Dielectric layer
A dielectric layer and silicide technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, transistors, etc., can solve problems that affect component characteristics, increase interface defects, and difficulties, and achieve the effect of improving component characteristics and improving component characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
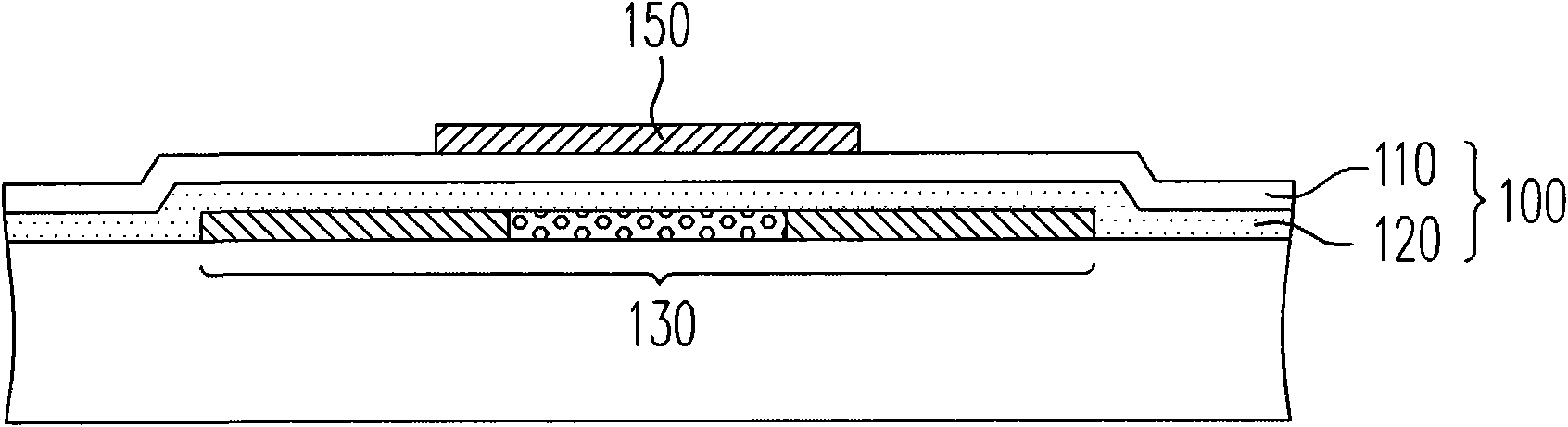
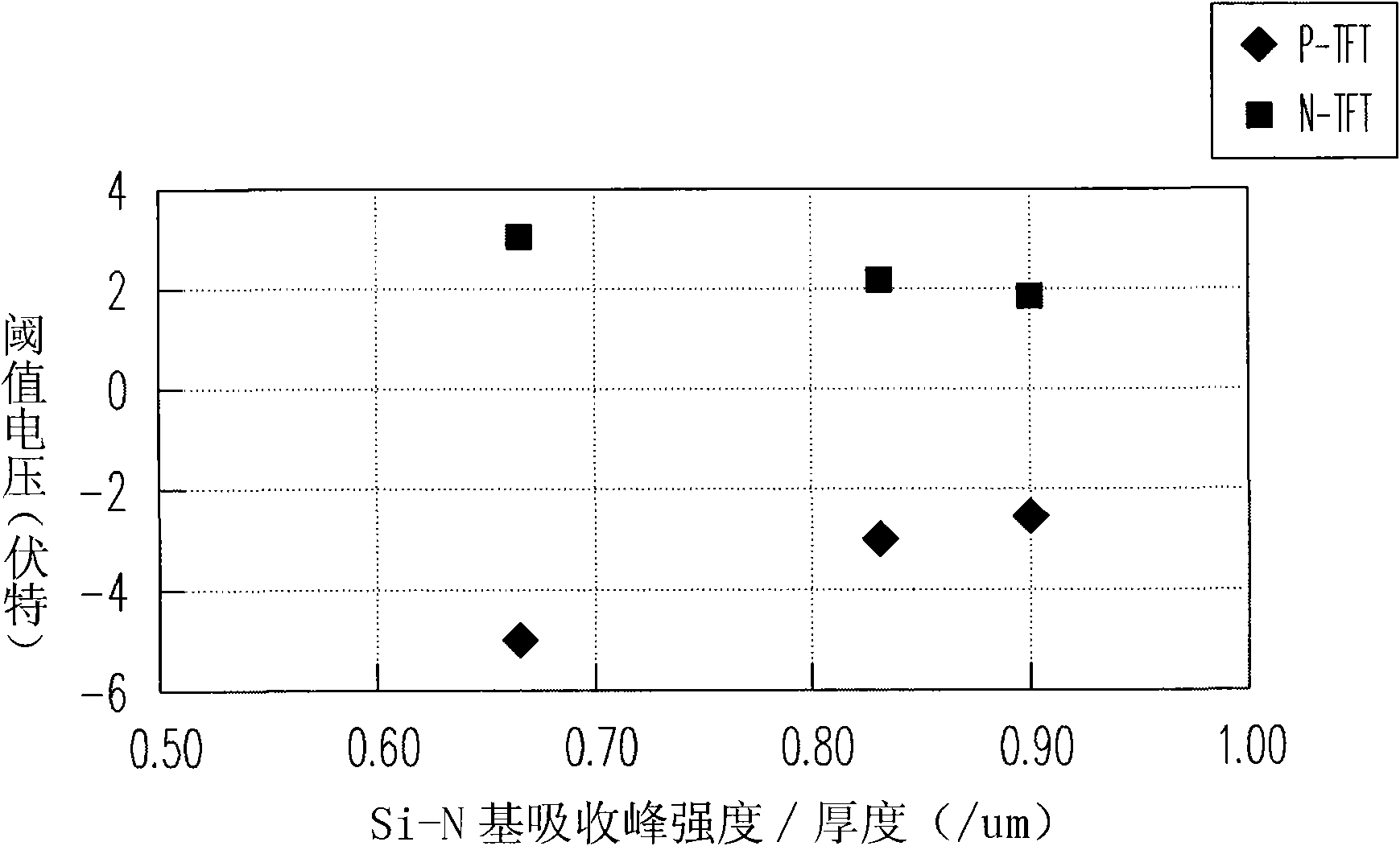
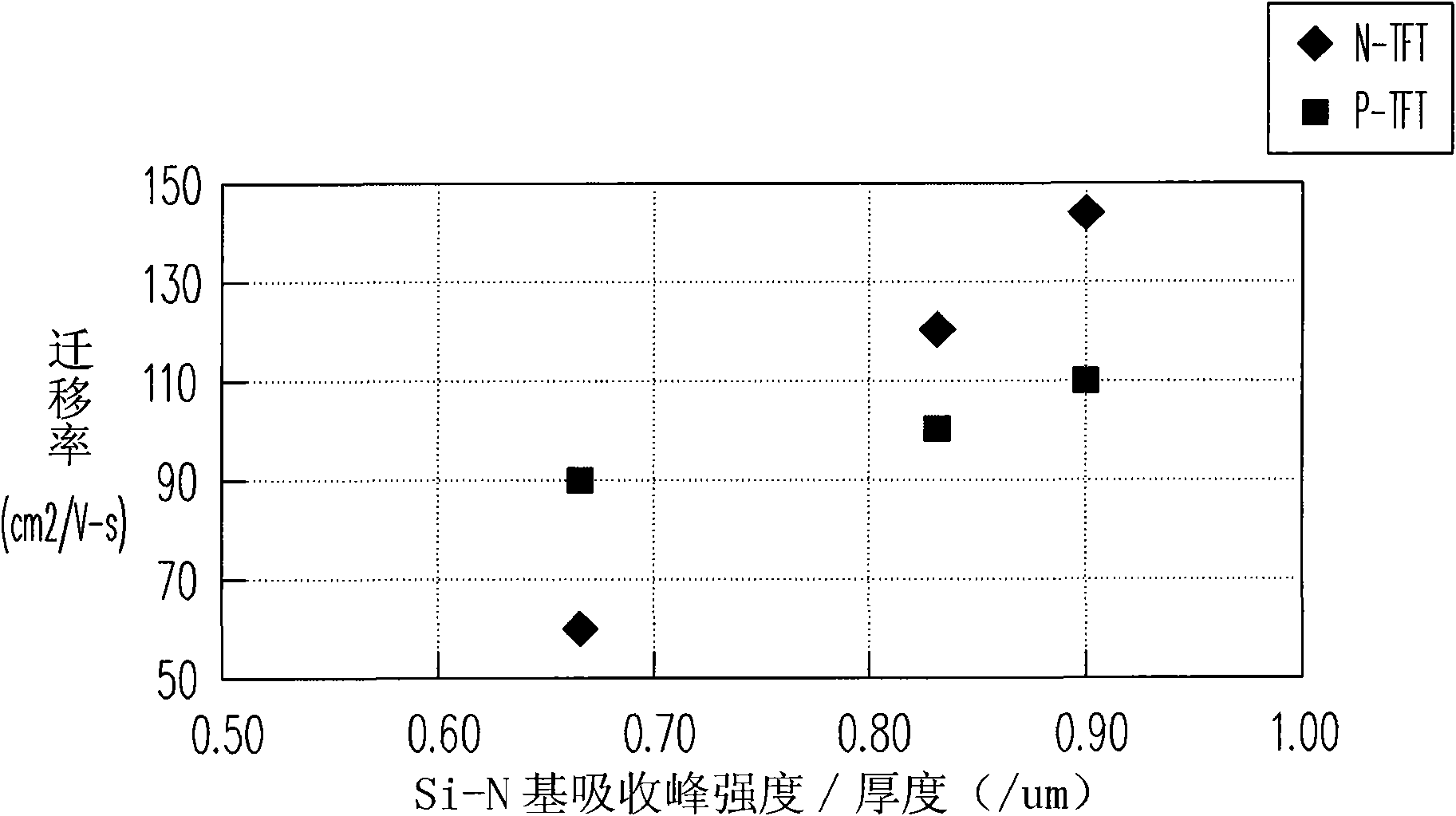
[0050] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of applying a dielectric layer proposed by the present invention to a thin film transistor. Please refer to figure 1 In this embodiment, the dielectric layer 100 includes the oxygen-containing silicide film 120 and the nitrogen-containing silicide film 110 as an example. In this embodiment, the nitrogen-containing silicide film 110 is, for example, a nitrogen source, such as: laughing gas (N 2 O) and silicon sources, such as: silane (SiH 4 ) is a reactive gas, which is formed by a chemical vapor deposition process, but is not limited to these reactive gases, and other reactive gases can also be used selectively, for example: nitrogen source (such as: nitrogen, ammonia, nitrogen / ammonia mixture, Nitrogen / laughing gas mixture, laughing gas, or other gases, or mixtures of the above) and silicon sources (such as: disilane, tetramethylsilane, tetramethoxysilane, tetraethoxysilane, or other gases, or combinations of the above). By adjus...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The present invention further proposes a thin film transistor 200 comprising a substrate 202, an active layer 210, a first dielectric layer 220, a gate 250, a second dielectric layer 260, a source region 212 / drain region 214 , a third dielectric layer 290 and a pixel electrode 292 . The active layer 210 is disposed on the substrate 202 and has a source region 212 , a drain region 214 and a channel region 216 between the source region 212 and the drain region 214 . The first dielectric layer 220 is disposed on the substrate 202 to cover the active layer 210 . The gate 250 is disposed on a part of the first dielectric layer 220 . The second dielectric layer 260 is disposed on the substrate 202 and covers the gate 250 . The source 270 / drain 280 are disposed on part of the second dielectric layer 260 and electrically connected to the source region 212 / drain 214 of the active layer 210 . The third dielectric layer 290 is disposed on the substrate 202 and covers the sour...
Embodiment 3
[0063] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of another thin film transistor proposed by the present invention. Please refer to image 3 The thin film transistor 300 includes a substrate 302 , a gate 350 , a first dielectric layer 320 , an active layer 310 , a source 370 / drain 380 , a second dielectric layer 360 and a pixel electrode 392 . The gate 350 is disposed on the substrate 302 . The first dielectric layer 320 is disposed on the substrate 302 to cover the gate 350 . The active layer 310 is disposed on a part of the first dielectric layer 320, and the active layer 310 has a source region 312, a drain region 314, and a trench between the source region 312 and the drain region 314. Road District 316. The source 370 / drain 380 are connected to the source region 312 / drain 314 of the active layer 310 . The second dielectric layer 360 is disposed on the substrate 302 and covers the source 370 / drain 380 , the active layer 310 and the first dielectric layer 320 . The pixel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com