Penicillium oxalicum capable of degrading 2-phenethyl alcohol produced from rice straw and application thereof
A technology of Penicillium oxalicum and phenylethyl alcohol, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of no Penicillium oxalicum and no Penicillium oxalicum fermenting natural straw, and achieve good cellulose degradation ability and strong endoglucosidase activity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The screening of embodiment 1 degrading cellulose strain
[0035] Screening medium: CMC-Na 10g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.4g, MgSO 4 0.3g, KH 2 PO 4 2g, MnSO 4 1.6mg, FeSO 4 5mg, ZnSO 4 2.5mg, CoCl 2 2.0mg, 20g agar, pH=7.0, dilute to 1000mL;
[0036] Seed medium: CMC-Na 10g, peptone 3g, KH 2 PO 4 4g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.03g, pH=6.0, dilute to 1000mL;
[0037] Fermentation enzyme production medium: CMC-Na 10g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 4.0g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g, K 2 HPO 4 2g, 5g of beef extract, 10g of peptone, natural pH, dilute to 1000mL;
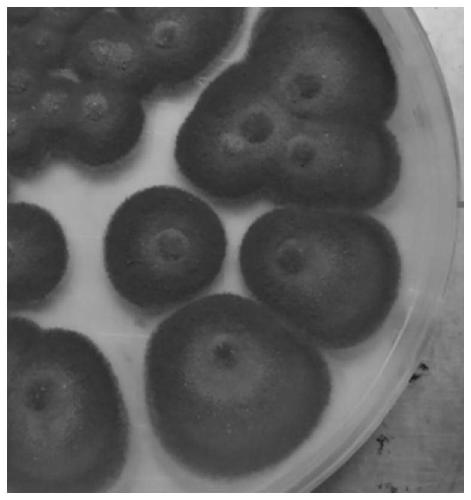
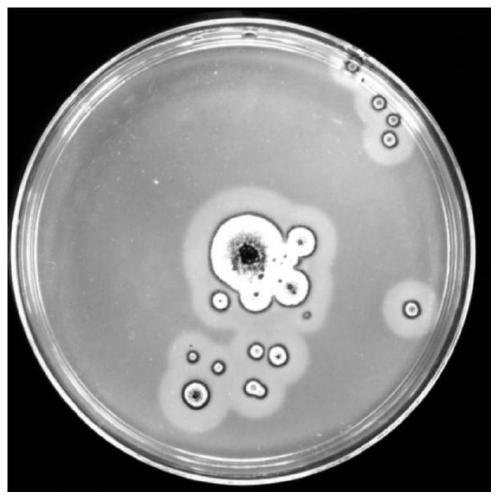
[0038] Preliminary screening: Weigh 10g of soil sample, put it into a conical flask filled with 90mL of sterile water, place it on a shaker at 150rpm for 30min, take it out, and dilute it step by step to 10 -1 , 10 -2 , 10 -3 , 10 -4 , 10 -5 , 10 -6 6 kinds of concentrations, the dilutions of 6 kinds of concentrations were spread on the screening medium, repeated 3 times, and cultured at 25°C for 3 days. After the hypha...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Degradative enzyme activity assay of embodiment 2 degrading cellulose strain
[0042] 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method (DNS method) was used to measure filter paper enzyme activity, endo-glucosidase activity, exo-glucosidase activity and β-glucosidase activity.
