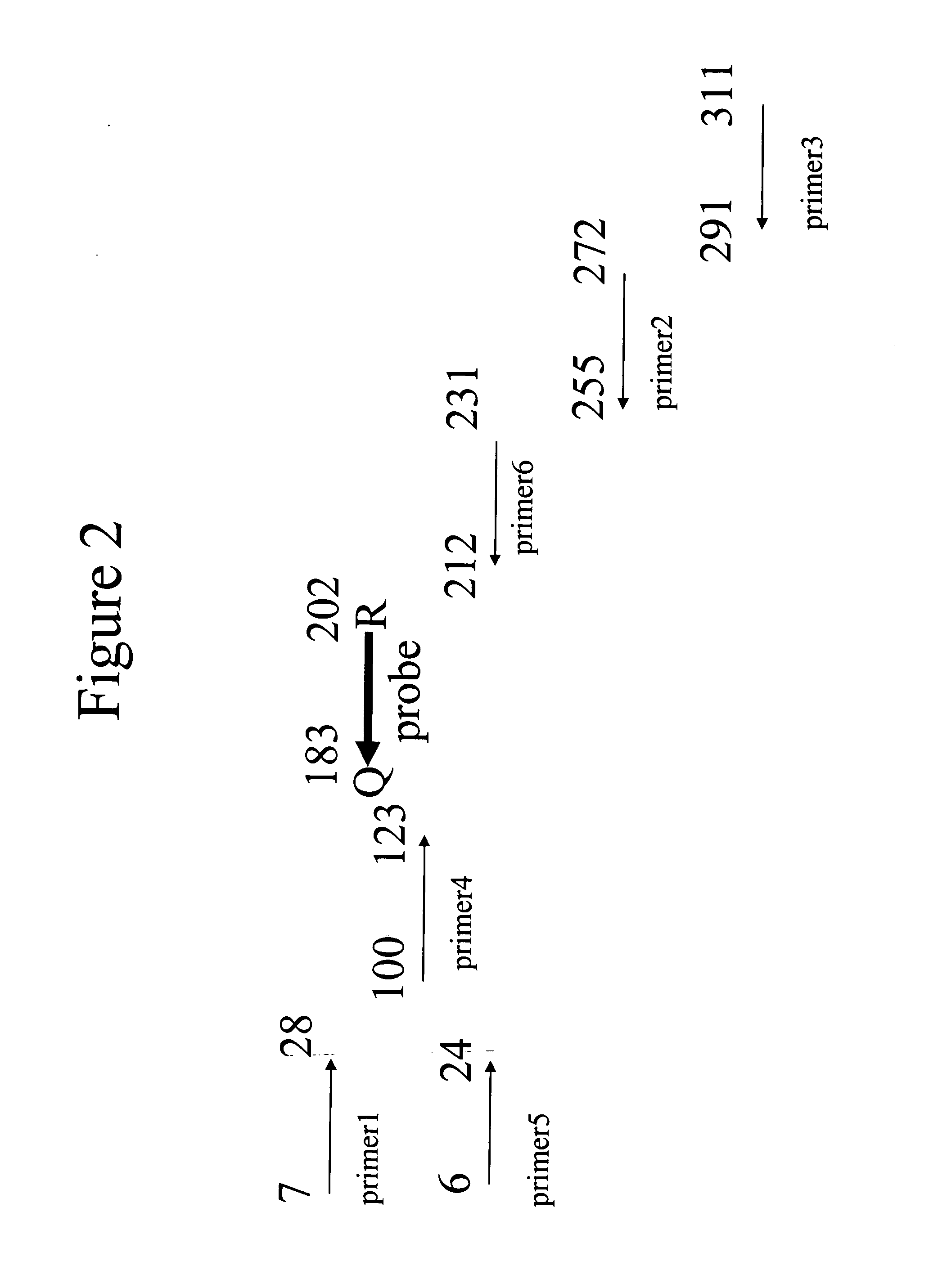
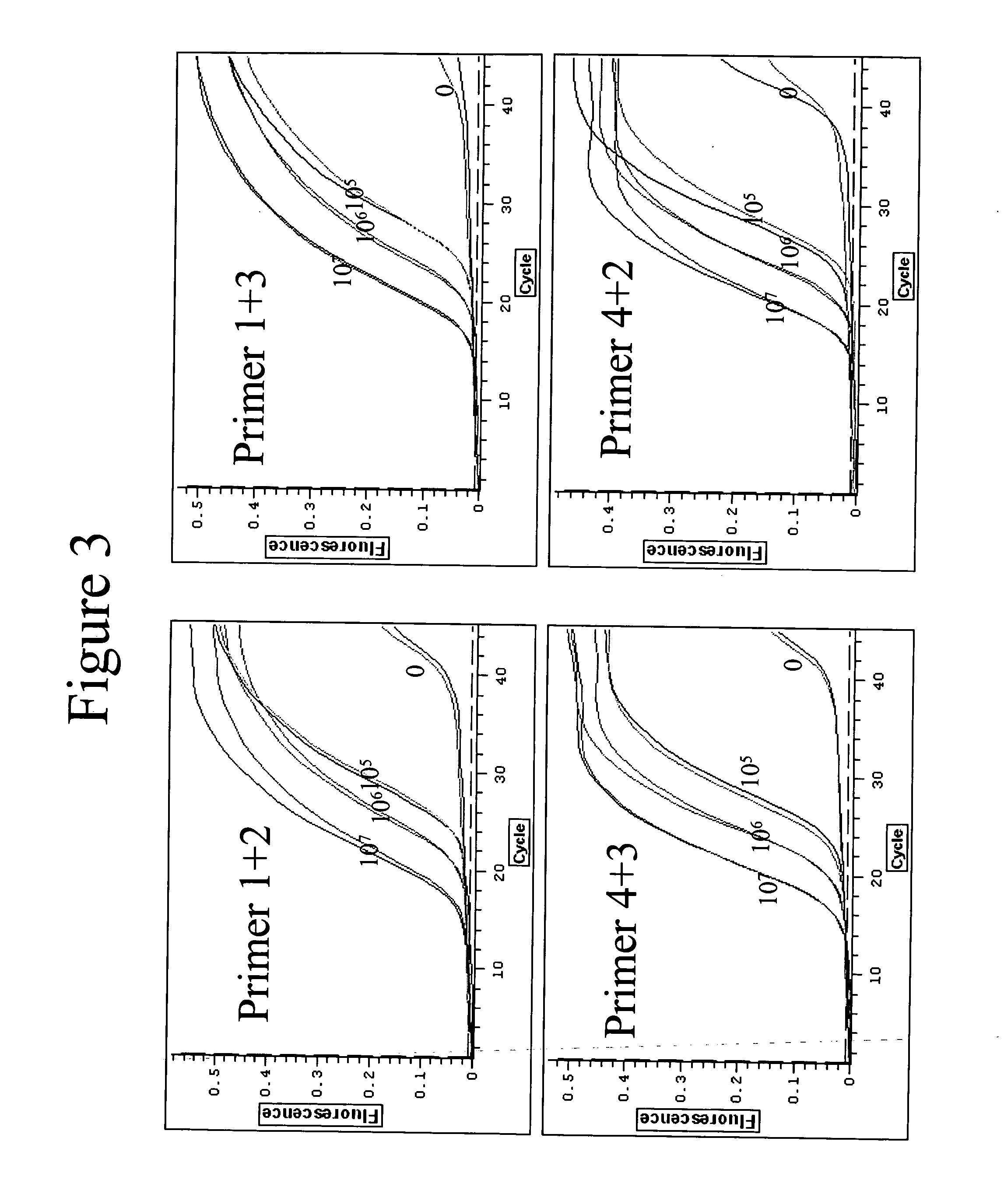
Quantitative amplification with a labeled probe and 3' to 5' exonuclease activity
This invention provides methods and kits for performing a quantitative amplification reaction. The method employs a polymerase enzyme and an enzyme having a 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity that cleaves the 3′ oligonucleotide of the probe.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Thermostable enzyme promoting the fidelity of thermostable DNA polymerases-for improvement of nucleic acid synthesis and amplification in vitro
A purified thermostable enzyme is derived form the thermophilic archaebacterium Archaeoglobus fulgidus. The enzyme can be native or recombinant, is stable under PCR conditions and exhibits double strand specific exonuclease activity. It is a 3′-5′ exonuclease and cleaves to produce 5′-mononucleotides. Thermostable exonucleases are useful in many recombinant DNA techniques, in combination with a thermostable DNA polymerase like Taq especially for nucleic acid amplification by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH +1
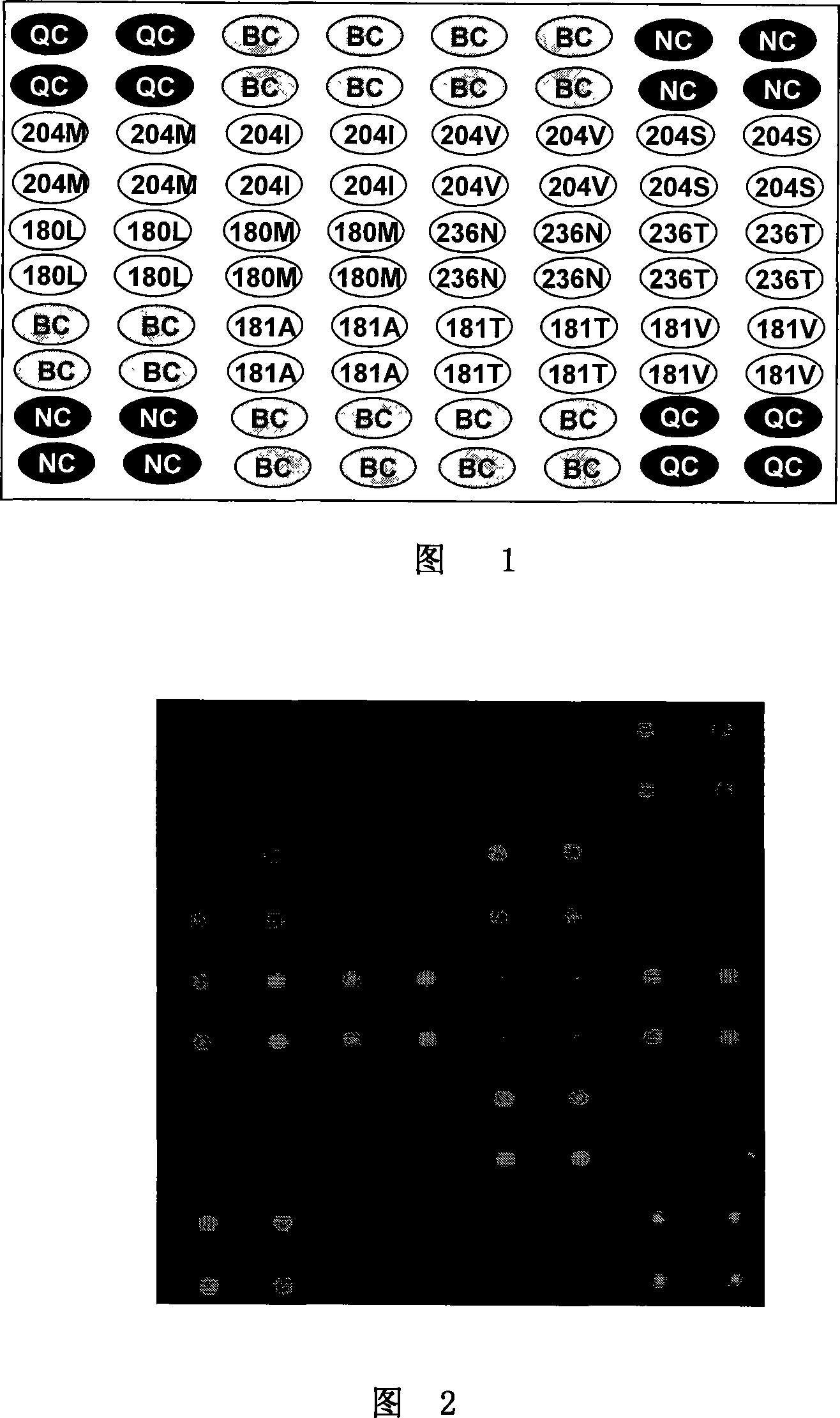
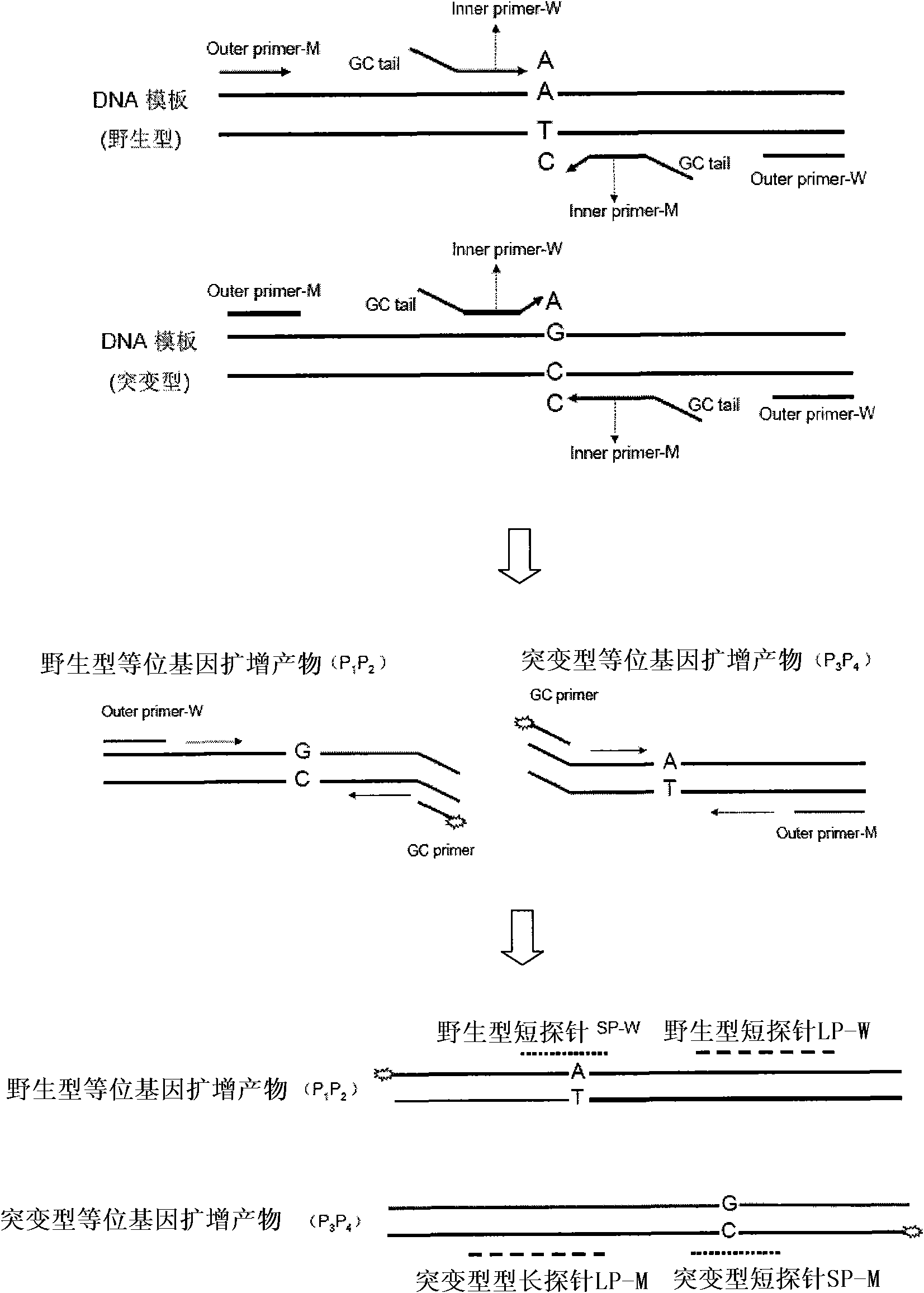
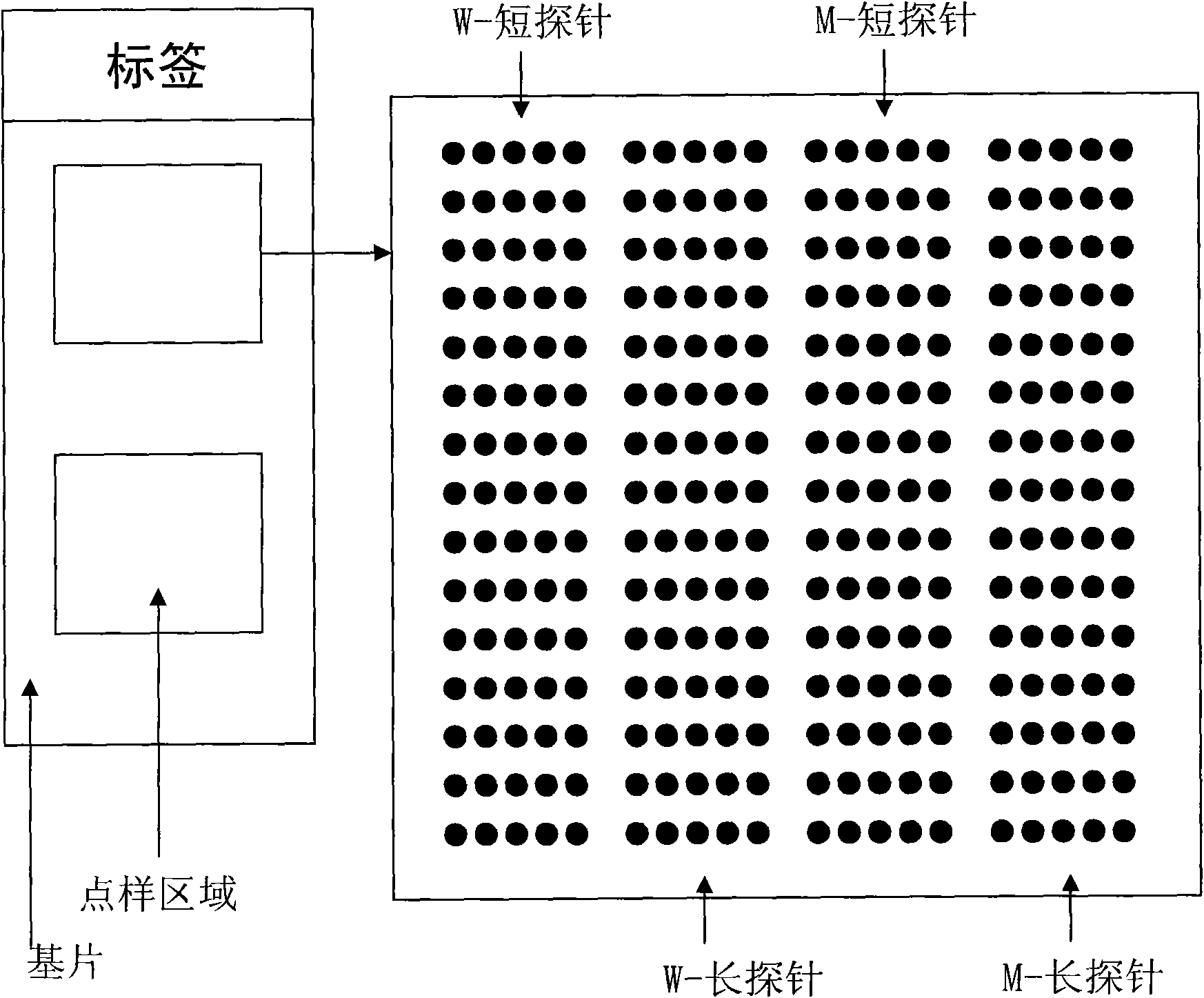
Double-probe gene mutation detecting method based on allele special amplification as well as special chip and kit thereof
ActiveCN101619352AEasy to detectAvoid the hassle of markingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeOligonucleotide
The invention relates to a method for identifying gene mutation types in the field of gene analysis as well as a special chip and a kit thereof. The gene mutation detecting method comprises the following steps: taking a genome to be detected from a human tissue as a template, carrying out multiple allele special PCR amplification by a primer