Method for measuring coaxial error of thru-beams
A measurement method and beam technology, applied in the field of optical systems, can solve problems such as large residual angle error, difficult judgment, and inability to meet precision requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0041] In embodiment 2, for non-polarized light, the measurement optical path is simpler, only need to change the polarizing beam splitting prism into a beam splitting prism, and remove the quarter wave plate at the same time.
[0042] The method for measuring the coaxial error of the beam of light includes the following steps:
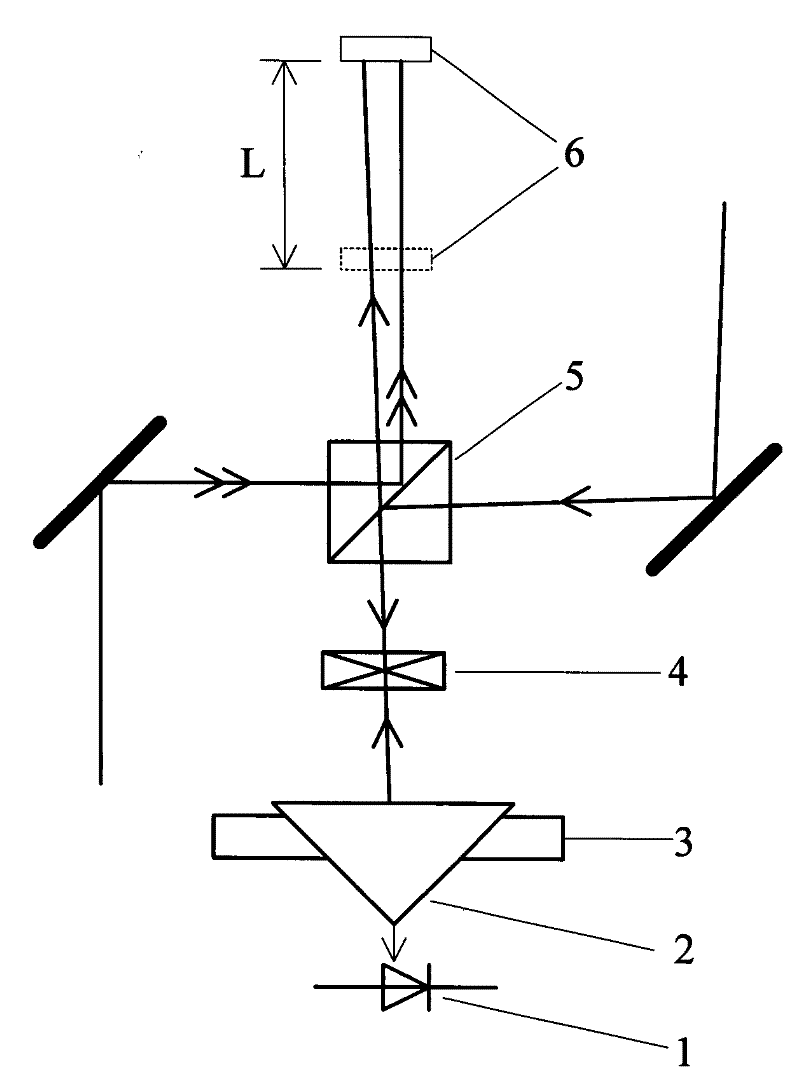
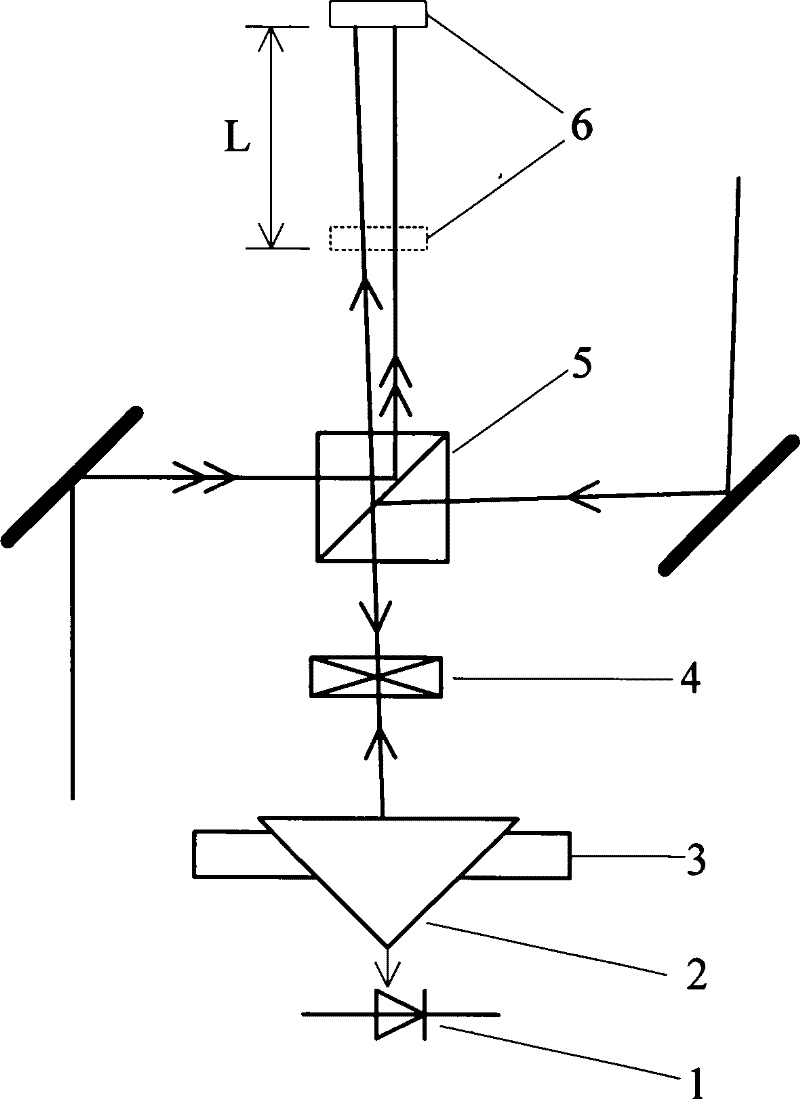
[0043] 1. The two pairs of beams to be measured are respectively called the first beam and the second beam, and a beam splitting prism 5 is inserted in the optical path of the two pairs of beams, so that the beam splitting surface of the beam splitting prism 5 and the The beam is at 45°;
[0044] ②In the direction of the reflected light of the second light beam of the beam splitting prism 5, a corner reflector 2 and a light intensity detector 1 are arranged in sequence, the corner reflector 2 is placed on the two-dimensional translation adjustment frame 3 and the corner reflector 2 The hypotenuse is perpendicular to the reflected light beam, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com