Mixing degree extracting method for Missile-borne non-ideal staring spotlight SAR (synthetic aperture radar)
An extraction method and a technology of mixing degree, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems affecting coherent accumulation time, side lobe depression, and affecting imaging quality, and achieve the effect of simplifying the simulation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
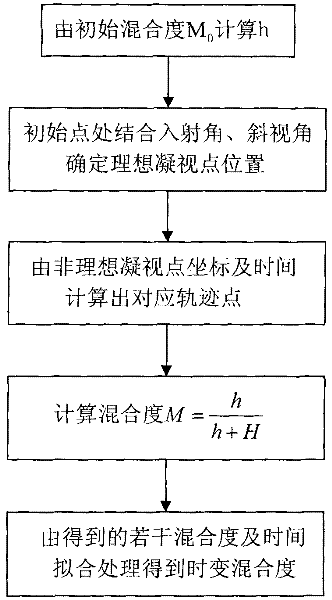
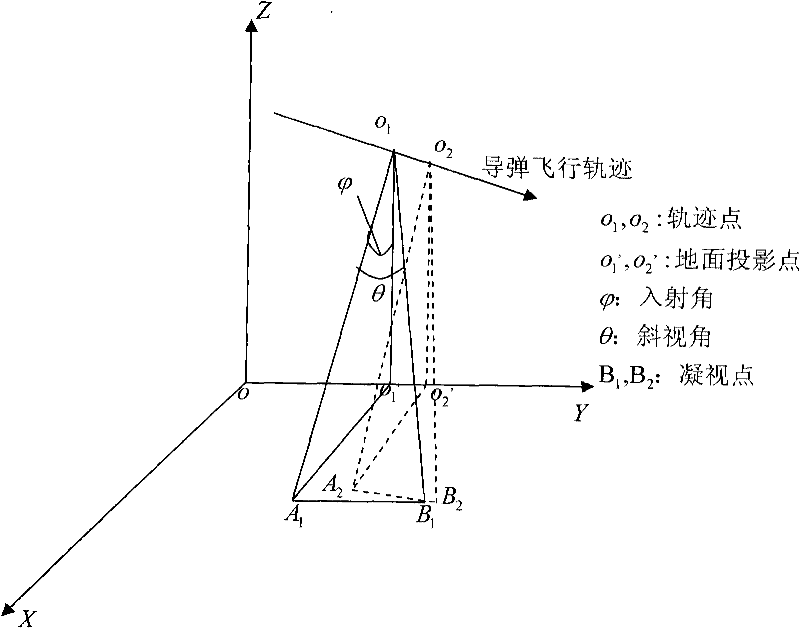
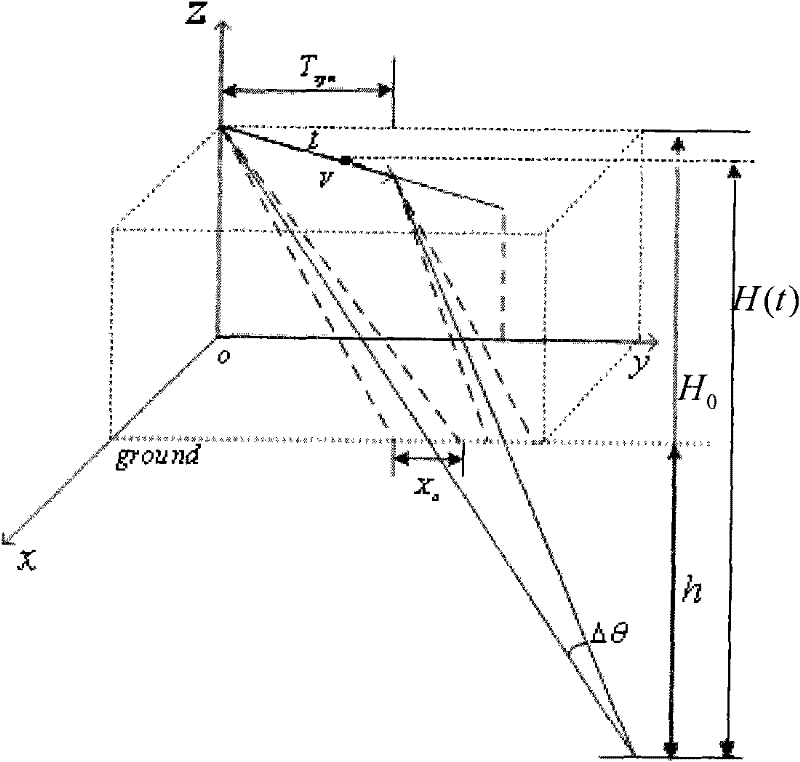
[0064] Due to the existence of non-ideal gaze points on the ground, the missile-borne SAR is no longer in the ideal spotlight mode at this moment, but presents the characteristics of a mixed mode (sliding spotlight mode). The extension line of the ideal gaze point and the non-ideal gaze point converges at a certain point under the ground, thus introducing the concept of mixing degree.
[0065] M = h h + H 0 - - - ( 9 )
[0066] image 3 A schematic diagram of the non-ideal staring SAR during the dive is given. The missile flies in a dive and places its trajectory on the YOZ plane. The center of the beam irradiates on the ground to form two gaze points, which is no longer an ideal spotlight mode. Extending the center of the beam to intersect at a point below the ground presents a mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com