group that is designed aiming at special mutant sites and DNA polymerase without 3'-5' end exonclease activity, then hybridizing the obtained PCR product and an oligonucleotide probe (allele special probe) on the gene chip, and confirming mutation types of all gene sites according to the hybridizing result. The allele special probe is designed aiming at special gene types of gene mutant sites to be detected. The invention can detect gene mutations in comprehensive, systemic and high-flux ways and has light environmental pollution as well as simple and rapid operation compared with PCR-RFLP and a sequencing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Thermostable DNA polymerases and methods of use
InactiveUS20120083018A1Improve stabilityIncrease rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPolymerase LPrimase
Thermostable viral and microbial polymerases exhibiting a combination of activities selected from proofreading (3′-5′) exonuclease activity, nick translating (5′-3′) nuclease activity, synthetic primer-initiated polymerase activity, nick-initiated polymerase activity, reverse transcriptase activity, strand displacement activity, terminal transferase activity, primase activity, and / or efficient incorporation of chain terminating analogs. Some of the polymerases provided herein include a first motif and a second motif. The first motif preferably has the sequence X1X2X3DX4PX5IELRX6X7X8, wherein X1 is I or V; X4 is F or Y; X8 is G or A; and X2, X3, X5, X6, and X7 are any amino acid. The second motif preferably has the sequence RX9X10X11KSANX12GX13X14YG, wherein X11 is G or A; X12 is F, L, or Y; X13 is L or V; X14 is I or L; and X9 and X10 are any amino acid. Also provided are reagents for expressing the polymerases, polynucleotides encoding the polymerases, host cells expressing the polymerases, and methods of using the polymerases.
