Multi-physical server load equalizing method and device capable of meeting requirement characteristic
A physical server and load balancing technology, applied in the field of computer communication, can solve the problems of physical server specification configuration, physical server load imbalance, inconsistent specification configuration, load imbalance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
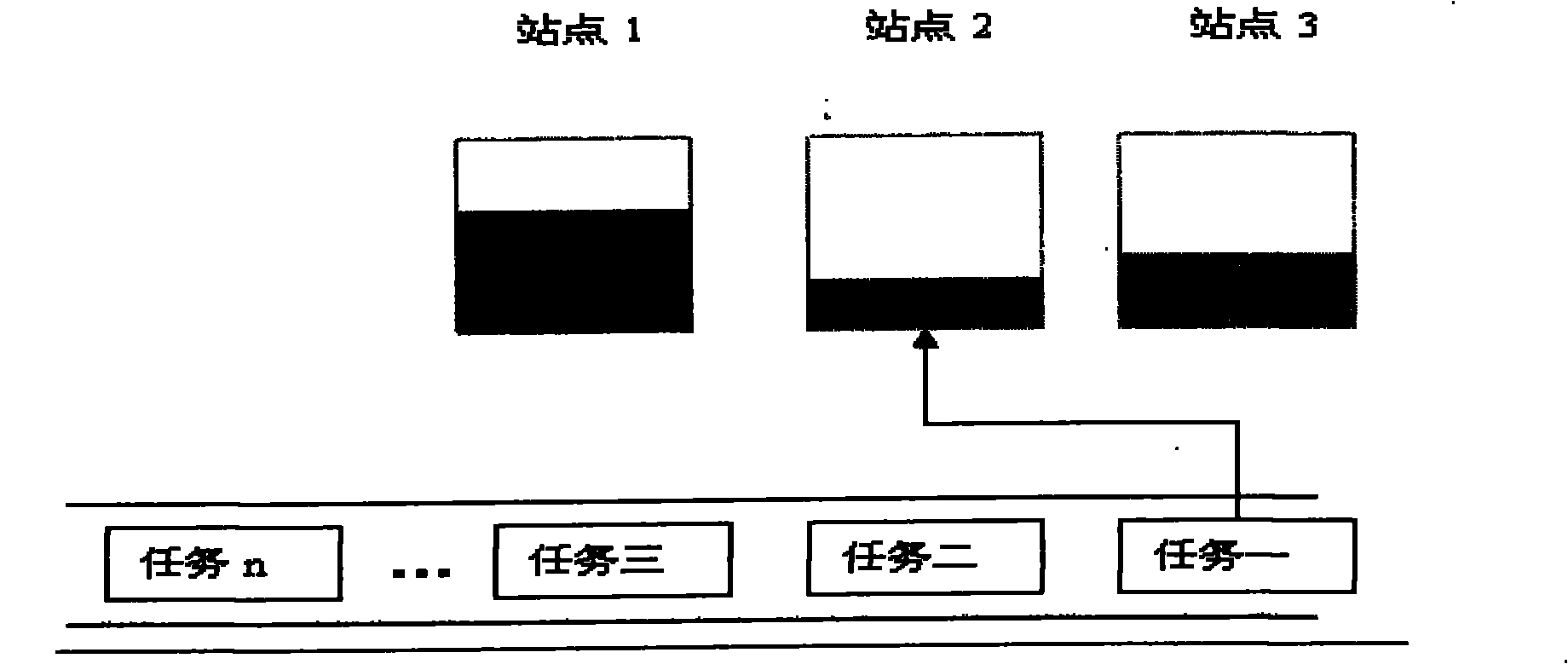
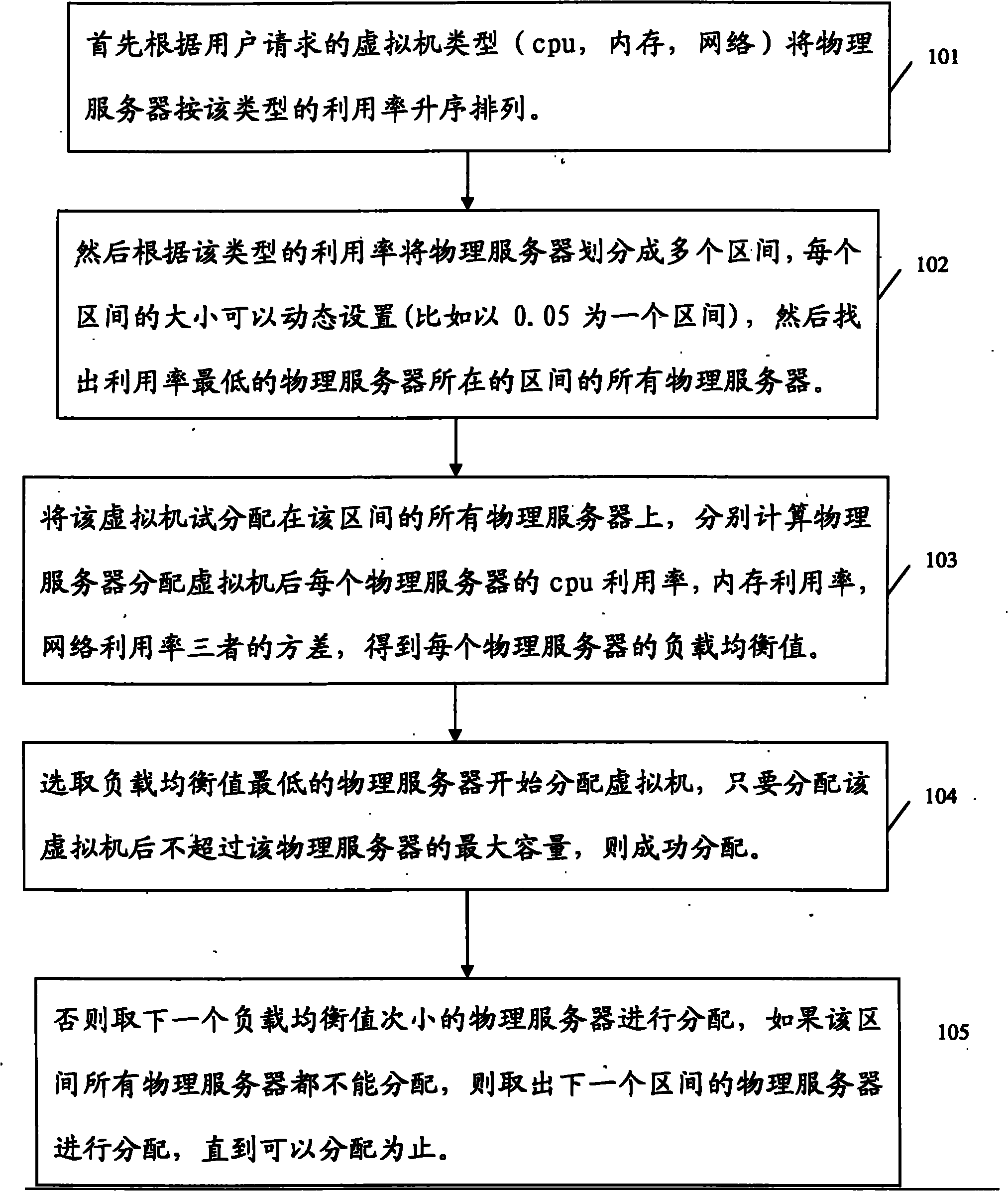
[0034] This embodiment provides a method for implementing load balancing among multiple physical servers, such as image 3 As shown, the method includes:
[0035] 101. Firstly, according to the virtual machine type (cpu, memory, network) requested by the user, the physical servers are arranged in ascending order according to the utilization rate of the type.
[0036]102. Then divide the physical server into multiple intervals according to the utilization rate of this type. The size of each interval can be set dynamically (for example, 0.05 is a interval), and then find out all the physical servers in the interval where the physical server with the lowest utilization rate is located. server.
[0037] 103. Try to assign virtual machines to all physical servers in this interval, and calculate the variance of the cpu utilization rate, memory utilization rate, and network utilization rate of each physical server after the physical server allocates virtual machines, and obtain each...
