Photosensitive drum driving assembly
A photosensitive drum driving and photosensitive drum technology, applied in optics, electrographics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as loss of drive connection function, ball-type universal joint disengagement, unstable operation, etc., to achieve simple assembly and reliable performance. , the effect of stable work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
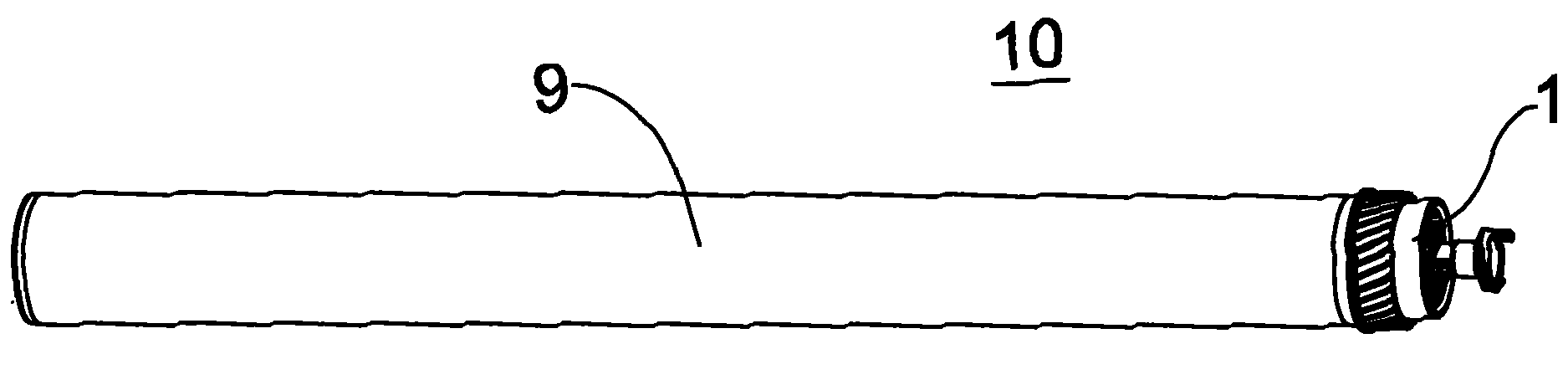
[0040] figure 1 Shown is a photosensitive drum 10 to which a driving assembly 1 according to an embodiment of the present invention is applied. The driving assembly 1 is fixed at one end of the drum main body 9 of the photosensitive drum 10. The peripheral surface of the drum main body 9 has a photosensitive layer. The driving assembly 1 is used to receive the rotational driving force from the printer driving mechanism, and transmit the rotational driving force to the drum main body 9, so that the drum main body 9 rotates around its axis under the action of the rotational driving force.
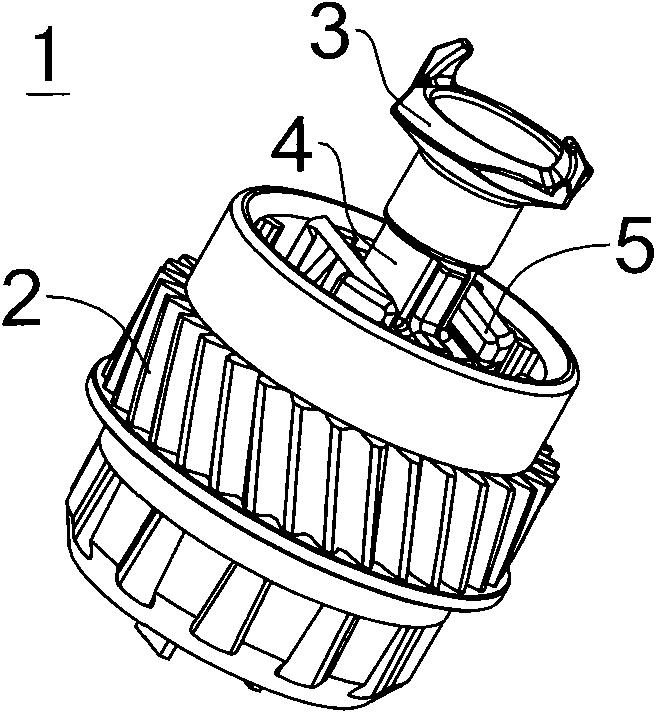
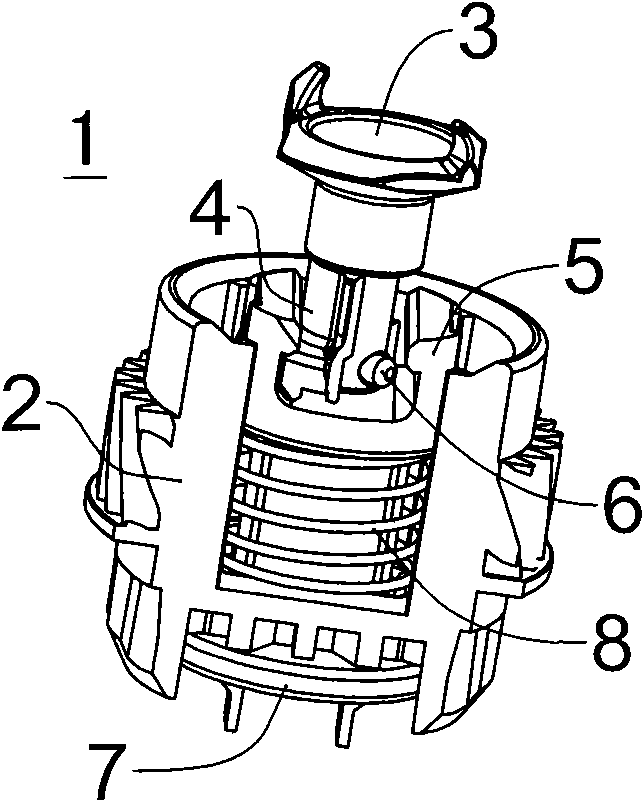
[0041] Figure 2 ~ Figure 4 The basic composition of the driving assembly 1 is shown, and its structure mainly includes a gear 2 , a rotating driving force receiving head 3 , an adjusting slider 4 , an adjusting rod 5 , a rotation limiting pin 6 , a limiting bottom plate 7 and a helical compression spring 8 . The gear 2 is closely matched with one end of the drum main body 9, the axis of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com