Owner:SCHOENFELD THOMAS W +1
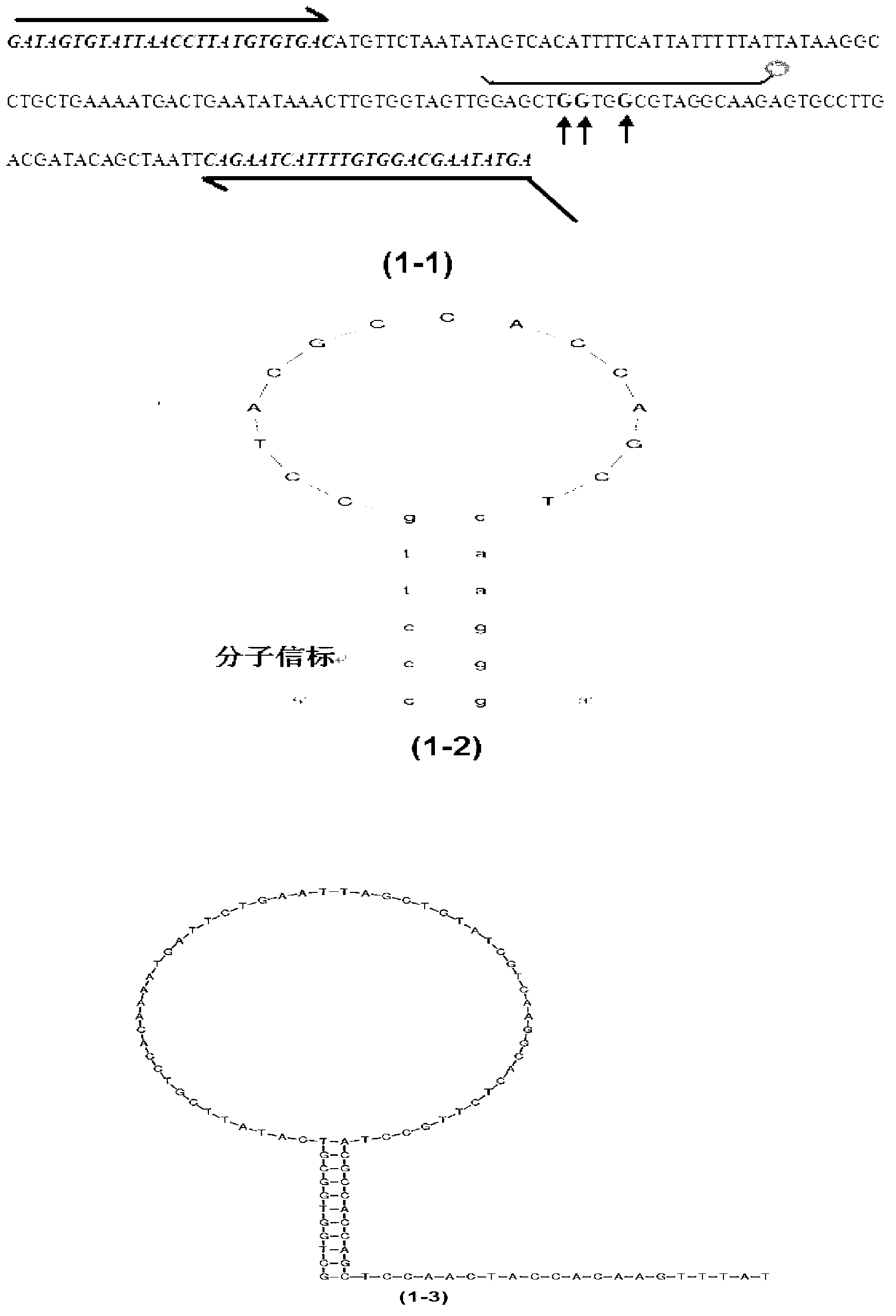
Fluorescence probe for hgih temperature polyase exonuclease activity in real time PCR test
ActiveCN1900312AImprove performanceEliminate non-specific signalsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescencePolymerase L
The present invention relates to fluorescent probe, and is especially fluorescent probe for real-time PCR detection and capable of resisting high temperature polyase exonuclease activity. The fluorescent probe has two-stage structure containing complementary sequences and including replacing probe, molecular beacon probe, scorpion primer, etc. The fluorescent probe includes a fluorescent probe such modified that it can resist the 5'-->3' exonuclease activity of high temperature polyase without generating non-specific signal, a fluorescent probe such modified that it can resist the 3'-->5' exonuclease activity of high temperature polyase without generating non-specific signal in real-time PCR detection, and a fluorescent probe such modified that it can resist both 5'-->3' exonuclease activity and 3'-->5' exonuclease activity of high temperature polyase without generating non-specific signal.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction fluid and method
InactiveCN106498060AImprove stabilityLong validity periodMicrobiological testing/measurementMgb probeBiology
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction fluid and a method; the fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction fluid at least includes DNA polymerase with ordinary excision enzyme activity, a basic fluorescent stabilizer, DNA polymerase enhancer and protection agent. The fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction fluid of the invention is able to obviously improve the 5'-3- excision enzyme activity of the DNA polymerase, so that the ordinary DNA polymerase can hydrolyze Taqman-MGB probe, improve the amplification efficiency and keep strong stability. The fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction fluid has stronger sensitivity in the application of Taqman-MGB probe, the effect is obviously better than that of the prior art; therefore, the fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction fluid has very wide market prospect.
Owner:江苏然科生物技术有限公司
Method for detecting activity of DNA methylase and DNA methyltranseferase by unlabeled fluorescent detection based on restriction endonuclease and exonuclease III
InactiveCN103993083ALow costAvoid accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSignalling moleculesSingle strand dna
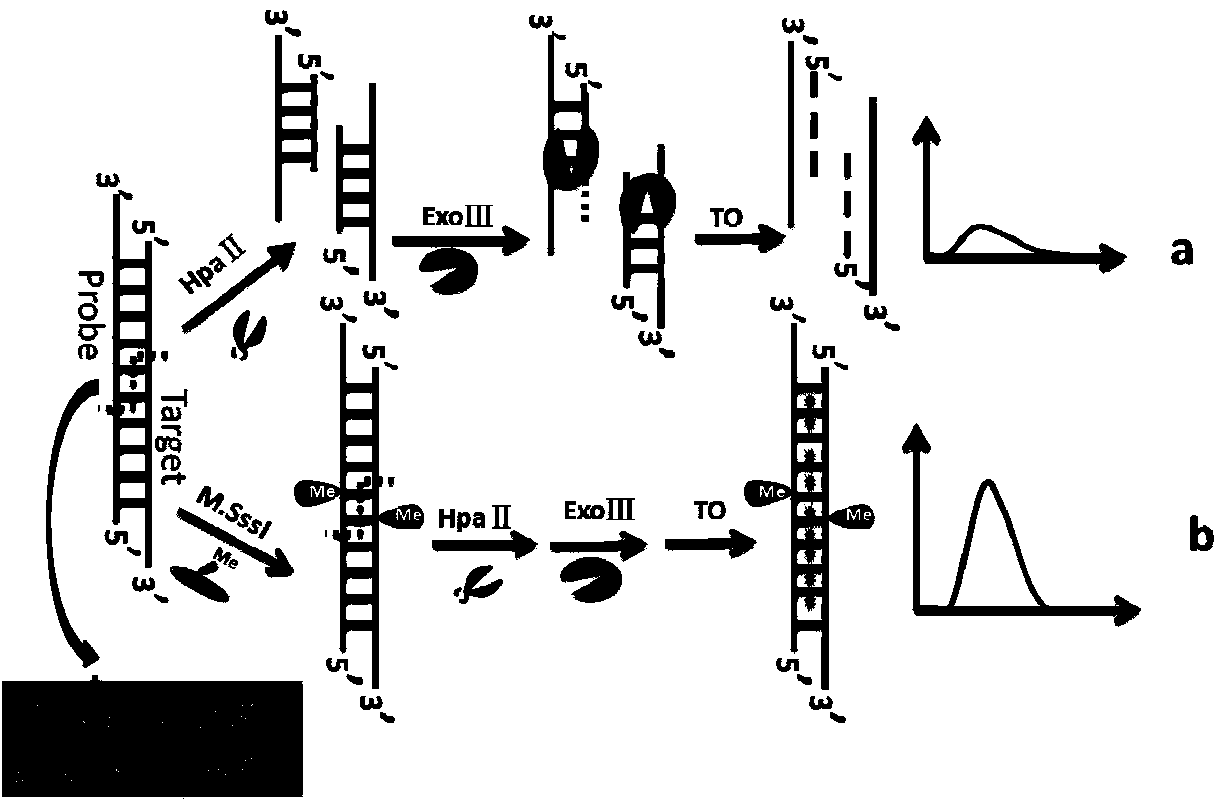
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of DNA methylase and DNA methyltranseferase based on restriction endonuclease Hpa pi and exonuclease III. An unlabeled DNA probe is prepared and the sequence of the probe comprises a cleavage site of the restriction endonuclease and a methylated CpG site. The purpose of detecting the activity of the methylase and methyltranseferase is reached by steps of hybridizing the unlabeled DNA probe with the target DNA, carrying out methylation treatment by the methylase, carrying out the specific cleavage of the restriction endonuclease Hpa pi and enabling exonuclease III having the activity of 3'->5' exonuclease to act on the double-stranded DNA and then adding fluorescence signal molecules thiazole orange which having different signals to single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA. According to the method, since no complex material or labeling of DNA probes need to be prepared, the defects of high detection cost, cumbersome operations and poor reproducibility caused by the preparation of the material and labeling of DNA probes are avoided. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost and high sensitivity and is fast and simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for identifying HBV gene mutation type, special chip and reagent kit
The invention discloses a method for identifying HBV gene mutation type and a chip and a reagent box which are especially used with the method. The method for identifying the HBV gene mutation type takes the detected the genome of the hepatitis B virus as the template and uses the following primer group and a DNA polymerase which has no exonuclease activity from the 3'end to 5' end for implementing multiple PCR magnification; the primer group comprises a universal primer and a or more than one special primers; the special primer 5' end is a bar code sequence and the length of the bar code sequence is 5 to 25 nt; the bar code sequence has a comparatively low homology with the hepatitis B virus; the special primer totally matches with the corresponding segment of the hepatitis B virus comprising wild base group or mutant base group at a mutation point; the gene chip comprises a plurality of probes and the probes are corresponding to the bar code sequence one to one and every probe only contains one bar code sequence.
