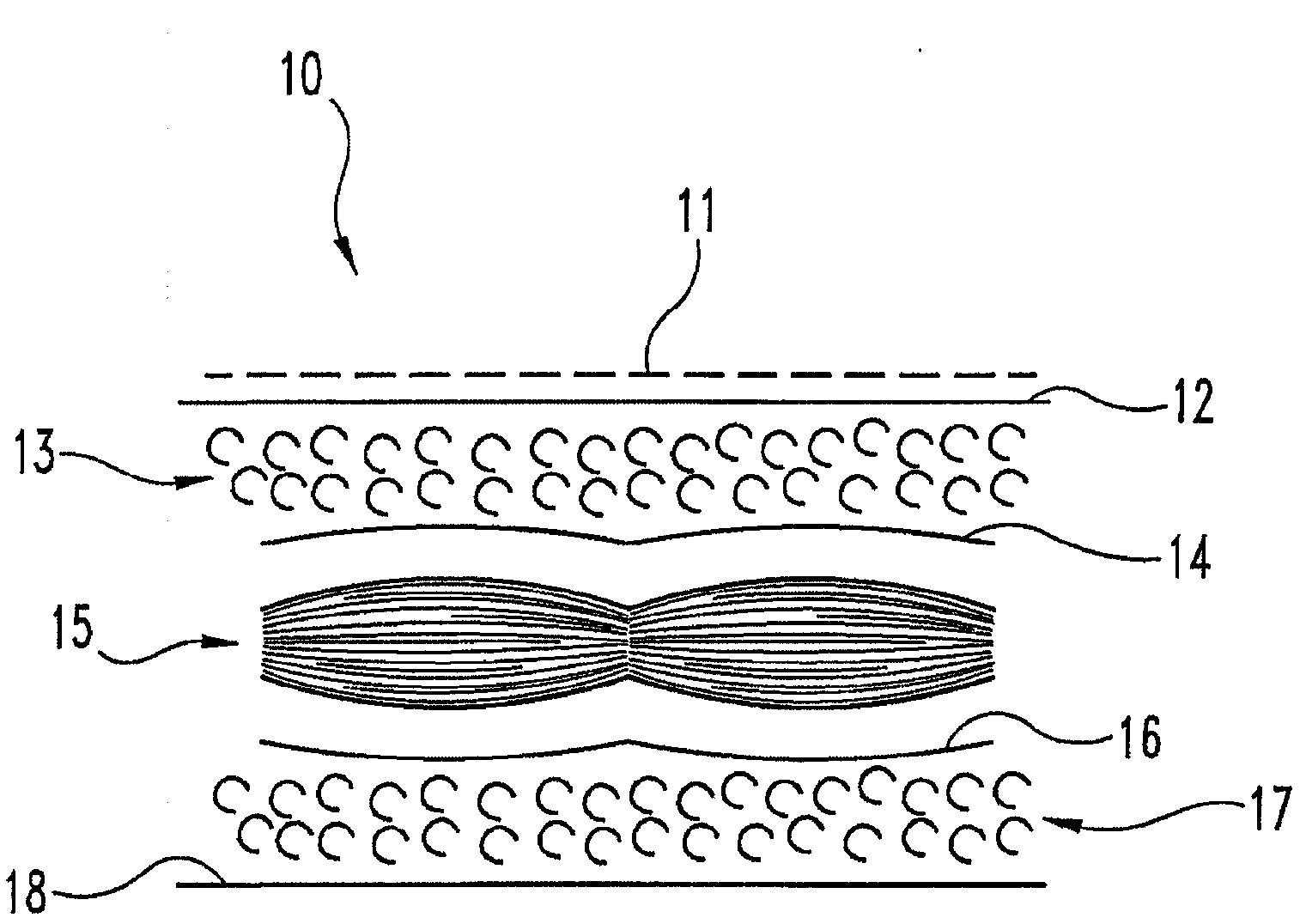
Isolated extracellular matrix material including subserous fascia
A technology of extracellular matrix and cells, applied in the field of medical materials, which can solve the problems of limited size and strength of materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Preparation of Extracellular Matrix Grafting Materials
[0048] At the food processing plant, tissue fragments were collected at points on the processing line where the full porcine body cavity was opened with a midline incision and the anterior ribs and all organs removed. An incision was made on the posterior edge of the body wall flap on each side of the body, and tissue fragments were removed on each side of the body wall to make two tissue fragments of approximately equal size (1 foot x 1.5 feet). These segments contain peritoneum, subserous fascia, and subserous fat. It was determined that the posterior fascia was not part of this tissue segment. The subserosal fat is about 0.5 to about 1 centimeter thick, depending on the location along the segment. The peritoneum containing both visceral and parietal peritoneum is placed. The visceral peritoneum, identified as a transparent membrane with a thick white network of blood vessels, was discarded.