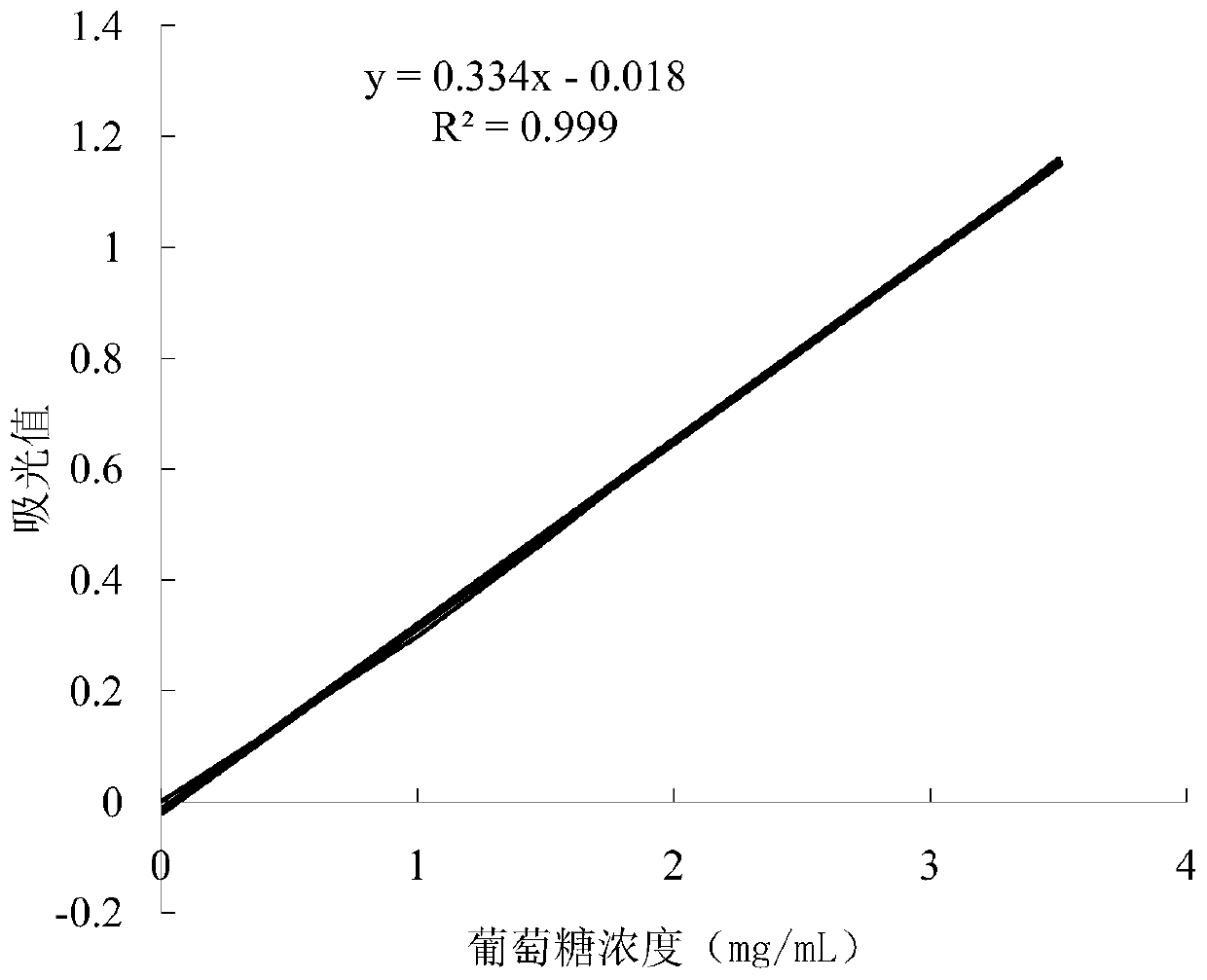
[0043] 2.1 Preparation of glucose standard curve
[0044] Glucose standard solution: weigh 1 g of anhydrous glucose dried at 103°C to constant weight, and dilute to 100 mL with water;
[0045] Phosphate buffer: 0.1mol / L pH 6.0 (suitable for neutral cellulase) Weigh 121.0 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate and 21.89 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, and dissolve them in 1 L of deionized water. Adjust the pH of the solution to 6.0;
[0046] DNS reagent: Weigh 10g of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid, put it in about 600mL of water, gradually add 10g of sodium hydroxide, stir and dissolve in a 50°C water bath (magnetic force), then add 200g of potassium sodium tartrate in turn , 2 g of ...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The filter paper degradation assay of embodiment 3 degrading cellulose strain
[0081] Filter paper degradation medium: (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.4g, MgSO 4 0.3g KH 2 PO 4 2g, MnSO 4 1.6mg, FeSO 4 5mg, ZnSO 4 2.5mg, CoCl 2 Add 2.0 mg of distilled water to 1 L, take 5 mL of culture base in a test tube, add 50 mg of filter paper, 121 ° C for 20 min. After sterilization, use an inoculation needle to pick up a small amount of T1 spores and inoculate them in a test tube, and incubate at 28°C.
[0082] The result is as Figure 4 As shown (the test tubes 1 to 3 on the left are the strain T1, and the test tube on the far right is the control), the strain T1 can disintegrate the filter paper, indicating that its filter paper enzyme activity is very high.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com