Owner:BOAO BIOLOGICAL CO LTD +1
Method for detecting related gene mutations of diabetes drug treatment as well as special chip and kit thereof
ActiveCN101619351ALittle pollutionEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDiabrezideDrug treatment
The invention discloses a method for detecting related gene mutations of diabetes drug treatment as well as a special chip and a kit thereof. The method comprises the following steps: taking a genome to be detected from a human tissue as a template, carrying out multiple PCR amplification by a primer group that is designed aiming at special mutant sites and DNA polymerase without 3'-5' end exonclease activity, then hybridizing the obtained PCR product and an allele specific probe on the gene chip, and confirming mutation types of related genes of diabetes drug treatment according to the hybridizing result. The invention can detect known gene mutations closely related to the individual difference of anti-tumor medicine reaction in comprehensive, systemic and high-flux ways and greatly improve the accuracy and the specificity of chip detection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for rapidly detecting mutation of KRAS gene
ActiveCN102796817AStrong specificityGuaranteed specific amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementKras mutationTrue positive rate
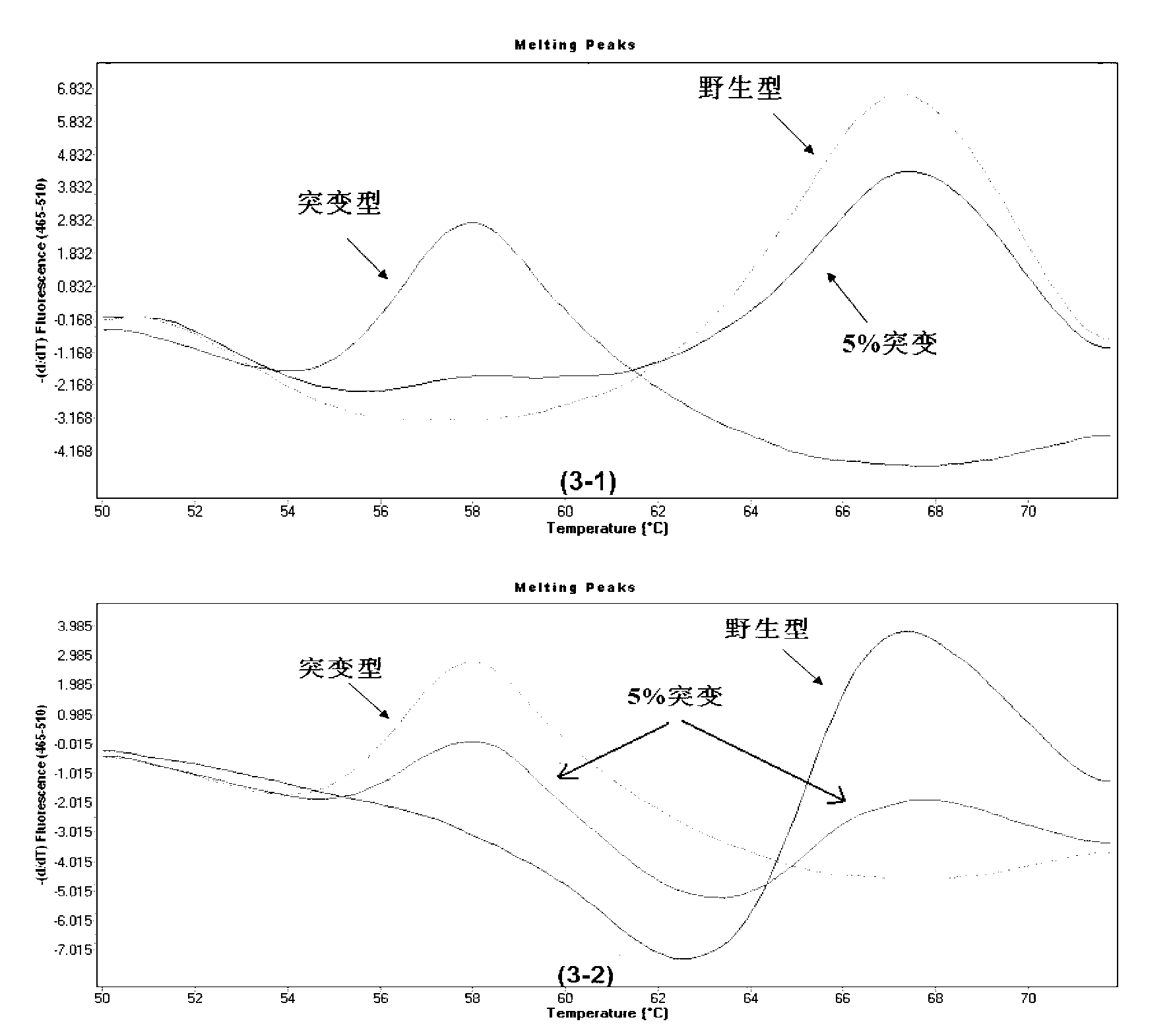
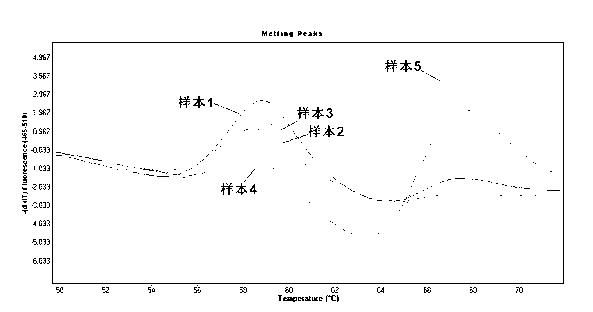
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting the mutation of KRAS gene, to overcome the disadvantages of low sensitivity and inaccuracy in conventional probe melting curve assay. The method for rapidly detecting the mutation of KRAS gene comprises the following steps: (1) designing and synthesizing molecular beacon probe and template amplification primers; (2) extracting the KRAS genome DNA of a detected sample; (3) preparing a reaction system; (4) performing PCR reaction; performing melting curve analysis after the PCR reaction is finished, and determining if a KRAS mutation occurs in the detected sample through the Tm value of a melting peak. The method combines the molecular beacon probe and extension retardance primers, and uses the DNA polymerase without 5'->3' exonuclease activity to detect KRAS mutation rapidly in vitro, thereby saving consumables simultaneously having the characteristics of high sensitivity and specificity which ensure a more reliable detection result.
Owner:陕西佰美医学检验有限公司
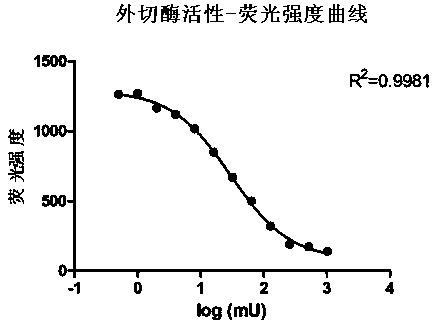
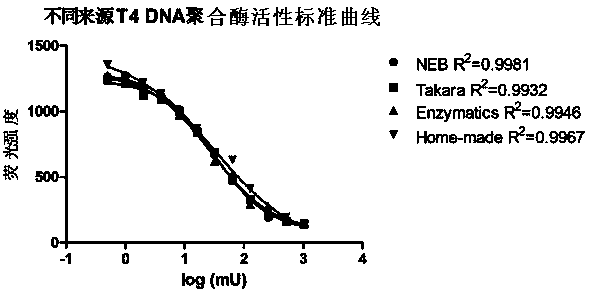
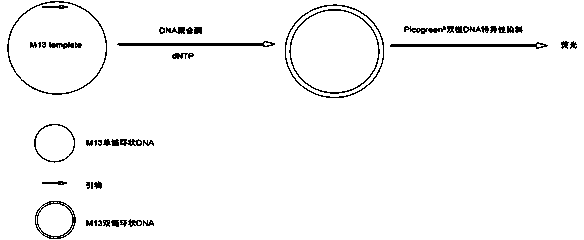
Measuring method of activity of T4 DNA polymerase
InactiveCN104313132AEasy to operateImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LRadioactive contamination
A measuring method of activity of a T4 DNA polymerase is disclosed. The method includes: under the circumstance of no dNTP, adding the T4 DNA polymerase into a reaction system adopting a double-strand linear DNA template as a substrate, detecting the relative amount of double-strand DNA after a reaction is finished so as to measure the excision enzyme activity of the T4 DNA polymerase, and allowing the excision enzyme activity of the T4 DNA polymerase to be related to the polymerase activity so as to obtain the polymerase activity degree of the T4 DNA polymerase. The polymerase activity is measured by conveniently measuring the excision enzyme activity and by utilization of relevance between the excision enzyme activity and the polymerase activity of the T4 DNA polymerase. Compared with methods in the prior art, the method is free of radioactive contamination and simple and rapid in operation, and the method overcomes interference of the excision enzyme activity on the measurement of the polymerase activity, so that a result of the method is more accurate.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
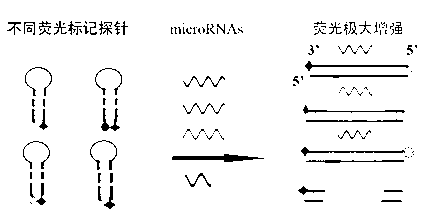
Micro RNAs (ribonucleic acids) fluorescence detection probe
InactiveCN102899417AMeet different testing needsResponsiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescencePolymerase L
The invention relates to a micro RNA (ribonucleic acid) fluorescence detection probe. The probe has a folding structure, and comprises a tail-end area and an annular area, wherein the tail-end area has a double-chain structure; the annular area has a single-chain structure and comprises a complementary sequence and an interval sequence of a target to be detected; and the interval sequence does not form a secondary structure with other sequences of the probe. By the tail-end area of the probe, the relative stability of the folding structure of the probe can be maintained; the folding structure is opened when a sample containing a detection object is added, a complementary primer of the tail-end area of the detection probe is added, and a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase without excision enzyme activity is added; micro RNA is released by extension of the primer and replacement of corresponding chains to allow the probe to recover and generate a fluorescence signal; the corresponding target micro RNA is detected by the generated detection fluorescence signal; and different fluorescence is marked according to the probes of the different RNAs, so that the simultaneous detection of the different micro RNAs can be realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for inserting target DNA fragment into vector
InactiveCN101899467AFlexible choiceSolve efficiency problemsVector-based foreign material introductionDual effectDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for inserting a target DNA fragment into a vector. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) designing and synthesizing a primer for amplifying the target DNA fragment and amplifying by using the primer to obtain the target DNA fragment, wherein 3 to 20 bases on the outmost side of the primer are completely complementary with the outmost side of a linear vector; and 2) mixing the target DNA fragment and the linear vector, and adding a recombinant enzyme with the excision enzyme activity and the homologous recombination enzyme activity from ends 3' to 5' for reaction to obtain a recombinant vector into which the target DNA fragment is inserted. The method has the advantages of dual effects of excision and homologous recombination, more flexible selection for the number of bases at the recombinant ends by selecting the number of homologous bases of a PCR product and the linear vector in a wider range (namely 3 to 20 bases), no need of DNA ligase, linearization for the target vector only, no need of enzymatic treatment on the PCR product, direct mixing with a target vector, one-stop solution for all the problems within 20min, realization of perfect seamless connection, simple operation and low cost.