[0049] The tis...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Test for natural lipid content
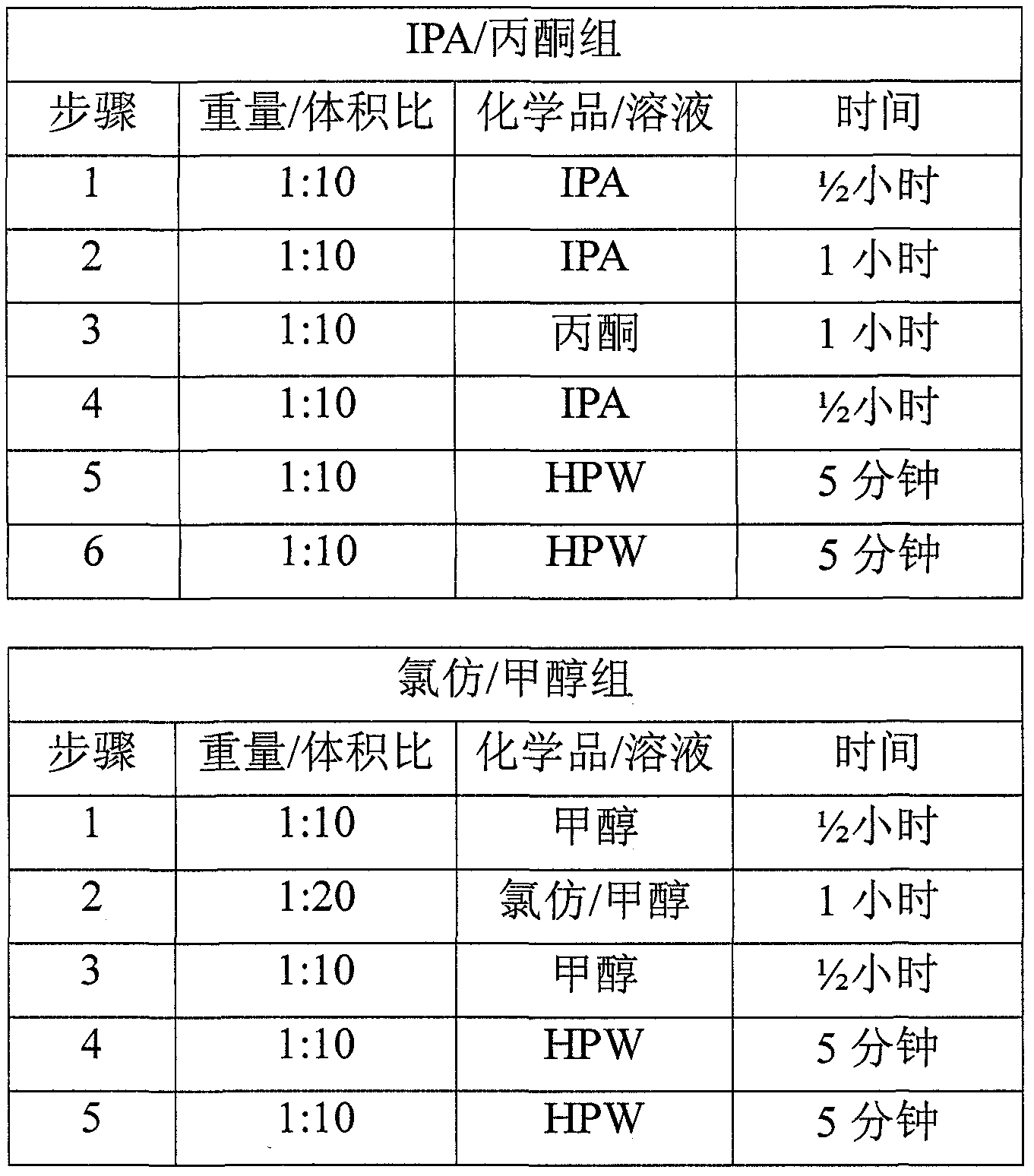
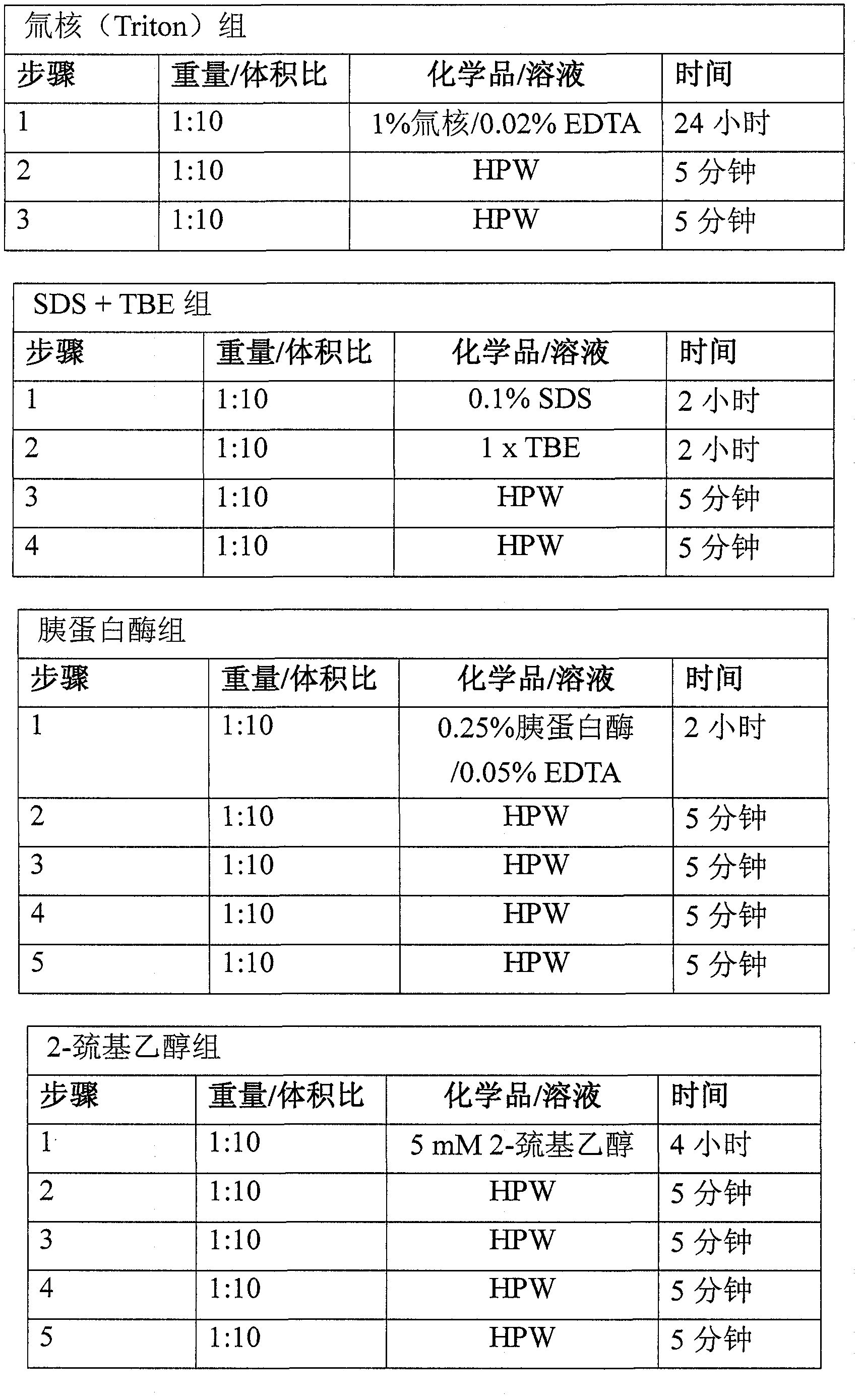
[0054]Typically 2 batches of material were obtained as described in Example 1. Abdominal wall tissue fragments were processed by mechanical scraping, three treatments with 100% isopropanol (IPA) (1:10 weight:volume), chemical degreasing, disinfection with peracetic acid (PAA) solution, and four washes with high-purity water. Each batch consisted of 2 slices and a total of four slices were tested. Four 4x7 cm samples were cut from each sheet, resulting in a batch of 8 samples for a total of 16 samples. Each sample was weighed (initial weight), rolled and placed in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube with 10 mL of 100% ethanol. Place the tubes in a tube holder and place the holder on the side of a rotary shaker at room temperature for approximately 24 hours. After 24 hours, the ethanol was drained and 10 mL of 100% acetone was placed into each tube. The rack was then placed back on the shaker at room temperature for approximately 24 hours. After...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Tested for natural hyaluronic acid content
[0058] Typically 2 batches of material were obtained as described in Example 1. Abdominal wall tissue fragments were processed by mechanical scraping, three treatments with 100% isopropanol (IPA) (1:10 weight:volume), chemical degreasing, disinfection with peracetic acid (PAA) solution, and four washes with high-purity water. Each batch consisted of 2 slices and a total of four slices were tested. Four 12 mm disk samples were cut from each sheet, yielding a batch of 8 samples for a total of 16 samples. Each sample was weighed (initial weight), rolled and placed in a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube with 450 microliters of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and 50 microliters of proteinase K for 45 minutes at 56°C. Samples were then pulverized with a tissue grinder for 90 seconds per sample. Tubes with samples were centrifuged at 12000 g for 5 minutes at 4°C to pellet any undigested material. A 1:40 dilution of the supernatant ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com