Photometry device
一种光谱、测量值的技术,应用在测光装置领域,能够解决测量值低有效性、无法广泛应用等问题,达到改善测量精度的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
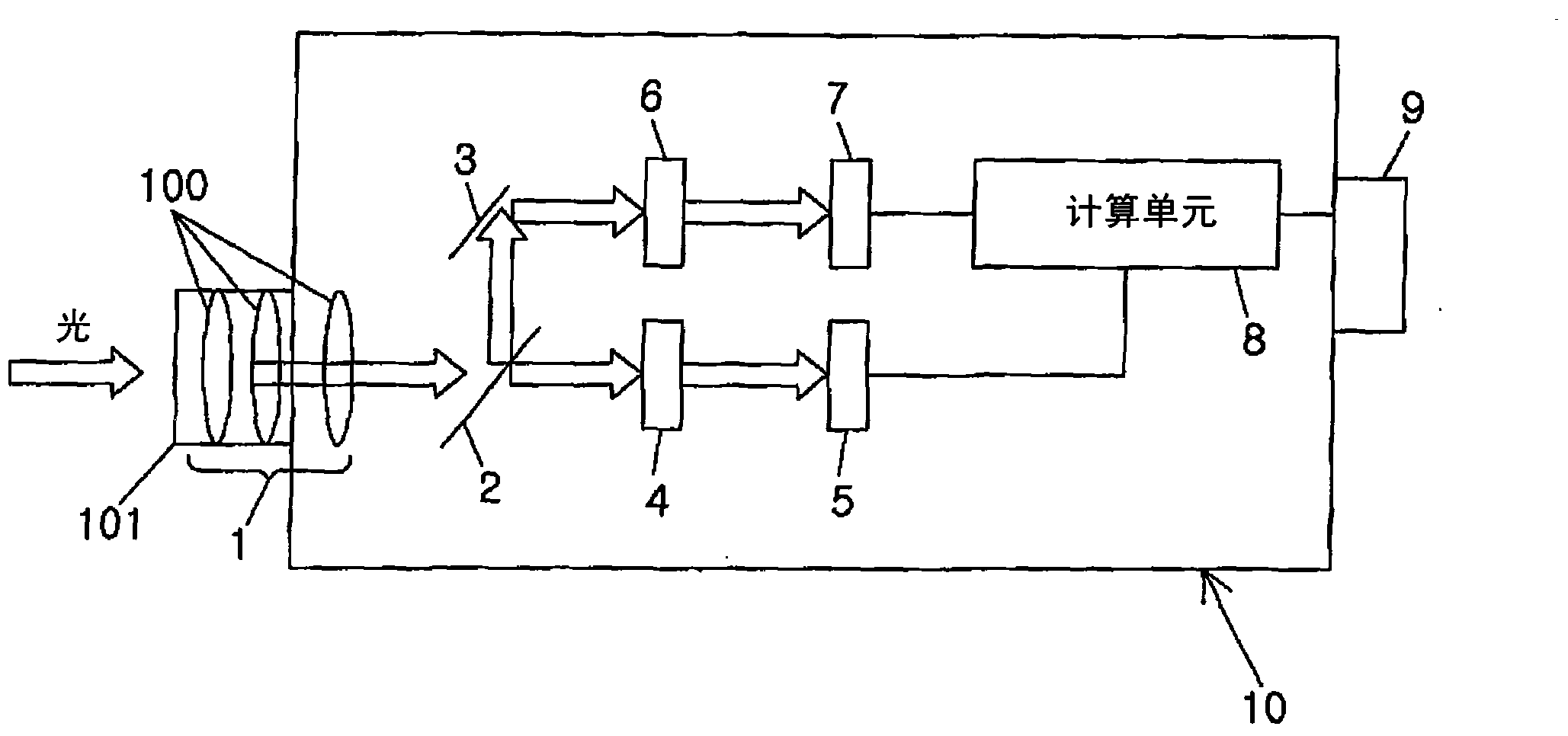
[0016] Such as figure 1 As shown, the photometric device of the current embodiment is provided with an optical component 1, a half mirror 2, a mirror 3, a first filter 4, a first photoelectric converter 5, a second filter 6, a second photoelectric converter 7, computing unit 8, display 9 and housing 10.
[0017] The housing 10 has a box-like shape and is made of synthetic resin or metal. Light is introduced into the housing 10 via a hole opened on the left side of the housing.
[0018] The optical part 1 includes a plurality of convex lenses 100 ; and a cylindrical body 101 supporting the convex lenses 100 and closing a hole of the housing 10 . Therefore, the light introduced through the hole is converged by the convex lens 100 of the optical component 1 .