Owner:JIERUI BIOENG SHANGHAI
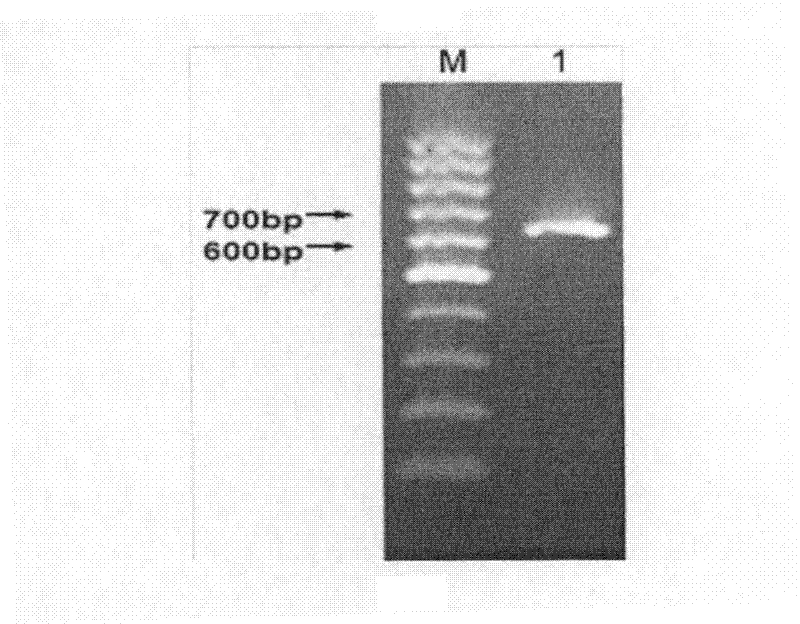
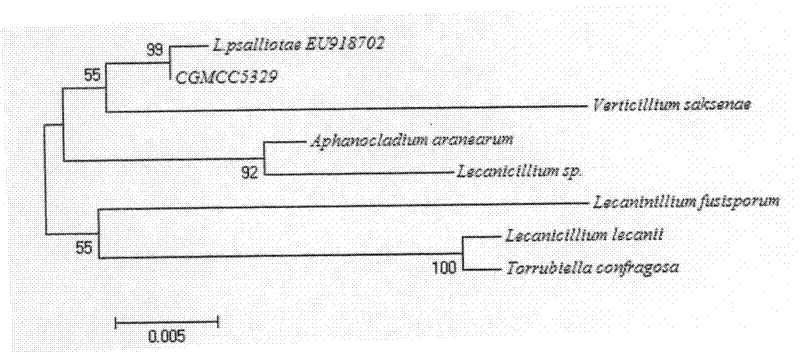
Lecanicillium psalliotae strain
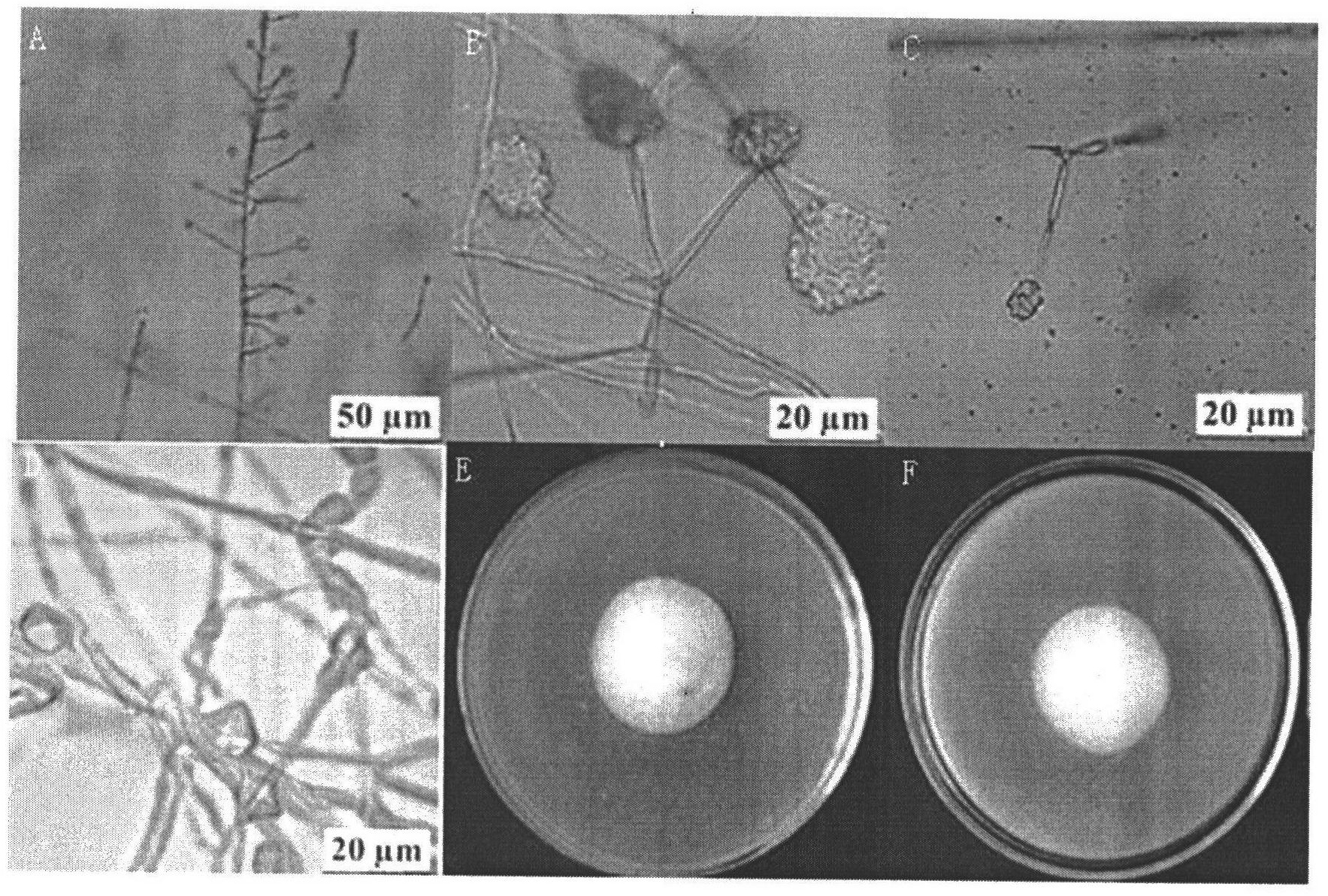
InactiveCN102417886AIncrease enzyme activityIncreased parasitic abilityBiocideFungiDegradative enzymeLife stage
The invention discloses a lecanicillium psalliotae strain with the preservation number of CGMCC NO: 5329. The strain can colonise spawns, two-year-old larvae and female adults at different life stages of rootknot nematode. Activations of chitinous substance degradative enzyme and excisionenzyme generated by the strain can be respectively determined through an N-acetyl glucosamine method and a p-nitrobenzene method, the enzymatic activities thereof can reach 3.98 U / h.mL and 0.38 U / h.mL, and higher activity of the produced chitinous substance enzyme can be detected at different temperature (27 DEG C-75 DEG C) and different pH (3.0-7.0); and the influence of chitinous substance enzyme extract produced by the strain on eclosion of rootknot nematode spawns is determined in vitro, and the inhibition ratio and the destruction ratio of enzyme solution on relative eclosion of the spawns are respectively 94.52 percent and 84.32 percent. The lecanicillium psalliotae strain disclosed by the invention is applied to biological control of crop rootknot nematodiasis, provides an effective way for protecting sweet potatoes, fruits, vegetables in north China and particularly controlling destructiverootknot nematodiasis, and has obvious ecological benefit, economic value and social value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
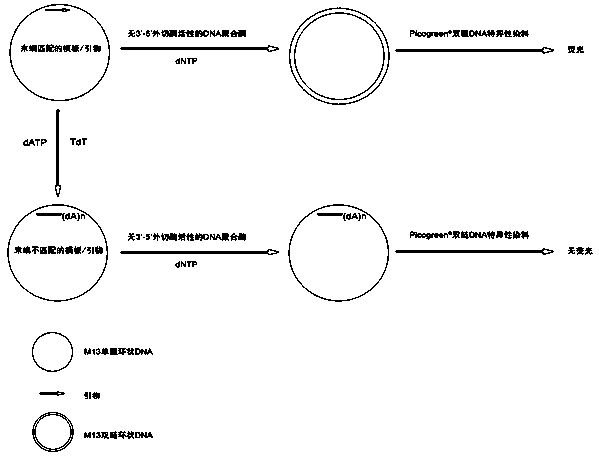
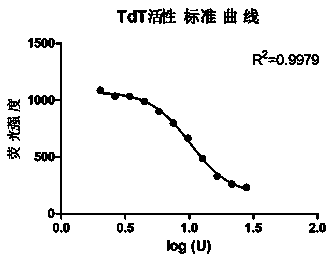
Method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
InactiveCN104293883ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
The invention discloses a method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, synthesizing a primer according to a single stranded template, annealing the single stranded template, then performing a 3' end tailing reaction catalyzed by TdT enzyme in the presence of one of four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, after the 3' end tailing reaction is completed, performing a polymerization reaction in the presence of enough DNA polymerase without 3'-5 'excision enzyme activity to generate double stranded DNA, finally measuring the relative quantity of the double stranded DNA or single stranded DNA in the reaction system after the polymerization reaction is finished, and deducing the activity degree of the Poly (A) polymerase according to the detection result, wherein the basic group at the first site on the used single stranded template in the 3' direction and the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate used in the tailing reaction are not complementary. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention is free of radioactive pollution, simple and quick to operate, low in reagent preparation cost and high in sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
High-specificity multiplex-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for base mutation
InactiveCN108103159ALarge capacityImprove the problem of heterogeneityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideExonuclease I
The invention discloses a high-specificity multiplex-PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for base mutation. The method comprises steps as follows: under the action of DNA polymerase without 3'-5' exonuclease activity and with pyrophosphorolysis activity, multiple pairs of modified primers are utilized for PCR amplification in the presence of pyrophosphate, dideoxy nucleotide is located at 3' ends of upstream and downstream primers of the modified primers, the 3' ends are complementary with upstream and downstream sequences of a to-be-detected mutant type template, the DNA polymerase relies on the template to perform pyrophosphorolysis on dideoxy nucleotide located at the 3' ends of the modified primers and complementary with the template, the multiple pairs of primers are specifically bonded with the template and extend normally, and multiplex-PCR amplification is realized. According to the method, the problems of non-specificity strip interference and primer dimer of multiplex-PCR are solved, detection specificity and sensitivity are improved, and capacity of a system for the primers is increased; the method can be used for detecting body fluid DNA collected from cancer patients or healthy persons.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +2
PCR method capable of eliminating non specific braid and RT-PCR chip prepared using said method
InactiveCN1718737ANon-specific band eliminationEfficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LBiology
