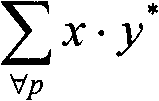Multi-channel audio signal processing
An audio signal, multi-channel technology, applied in the direction of two-channel system, electrical components, transmission system, etc., can solve the problem of how to operate without description, achieve the effect of reducing noise and improving the output sound quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0056] figure 2 A block diagram of a first embodiment of a signal processing device 200 according to the invention is shown in which an improved difference signal d is calculated under noisy signal conditions. The noisy sum signal s and the noisy difference signal d are input to the parameter estimation module 201 . Compute two gains g based on the signal power of the sum and difference signals and the cross-correlation of the sum and difference signals s and g sd . These two gains are used to define the following from the sum signal s and the decorrelated version of the sum signal s d to estimate the transfer function of the predicted signal d'.
[0057] d'=g s ·s+g sd ·s d
[0058] Compared to the way the difference signal is computed in WO 2008 / 087577, the above relation includes an additional decorrelated signal component term g sd ·s d .
[0059] The gain g can be calculated from the powers of the sum signal s and the difference signal d and the unnormalized c...
no. 2 example
[0069] According to the second embodiment, the signal processing apparatus of the first embodiment can be extended with noise information which can be obtained from the difference signal d. A trade-off can be made between signal properties corresponding to the stereo image and signal properties corresponding to the noise level of the signal, the two properties being separable to a certain extent.
[0070] Figure 3a yes figure 1 A reproduction of , showing a schematic representation of the power spectral density (PSD) of the input FM-multiplexed signal. The input signals include a baseband sum signal 301 (between 0 and 15 kHz), a 19 kHz pilot tone 302, and a double sideband suppressed carrier modulated difference signal 303 (between 23 and 53 kHz). There is also a noise signal 304 which increases with increasing frequency.
[0071] Effectively, the difference signal 303 is available twice, once in the frequency range from 23 to 38 kHz and once in the frequency range from 38...
no. 3 example
[0083] According to a third embodiment, the device of the second embodiment may be adapted to also allow scaling to be transparent to low noise levels. Figure 5 A signal processing device 500 according to the third embodiment is shown. In addition to the solution of the second embodiment of obtaining the SNNR estimate, in the third embodiment, the original difference signal d can also be used in another way. If the SNNR is above a certain threshold (eg 15dB), it is advantageous to use the raw difference signal instead of the synthesized difference signal d', the acquisition of which was described above in relation to the first and second embodiments. A hybrid scheme can be implemented where, for each T / F layer, a better quality can be obtained according to the actual SNNR.
[0084] In this embodiment as well as in the second embodiment, a metric needs to be used to control the behavior of the parameter estimation module 201 . This metric does not have to be the SNNR estimat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com