[0019] The half mirror 2 is provided on the optical path of the optical component 1, and divides the light condensed by the optical component 1 into two parts. On one optical path branched by the half mirror 2, a first...
no. 2 example
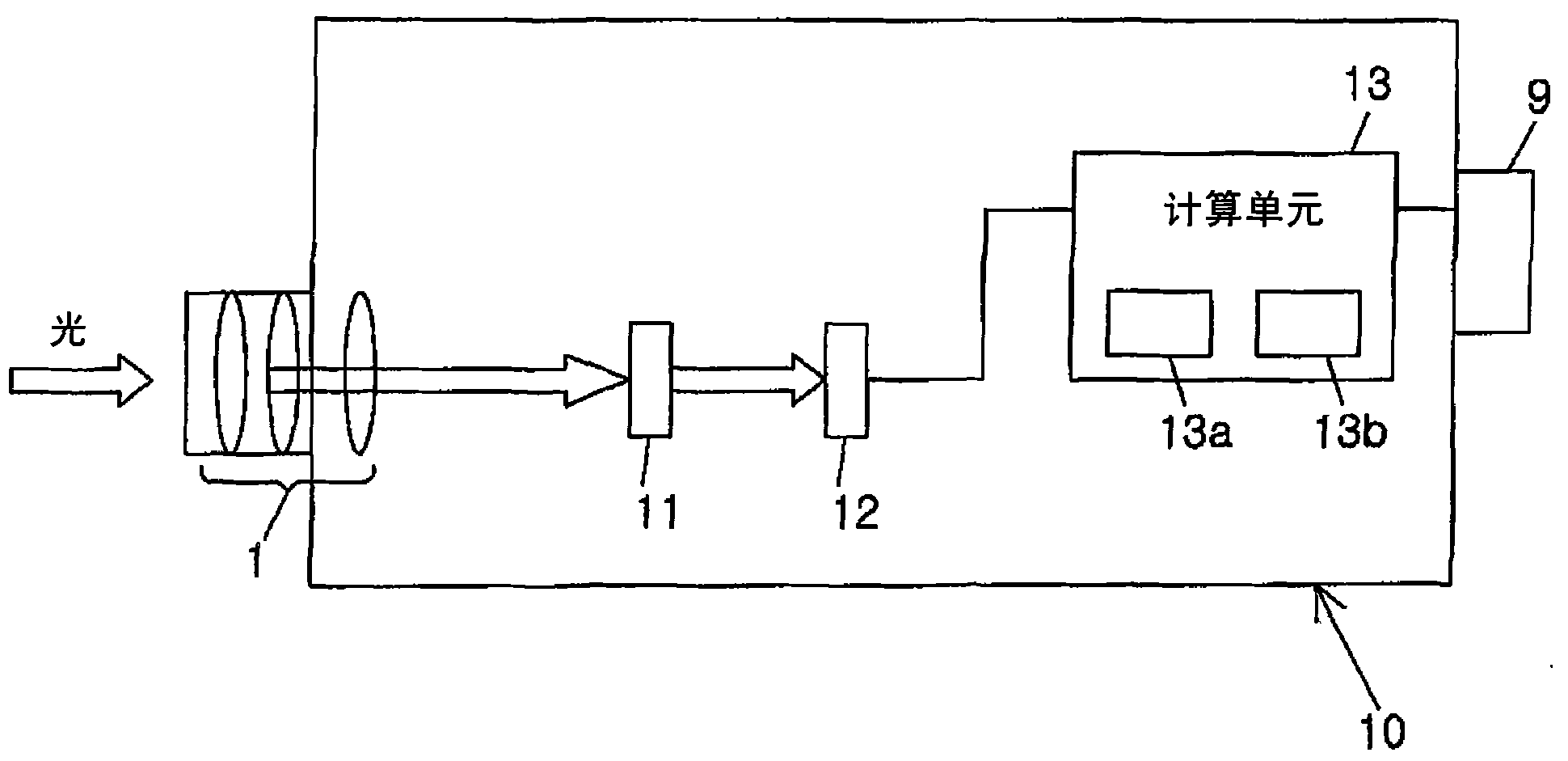
[0028] Such as image 3 As shown, the photometric device of the current embodiment includes: a spectral filter 11 for dispersing incident light; Measuring means 12; and calculating means 13 for calculating mesopic luminance. The same reference numerals are used for components common to the photometry device of the first embodiment, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0029] The spectral filter 11 is configured with a prism, and divides (disperses) incident light into a plurality of wavelength bands by utilizing its different refractive index depending on the wavelength of light. The measuring section 12 has a plurality of photoelectric transducers (not shown) corresponding to each wavelength band of light dispersed by the spectral filter 11; and a plurality of amplifiers (not shown) that amplify the output voltages of the respective photoelectric transducers. out).
[0030] The calculation section 13 mainly includes: an A-D converter (not shown) for quantizing (A-D c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com