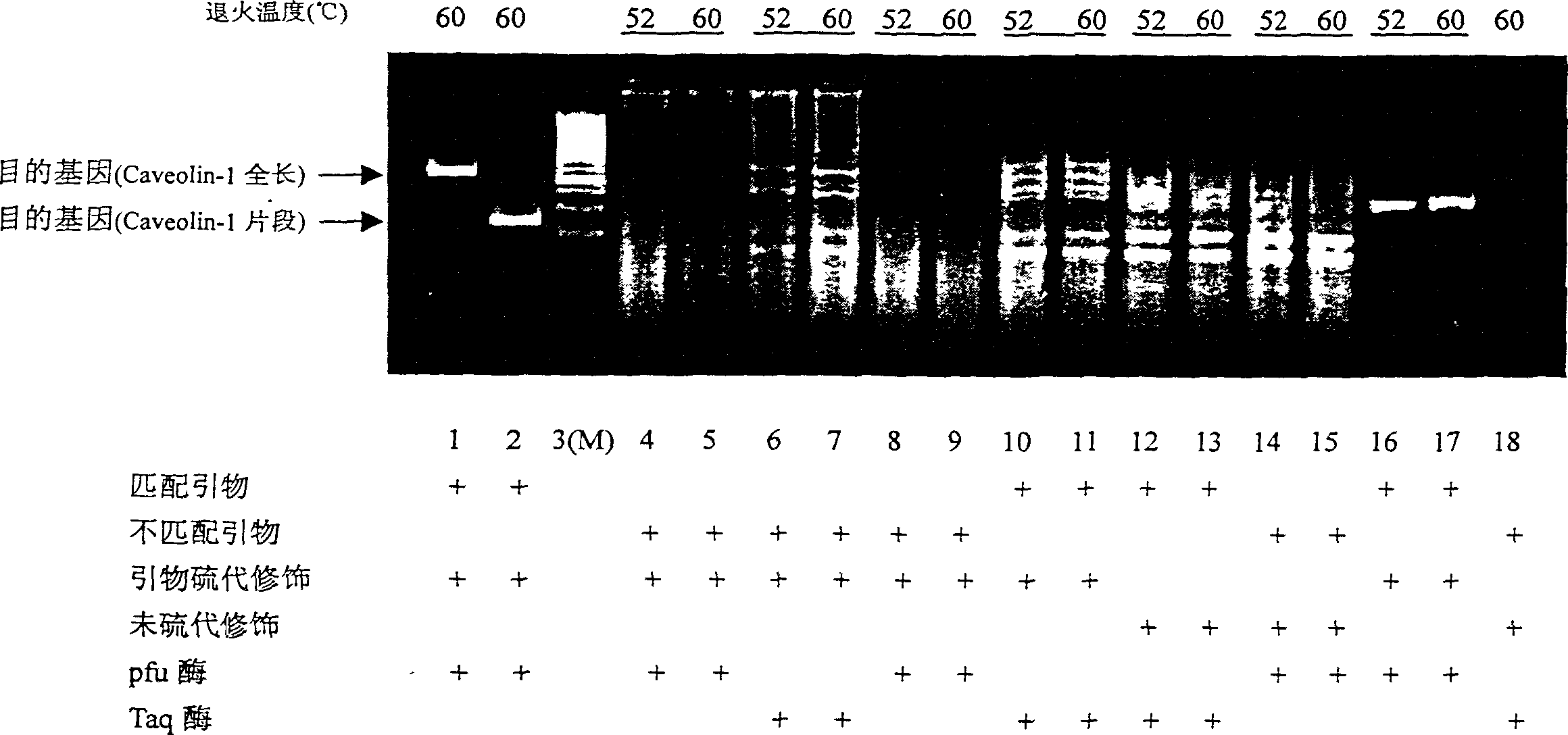
A PCR method for eliminating the non-specific band and precisely obtaining target gene by one step, and the RT-PCR chip prepared by said method are disclosed. When the primer of (PCR CRT-PCR or PCR) target gene is designed, the one or more bases at terminal 3' of primer are modified by thiophosphate. The polymerase used for extension reaction is the DNA polymerase with high Pfu fidelity. As a result, in various PCR reactions, only the template fully matched with 8bp at terminal 3' of primer can be extended with high fidelity to said template.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Reagent for nucleic acid real-time isothermal amplification, amplification system and amplification method and application of amplification system
InactiveCN108642145ARealize quantitative detectionAchieve hydrolysisMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
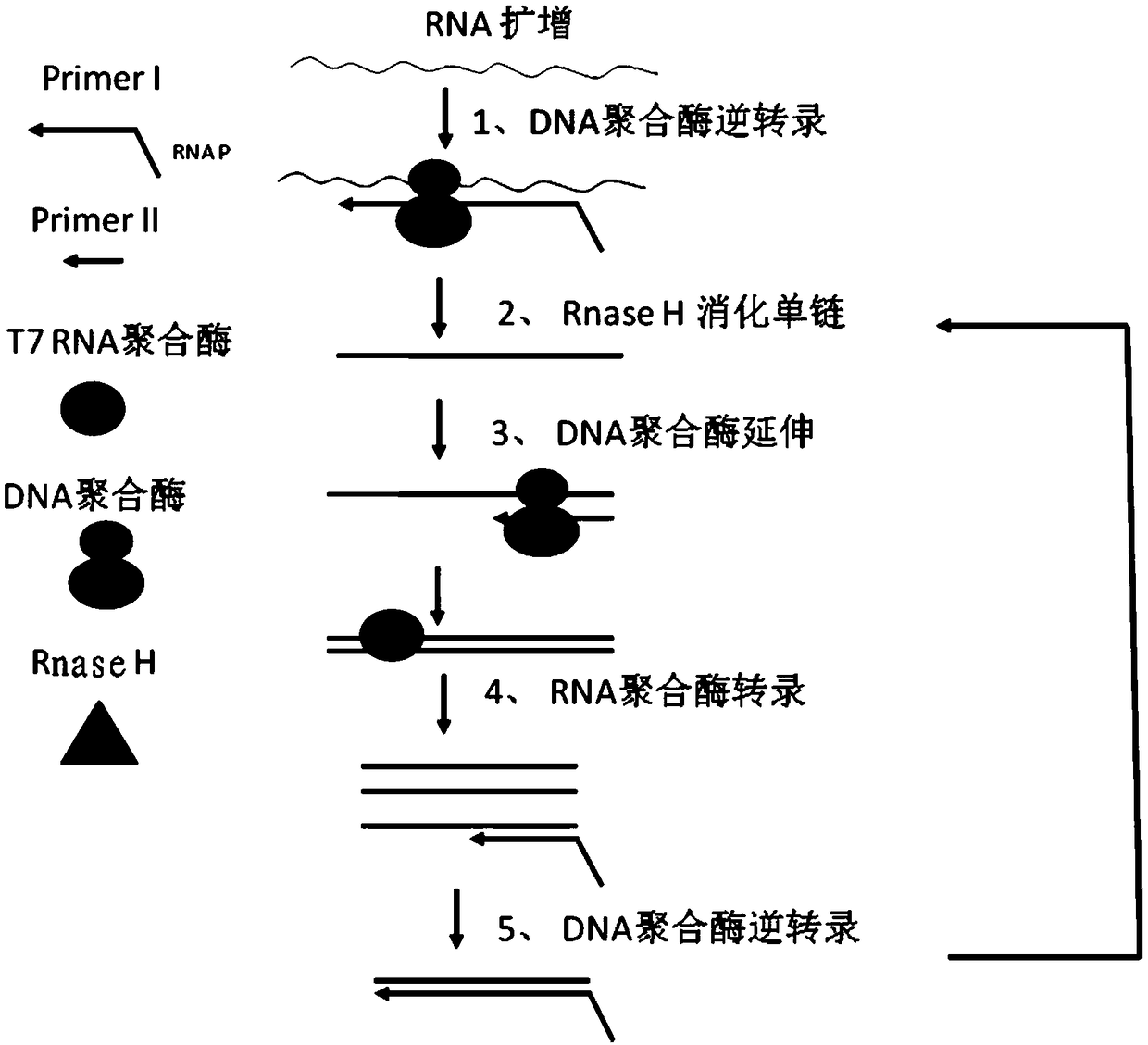
The invention relates to a reagent for nucleic acid isothermal amplification. The reagent comprises RNA polymerase, DNA polymerase with reverse transcription activity and RNase H, wherein the DNA polymerase with reverse transcription activity has 5'-3' DNA polymerization activity and reverse transcription activity and 5'-3' exonuclease activity. The reagent further comprises primers and a fluorescence probe, wherein the primers comprise the primer with an RNA promoter recognition sequence and the second cDNA synthesis primer, and the fluorescent probe is selected from a TaqMan probe and a Molecular Beacon probe. The invention further relates to a nucleic acid isothermal amplification system comprising the reagent and an amplification method thereof, and a kit comprising the nucleic acid isothermal amplification system and application thereof. By using the RNA polymerase, the DNA polymerase with reverse transcription activity and the RNase H, controllable RNA and DNA isothermal amplification is realized; the isothermal amplification is combined with the fluorescent probe technology, which can realize real-time fluorescence detection in the target RNA amplification process; besides,the whole process is completed in the same reaction system, and quantitative detection of nucleic acid is realized. The reagent, the amplification system and the kit are suitable for clinical promotion and application.
Owner:上海默礼生物医药科技有限公司
Lecanicillium attenuatum strain
InactiveCN102433264AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease hatch inhibition rateBiocideFungiDiseaseDegradative enzyme
The invention discloses a lecanicillium attenuatum strain with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) NO.5328. The strain can allow meloidogyne ova and female ova to parasitize in the strain. The activities of chitin degradative enzyme and excision enzyme are respectively measured by applying an N-acetyl glucosamine method and a paranitrobenzene methodto be 16.34U / h ml and 0.59U / h ml respectively; and higher activities of the generated chitin degradative enzyme system at different temperatures of 27-50DEG C and different pH values of 3.5-6.0 can be respectively detected. According to the measurement of the activity of chitin enzyme by electrophoresis, five bands are measured with the molecular weights of 79.6kDa, 65.6kDa, 54.1kDa, 42.1kDa and 32.9kDa respectively. The relative hatching inhibition rate of chitin enzyme coarse liquid generated by the lecanicillium attenuatum to the meloidogyne ova is measured to be 83.17 percent under the invitro condition. The lecanicillium attenuatum is applied to biological control over meloidogyne diseases of crops, particularly provides an effective path for controlling the meloidogyne diseases seriously harming melon and fruit vegetables in protected land in northern area of China as well as has remarkable biological benefit, economic value and social value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
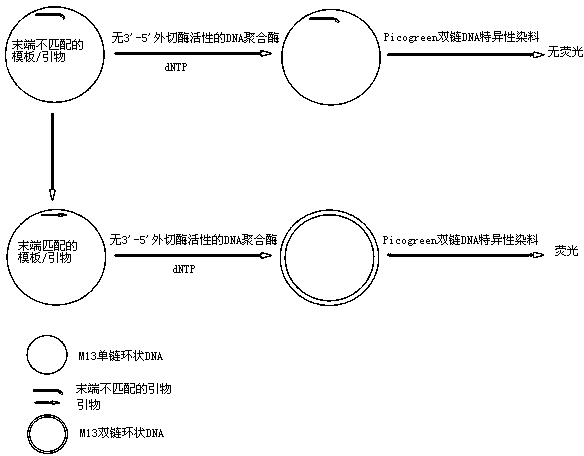
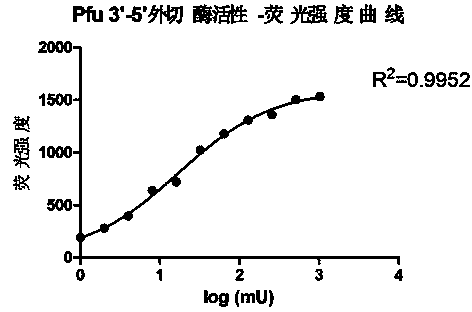
3'-5' excision enzyme activity measurement method
ActiveCN104293930AEasy to filterQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LActivity measurements
The invention discloses a non-radioactive 3'-5' excision enzyme activity measurement method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, synthesizing a primer with 3' mismatching according to a single chain template; mixing and annealing the primer and the single chain template; adding 3'-5' excision enzyme activity to reaction liquid and carrying out 3' base circumscribed reaction; adding a plenty of polymerase extension primers free of 3'-5' excision enzyme activity until a dual-chain DNA is obtained; detecting the relative quantity of the dual-chain DNA in a reaction system; and deriving the excision enzyme activity degree according to the detection result. Compared with an existing technique, the method is free of radioactive pollution, and simple and rapid in operation steps; high-flux automatic activity measurement can be achieved; and the method can be used for screening the closed activity of 3'-5' excision enzymes.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
