Belt transmission cross full shaft type two-degree-of-freedom universal joint mechanism
A technology of belt transmission and universal joints, which is applied in the direction of transmission devices, belts/chains/gears, couplings, etc., can solve the problems of motor reducers being easily damaged and poor load-bearing capacity, and achieve stable bevel gear transmission and improve load-carrying Ability to perform with high precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
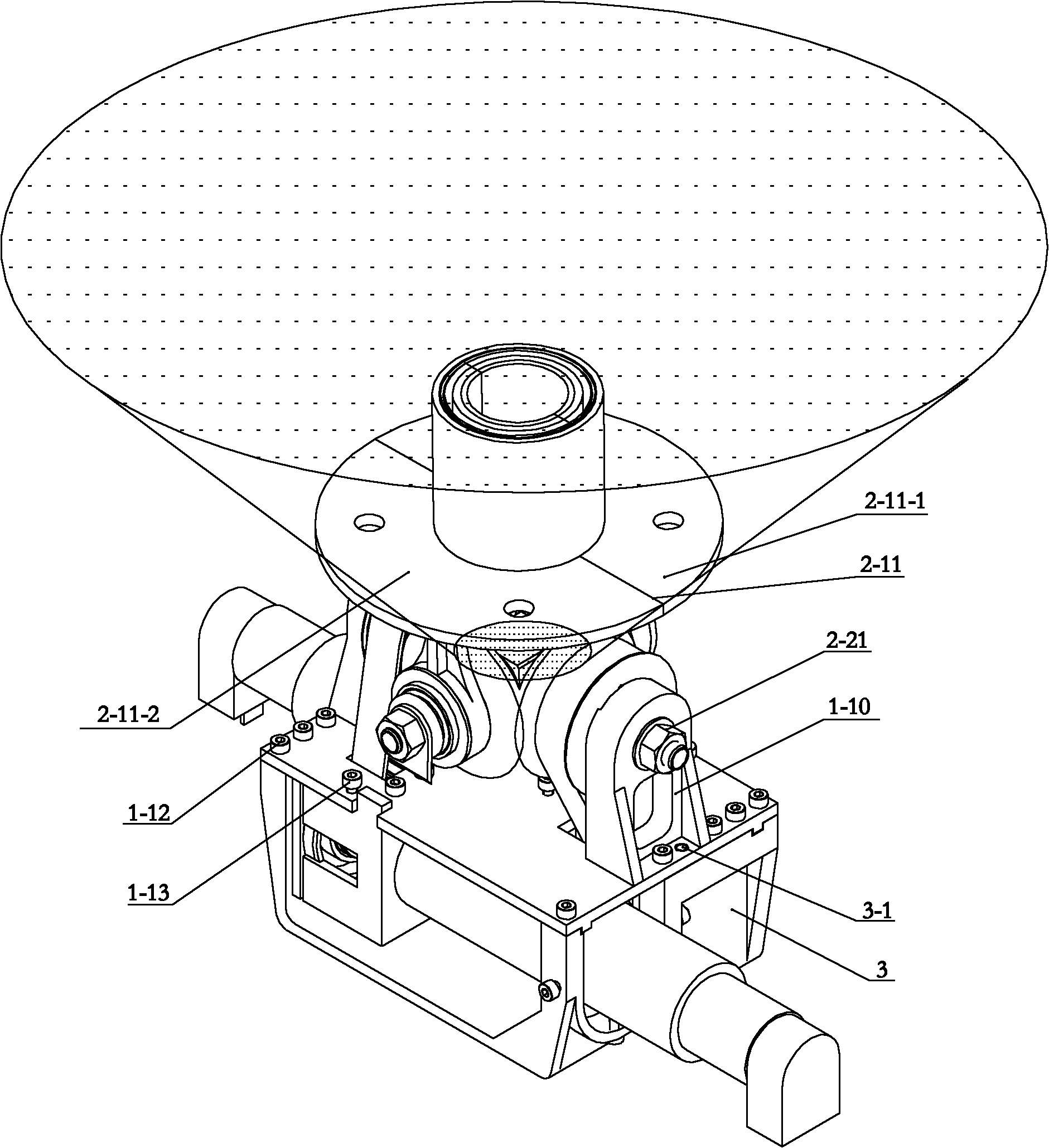
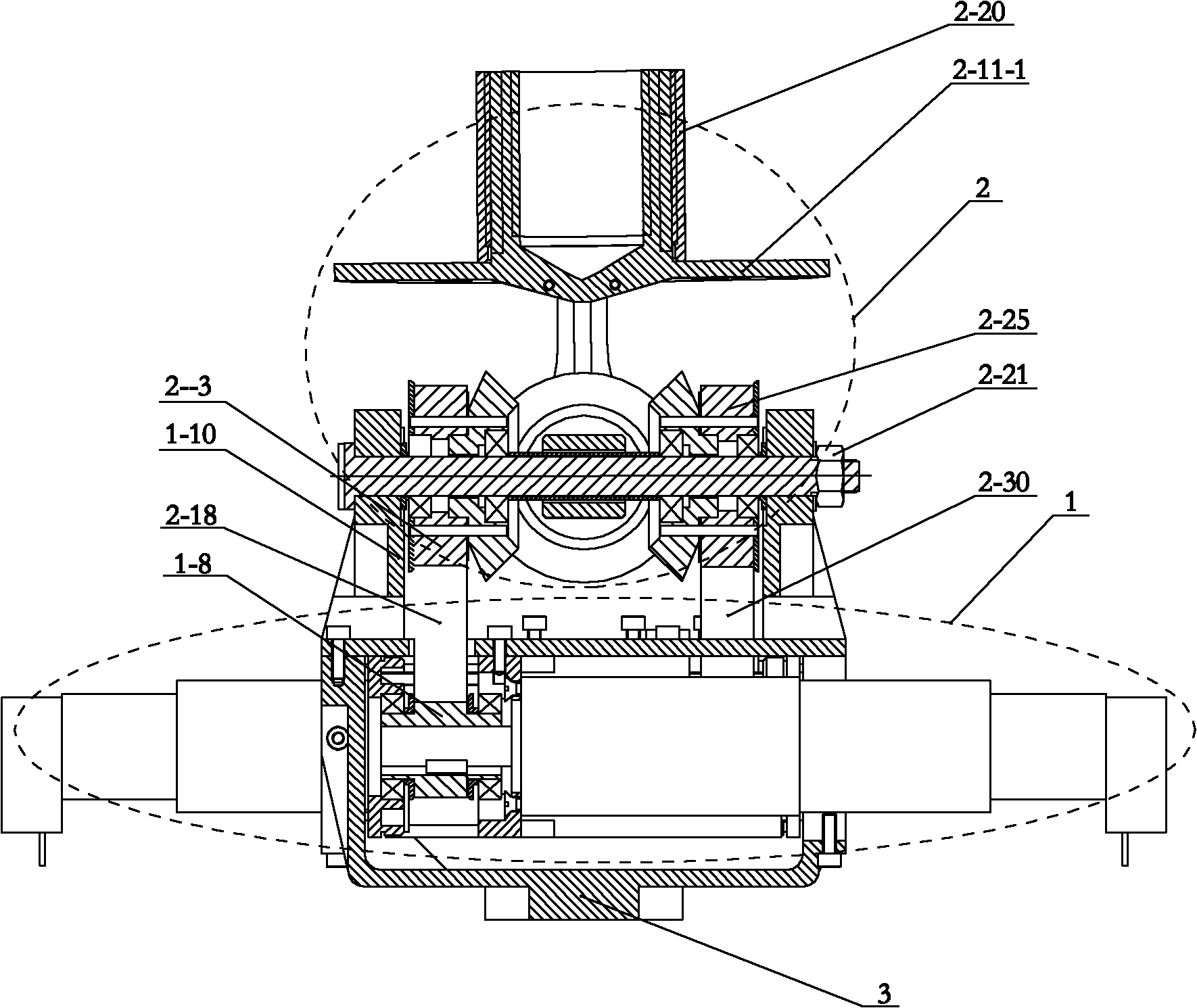
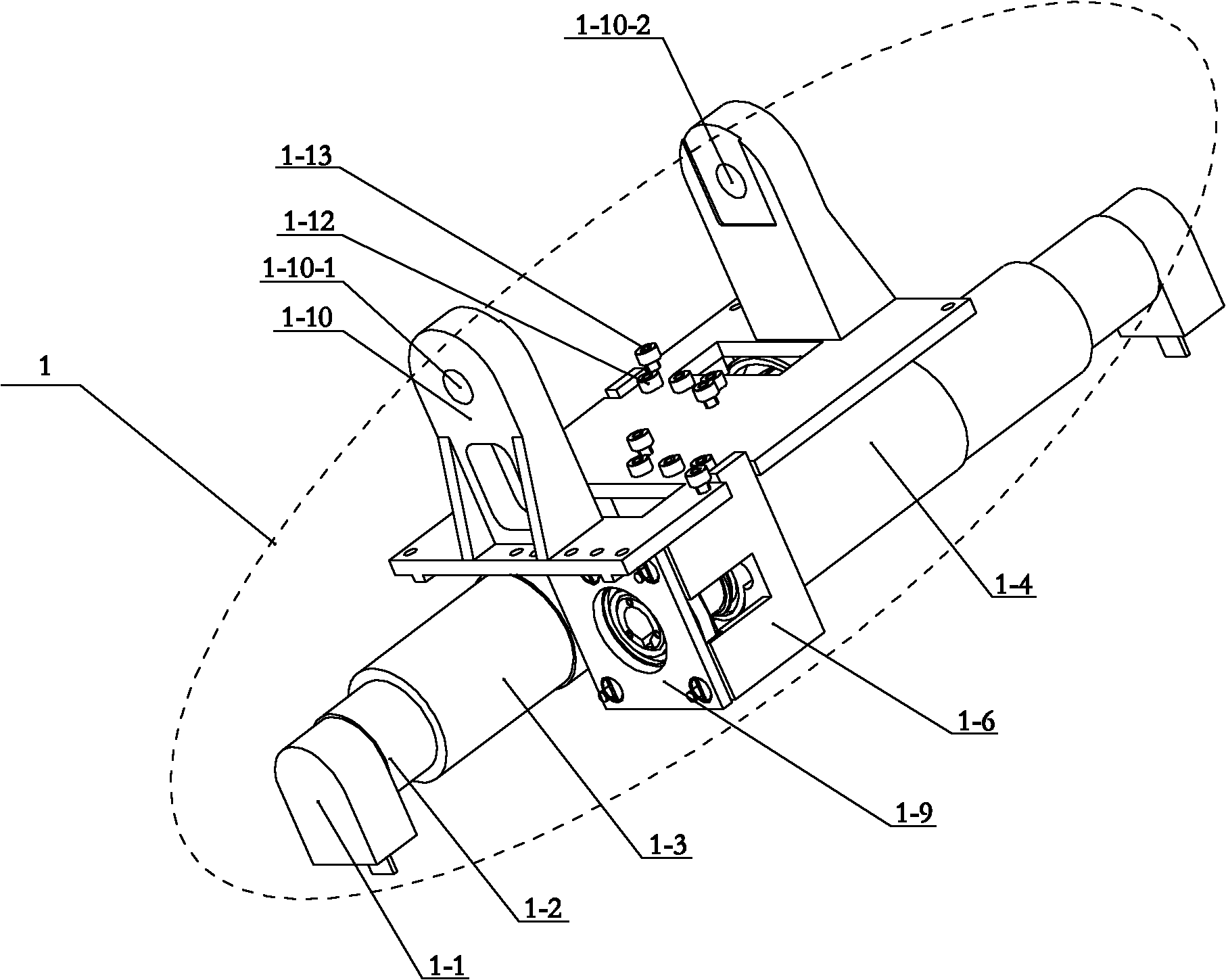
[0013] Specific implementation mode one: as Figure 1-7 As shown, the belt-driven cross full-axis two-degree-of-freedom joint mechanism of this embodiment is composed of a motor drive mechanism 1, a bevel gear differential coupling mechanism 2 and a base 3, and the motor drive mechanism 1 is fixed on the base 3 , the bevel