Embodiment 2
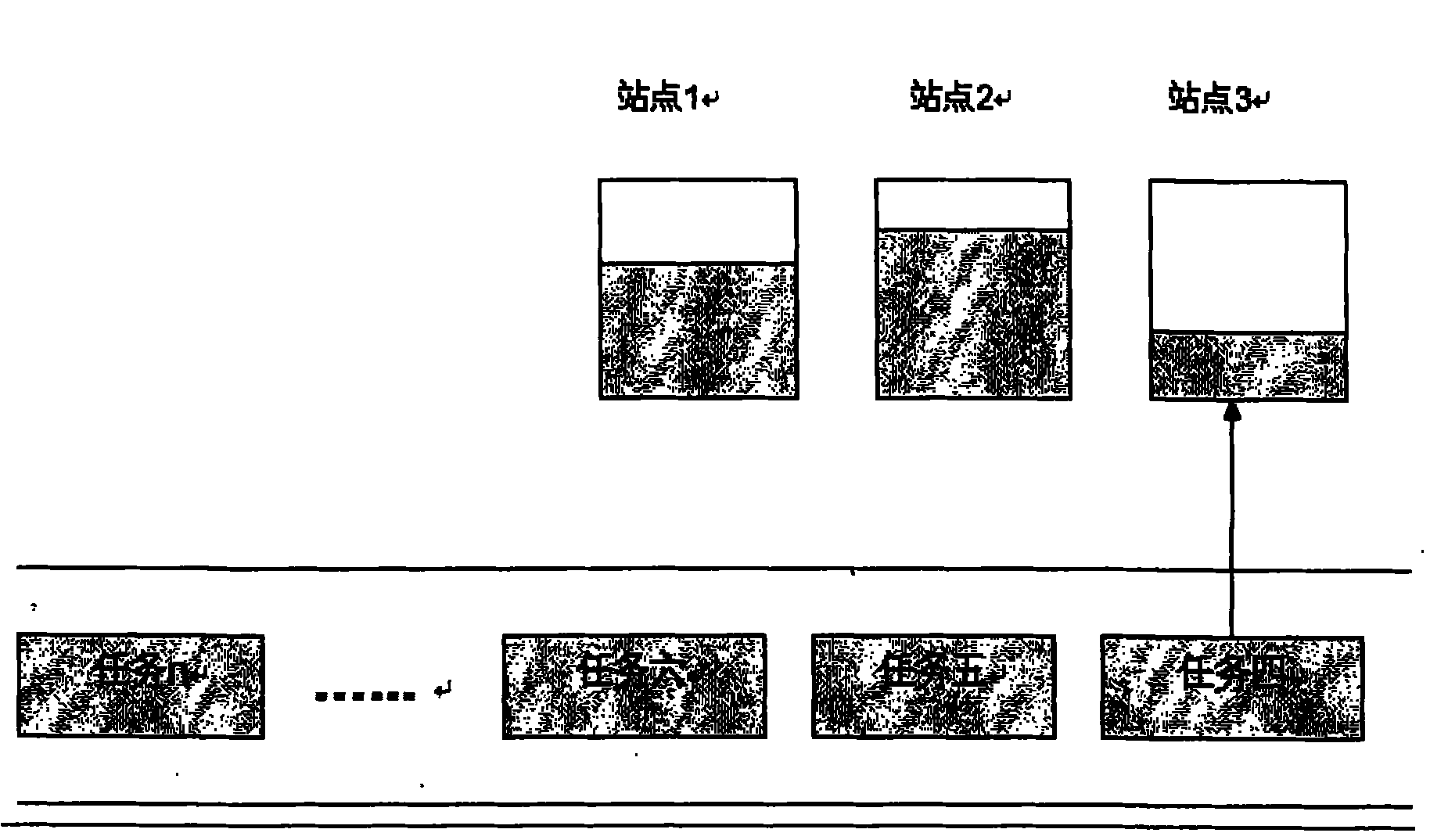
[0074] This embodiment provides a method for implementing load balancing among multiple physical servers, such as Figure 4 As shown, the method includes:
[0075] 201. Obtain the total cpu size, cpu utilization rate, total memory size, memory utilization rate, total network size, and network utilization rate of all physical servers at the current moment.
[0076] 202. Accept new task requests (the four queues with priority from high to low are defined as waiting, requesting, tuning, and deleting queues), tuning tasks are added to the tuning queue, and common user tasks are added to the request queue (press start chronological order).
[0077] 203. Check the waiting queue. If the waiting queue is not empty, take out the tasks in the waiting queue and allocate them. Refer to 208, 209, 210, and 211 for the specific allocation process.
[0078] 204. Check the request queue, if the request queue is not empty and the start time of the task has arrived, start allocation. If the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com