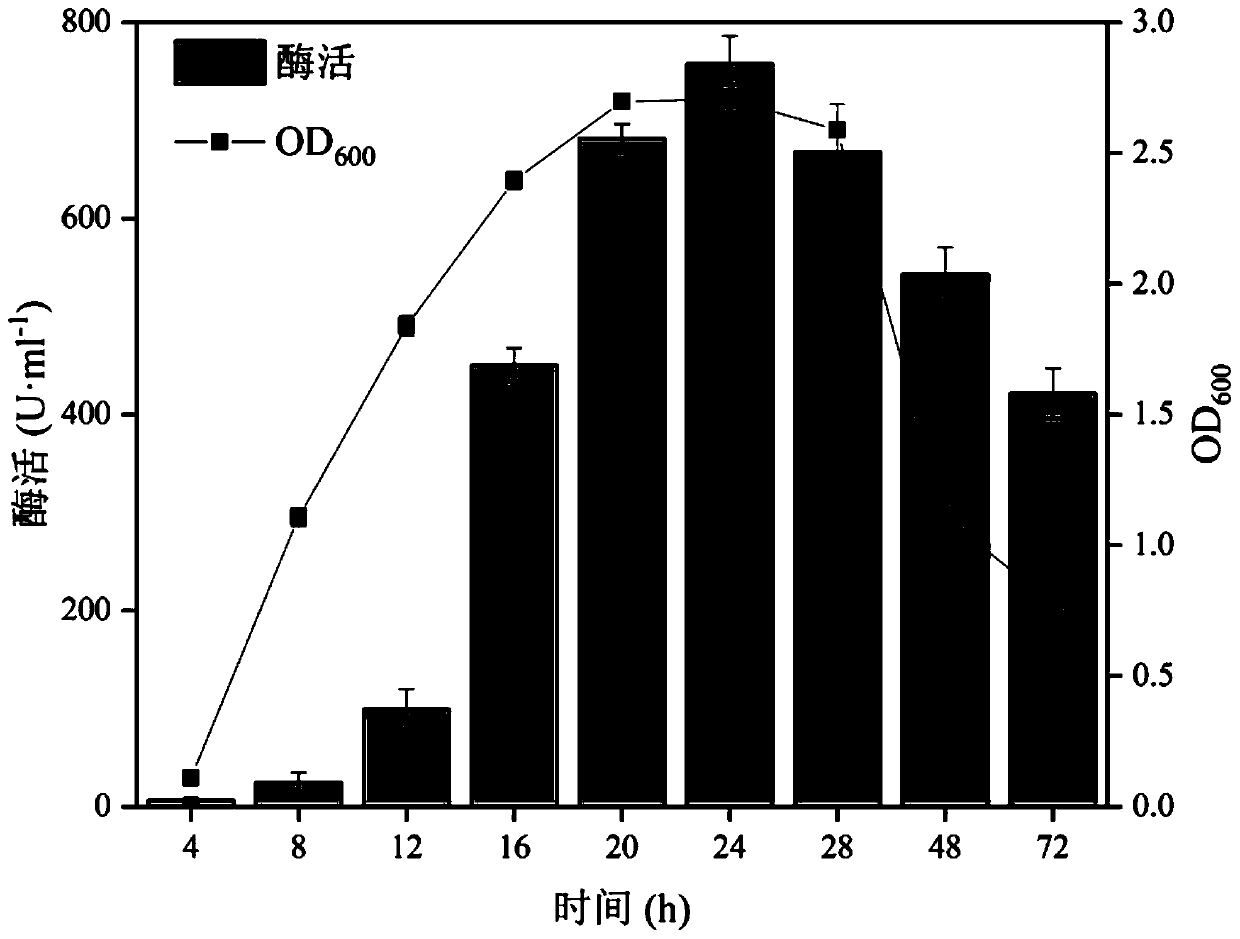
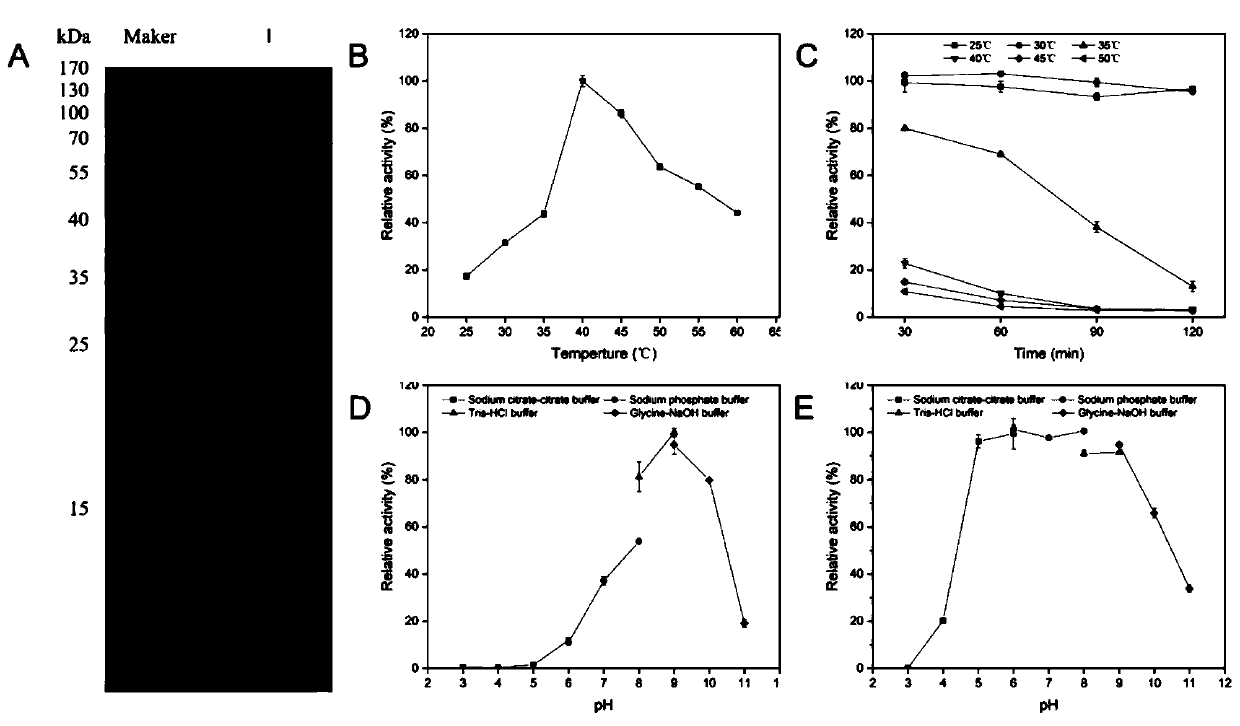
Strain SH-1 producing alginate lyase and application thereof
ActiveCN110218667AEasy to separateImprove stabilityBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides a strain SH-1 producing alginate lyase and application thereof. The strain SH-1 producing alginate lyase is named Microbulbifer sp. SH-1 and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in Beijing on December 7, 2018, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 16906. The strain can be used for producing alginate lyase by fermentation and can also bedirectly used for degrading brown algae. The invention also provides the alginate lyase with exonuclease activity; the alginate lyase is obtained by fermenting the strain SH-1, the enzymatic activityof the alginate lyase can reach 757.90 U / mL, the stability is good, and the activity is high. The invention also provides a preparation method of an algae extract; active ingredients in algae are retained, meanwhile, sodium alginate is efficiently degraded into active oligosaccharides, secondary metabolites of part of microorganisms are increased, the yield of the algae extract can reach 78-92%, and the preparation method has good industrial prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
New and effective method for building complex carrier
The invention provides a simple, general and effective method for building complex carrier. A randomly designed linker is added on a target fragment 5' in PCR primer design, the target fragment is cloned by PCR, then the PCR cloned target fragment is processed by 3'-5' excision enzyme activity of T4DNA polymerase, a plurality of end-to-end sticky ends are generated, multi-fragment orientation connection, conversion and recon identification are carried out. The method for building complex carrier has high efficiency of rearrangement, connection and conversion and is applicable to building various complex carriers.
Owner:YICHUN UNIVERSITY
Primer pair for detecting EGFR gene mutation, as well as kit, detection method and applications
ActiveCN107385066ATo achieve the purpose of detecting mutantEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWild typeEGFR Gene Mutation
The invention discloses a primer pair for detecting EGFR gene mutation, as well as a kit, a detection method and applications. The three primer pairs are used for detecting S492R mutation, G465E mutation and G465R mutation of EGFR gene, respectively. The method adopts ARMS PCR principle, Taq DNA polymerase lacks of 3'-5'exonuclease activity, and the sharp reduction of products can be caused by mismatching of 3' terminal of the PCR primer; by designing a specific primer, the amplification is blocked by a wild type template, so that the purpose of detecting mutant type can be achieved. The tolerance mutation of EGFR gene can be detected by the primer pair through a fluorescent quantitative PCR method, the operations are simple, accurate results can be obtained only through liquid biopsy, the sensitivity is high, and even 1% mutation can be detected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Taq enzyme 5'-3' exonuclease activity blocking monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN112409490AEasy to produceImprove qualityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeavy chainAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a Taq enzyme 5'-3' exonuclease activity blocking monoclonal antibody. The Taq enzyme 5'-3' exonuclease activity blocking monoclonal antibody comprises a light chain variable region containing LCDR1, LCDR2 and LCDR3 sequences and a heavy chain variable region containing HCDR1, HCDR2 and HCDR3 sequences, wherein the sequence of the LCDR1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 10, the sequence of the LCDR2 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 11, the sequence of the LCDR3 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 12, the sequence of the HCDR1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 6, the sequence of the HCDR2 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 7, and the sequence of the HCDR3 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 8. The invention further discloses application of the monoclonal antibody. The blocking effect of the monoclonal antibody is good. The stability ofa prepared double-blocking hot-start enzyme is good.