gear differential coupling mechanism 2 is installed on the motor drive mechanism 1; the bevel gear differential coupling mechanism 2 includes a longitudinal axis 2-1, a first large pulley 2-3, a second large pulley 2- 25. The first bevel gear 2-4, the second bevel gear 2-5, the third bevel gear 2-13, the fourth bevel gear 2-16, the first thrust bearing seat 2-6, the second thrust bearing seat 2-26, the first thrust bearing 2-7, the second thrust bearing 2-27, the first limit baffle 2-9, the second limit baffle 2-29, the end platform of the actuator 2-11, Central sleeve 2-14, transverse shaft 2-15, first belt 2-18, second belt 2-30, actuator end sleeve 2-20,...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Specific implementation mode two: as Figure 6As shown, the first bevel gear 2-4, the second bevel gear 2-5, the third bevel gear 2-13 and the fourth bevel gear 2-16 in this embodiment are all helical bevel gears. With such a design, compared with the straight bevel gear, the helical bevel gear has a higher load capacity, and at the same time, the transmission between the four bevel gears is more stable. Other components and connections are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0020] Specific implementation mode three: as Figure 7 As shown, the bevel gear differential coupling mechanism 2 in this embodiment also includes four large pulley pins 2-19, and the first large pulley 2-3 and the first bevel gear 2-4 pass through four large pulley pins. Two of the wheel pins 2-19 are fixedly connected, and the third bevel gear 2-13 is fixedly connected to the second large pulley 2-25 through the remaining two of the four large pulley pins 2-19. With such a design, the first large pulley 2-3 can be fixedly connected with the first bevel gear 2-4. Other compositions and connections are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com