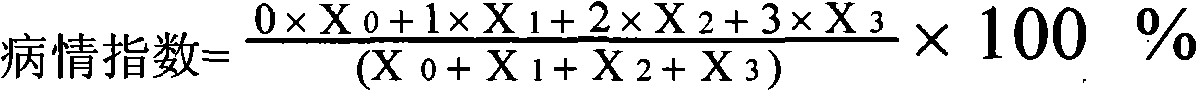Molecular marker tightly linked with wheat yellow mosaic resistant major quantitative trait locus (QTL) and application thereof
A molecular marker and wheat technology, applied in the field of wheat breeding and molecular biology, can solve the problem that there is no report on the main QTL molecular marker for resistance to wheat yellow mosaic disease, and achieve the goal of improving breeding efficiency, reducing workload and accelerating selection progress. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Determination of the resistance source CI12633 of wheat yellow mosaic disease
[0018] 1. Extract the DNA of wheat variety CI12633
[0019] The leaves of the plant of the wheat variety CI12633 were isolated and extracted the DNA obtained by the CTAB extraction method.
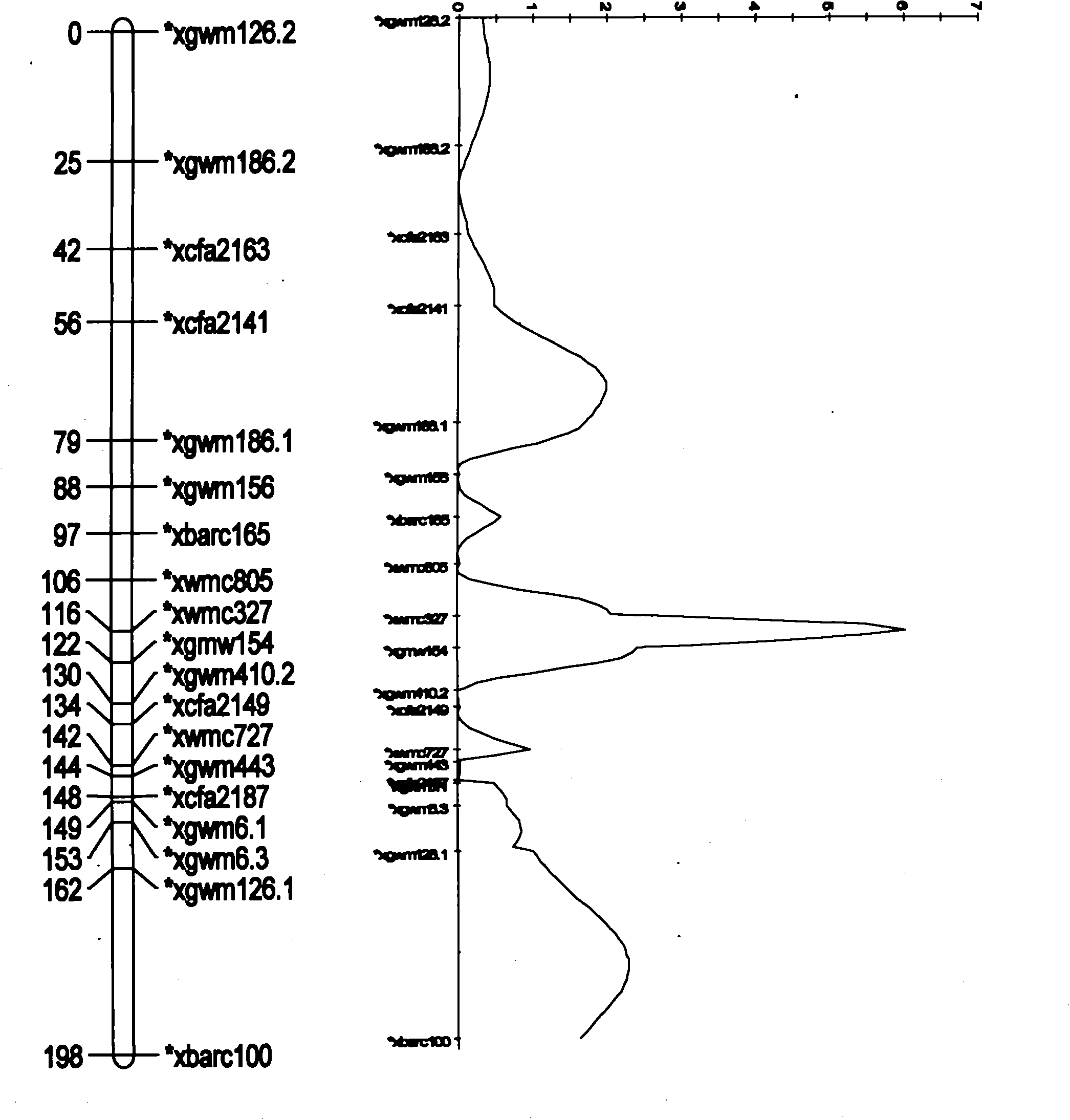
[0020] 2. Detect the DNA of wheat variety CI12633, and screen out the molecular markers closely linked to the main QTL for wheat yellow mosaic disease resistance:
[0021] PCR primer Wmc327:
[0022] Upstream primer: 5’TGCGGTACAGGCAAGGCT 3’;
[0023] Downstream primer: 5'TAGAACGCCCTCGTCGGA 3'.
[0024] PCR primer Gwm154:
[0025] Upstream primer: 5’TCACAGAGAGAGAGGGAGGG 3’;
[0026] Downstream primer: 4: 5'ATGTGTACATGTTGCCTGCA 3'.
[0027] PCR amplification:
[0028] The PCR primer Wmc327 was used to amplify the DNA of the obtained wheat variety CI12633 plant. After the amplified product was separated by electrophoresis on a 12% polyacrylamide gel, a molecular marker Xwmc327-180 with a size of 180 bp was obtained.
[0029...
Embodiment 2
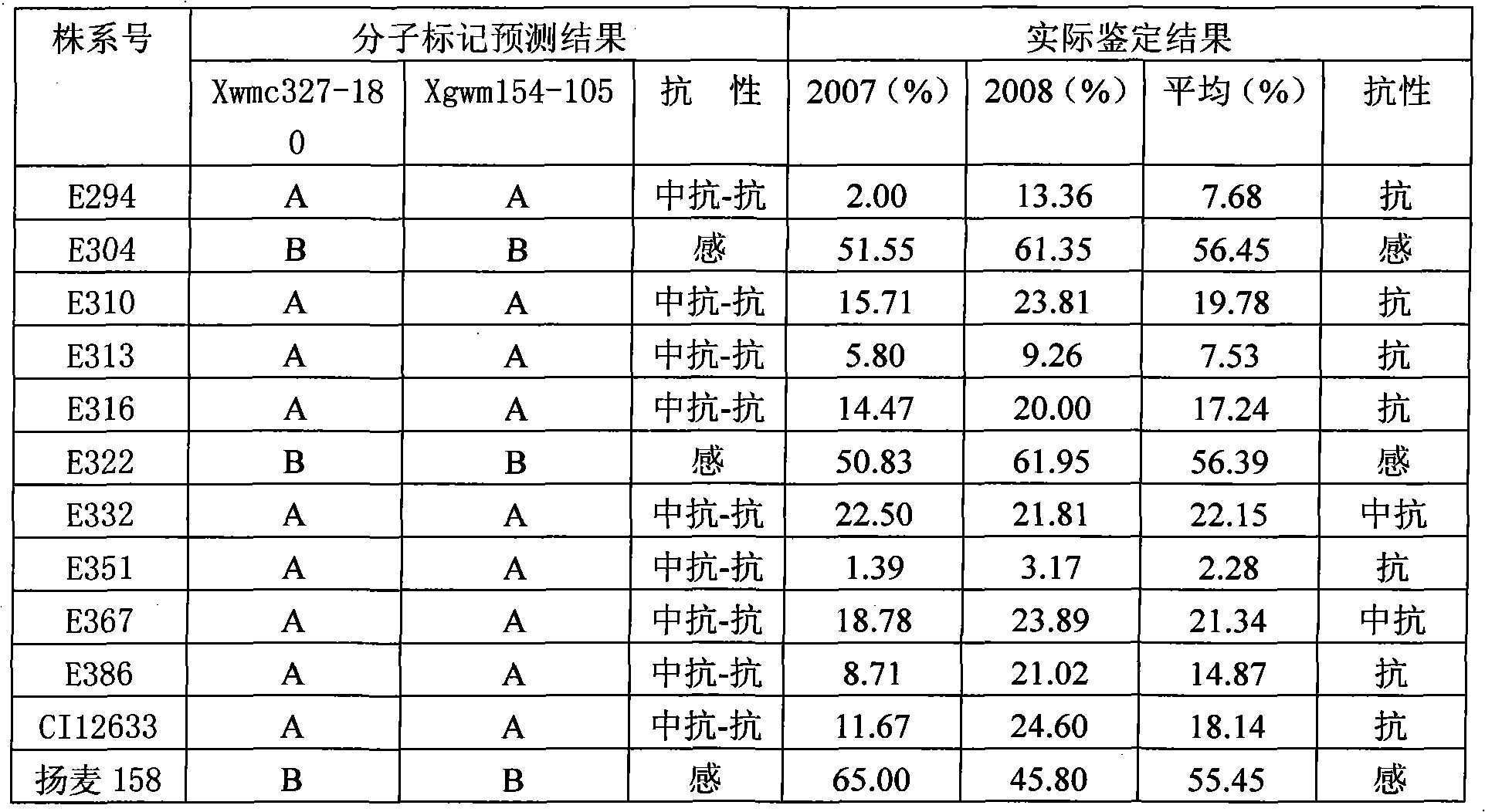
[0033] The molecular markers Xwmc327-180 and Xgwm154-105 with sizes of 180bp and 105bp were used to predict the resistance of wheat yellow mosaic disease to the derivative lines of wheat variety CI12633:
[0034] Identification object:
[0035] The wheat cultivar CI12633 was crossed with Yangmai 158 and bred to the offspring of F8 generation. The different line numbers were defined as: E294, E304, E310, E313, E316, E322, E332, E351, E367, E386. All of them were used as identification targets with unknown resistance to wheat yellow mosaic disease.
[0036] The wheat varieties CI12633 and Yangmai 158 with known resistance to wheat yellow mosaic disease were used as reference identification objects.
[0037] Identification process
[0038] a) Use molecular markers closely linked to the main QTL for wheat yellow mosaic disease resistance for identification
[0039] First, extract the DNA obtained from the leaves of each identified object using the CTAB extraction method, and then use the mo...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The molecular markers Xwmc327-180 and Xgwm154-105 with sizes of 180bp and 105bp were used to predict the resistance of wheat yellow mosaic disease to the derivative lines of wheat variety CI12633:
[0053] Identification object:
[0054] Use wheat variety CI12633 and Yangmai 158 to cross, and bred to F 8 The different strain numbers of the offspring of this generation are defined as: E303, E305, E327, E343, E362, E397, E330, E355, E376, E379. All of them were used as identification targets with unknown resistance to wheat yellow mosaic disease.
[0055] The wheat varieties CI12633 and Yangmai 158 with known resistance to wheat yellow mosaic disease were used as reference identification objects.
[0056] The identification process is completely the same as in Example 2, and will not be repeated, and their results are also summarized and recorded in Table 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com