Owner:YEASEN BIOTECHNOLOGY (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification system with high specificity as well as application thereof
ActiveCN108754032AAccurate detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceBiology
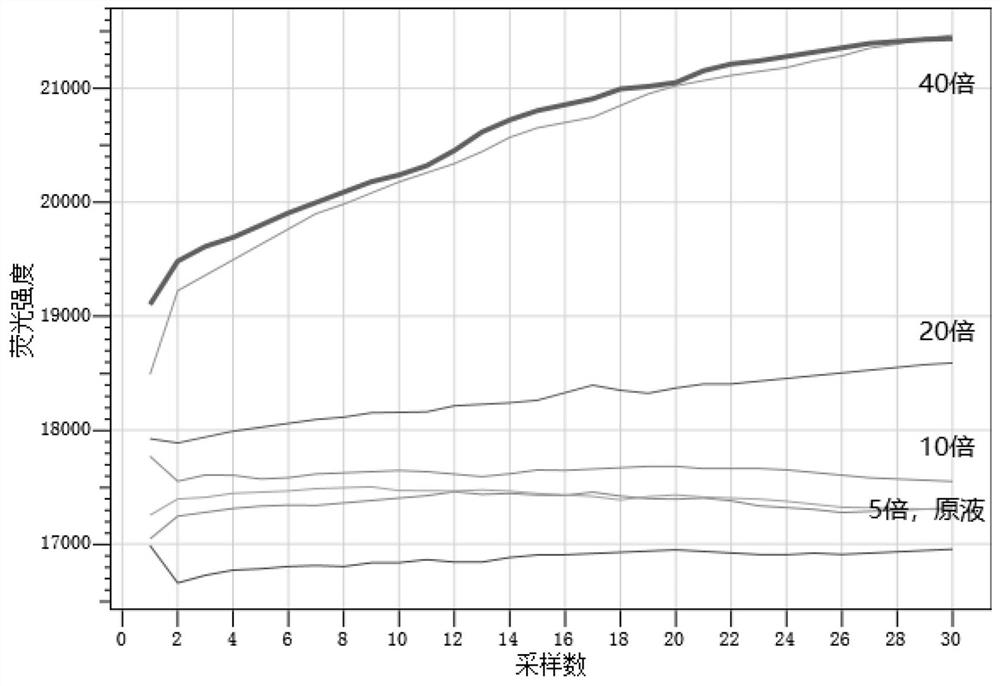
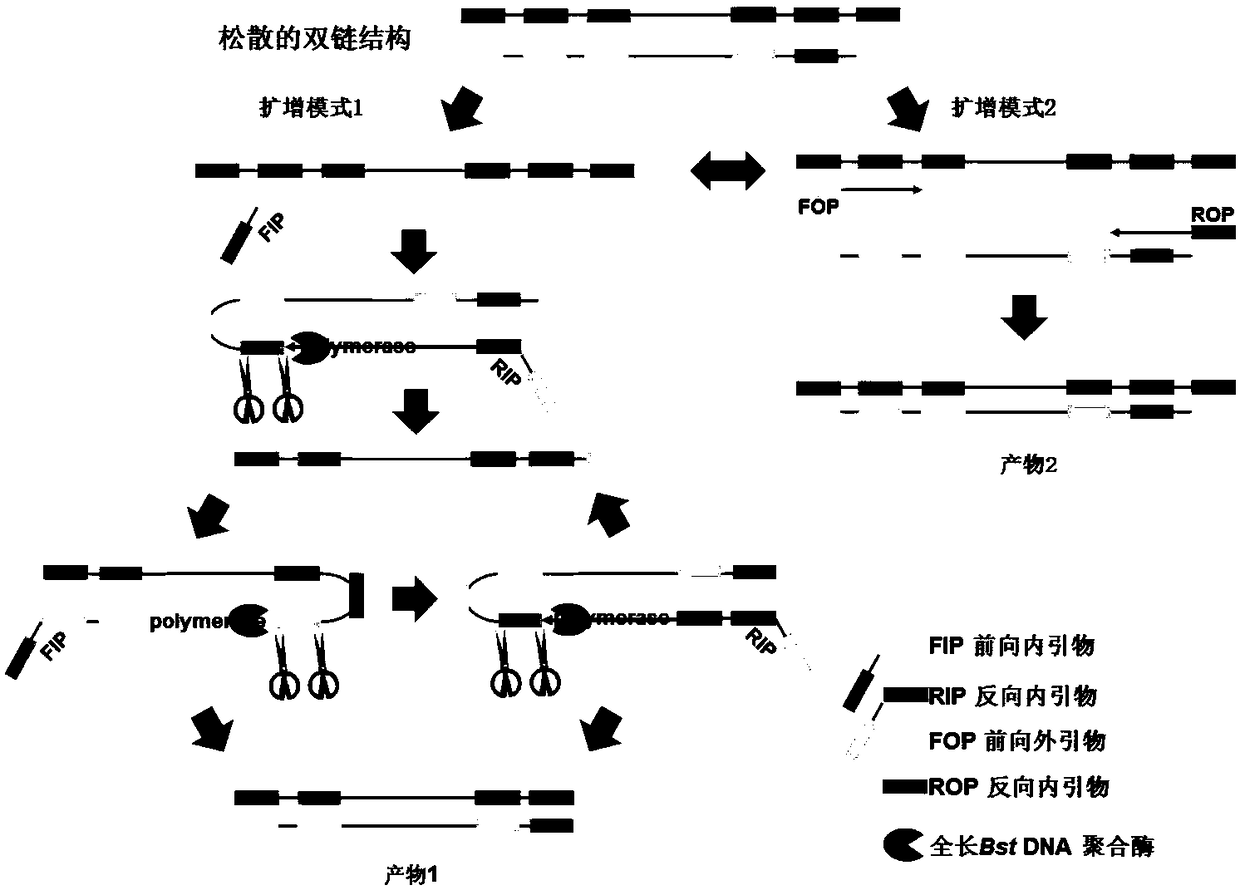
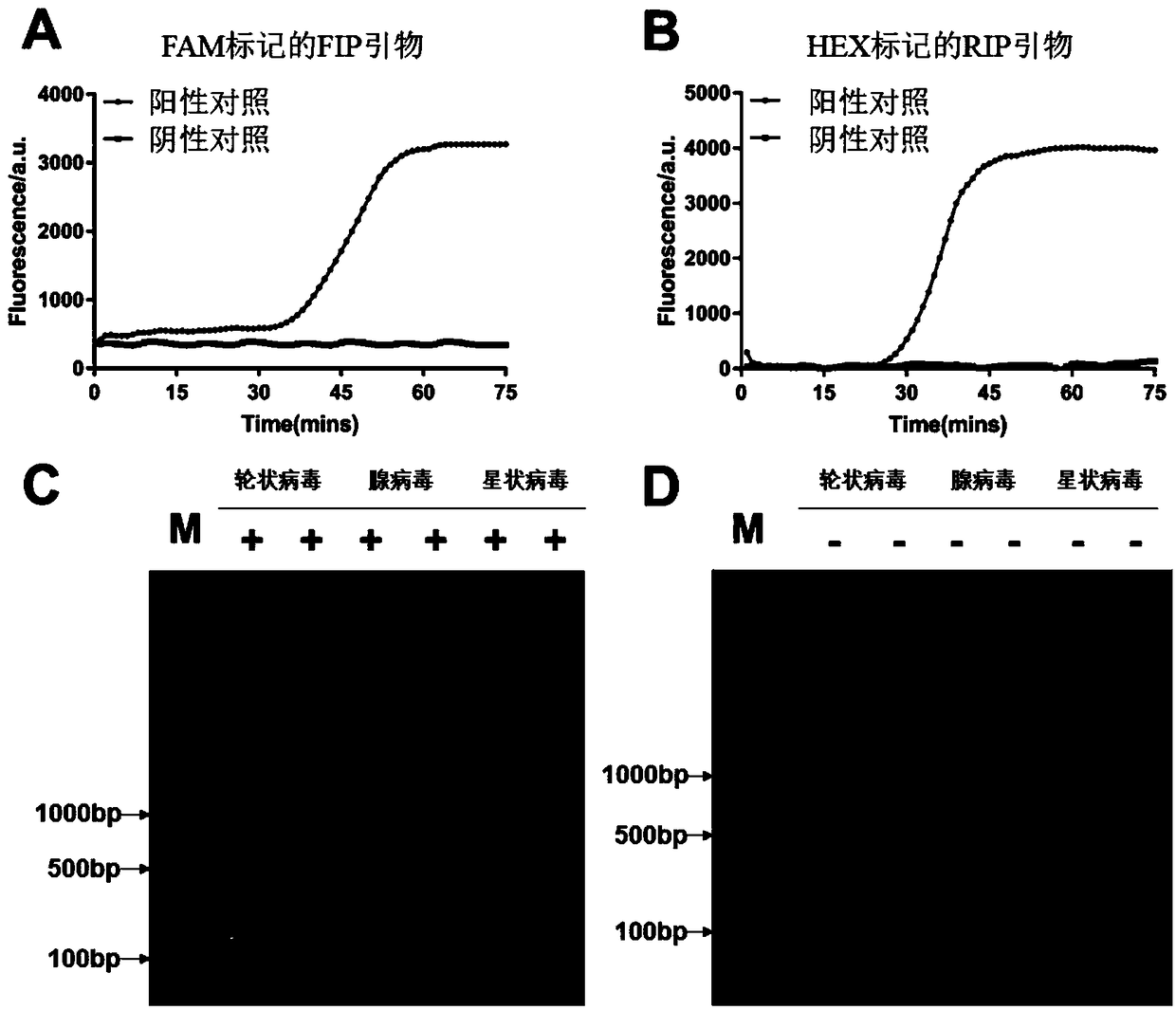
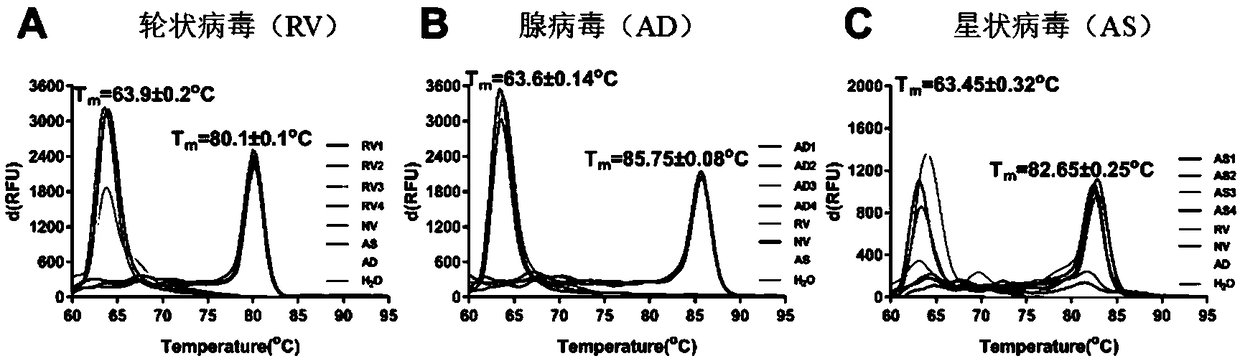
The invention relates to an isothermal nucleic acid amplification system with high specificity. The isothermal nucleic acid amplification system with high specificity comprises overall-length Bst DNApolymerase and also comprises embedded fluorescent dye. The invention also relates to a kit containing the isothermal nucleic acid amplification system as well as the application of the isothermal nucleic acid amplification system to childhood diarrhea pathogen detection. In the application, amplification primers comprise primer groups which are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.4, SEQ ID NO.5to SEQ ID NO.8 and SEQ ID NO.9 to SEQ ID NO.12 and are correspondingly used for detecting Group A rotaviruses, astroviruses and adenoviruses. The overall-length Bst DNA polymerase has 5'-3'-duplex-specific excision enzyme activity and polymerization activity, the characteristic is applied to the Exo-NAT method of the invention, the embedded fluorescent dye is added into the reaction system and melting curve analysis is cooperated, so that high-specificity and high-sensitivity multiple nucleic acid detection can be realized; and the isothermal nucleic acid amplification system is successfully applied to accurate detection of childhood diarrhea pathogens, and has an important clinical significance and a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI IGENETEC DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Thio probe for detecting nuclease with 3'-5' exo activity
ActiveCN104293917AAccurate analysisHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThio-Phosphate
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Penicillium oxalicum capable of degrading 2-phenethyl alcohol produced from rice straw and application thereof
ActiveCN110484452APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityFungiMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholPenicillium oxalicum
The invention provides penicillium oxalicum capable of degrading 2-phenethyl alcohol produced from rice straw and application thereof. The penicillium oxalicum is penicillium oxalicum T1, and was preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection. The preservation number is CCTCC M 2019608. The penicillium oxalicum T1 provided by the invention has good cellulose degradation ability, can produce cellulase, and has strong endoglucosidase activity, filter paper enzyme activity, exonuclease activity and beta-glucosidase activity; and the penicillium oxalate T1 can degrade 2-phenethyl alcohol produced by degradation of rice straw. The fermentation broth that degrades rice straw can inhibit Phomopsis sp., Magnaporthe grisea and Fusarium oxysporum.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis and application thereof
ActiveCN109929782APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsKiwi fruitStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis which is bacillus subtilis T8 deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 5, 2018 with the preservation numberof CCTCC NO: M 2018860. The bacillus subtilis T8 has good cellulose degradation capability, can produce cellulase, and has strong endoglucanase activity, filter paper enzymatic activity, exonucleaseactivity and beta-glucosidase activity. The bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit phomopsis, and an ethanol supernatant and a protein have inhibitory effects on the phomopsis. In addition, the bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit the growth of escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, shigella dysenteriae and enterobacter faecalis, and has a development and utilization value in inhibitinghuman pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides application of the bacillus subtilis T8 in producing cellulase and preventing kiwi fruit soft rot.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com