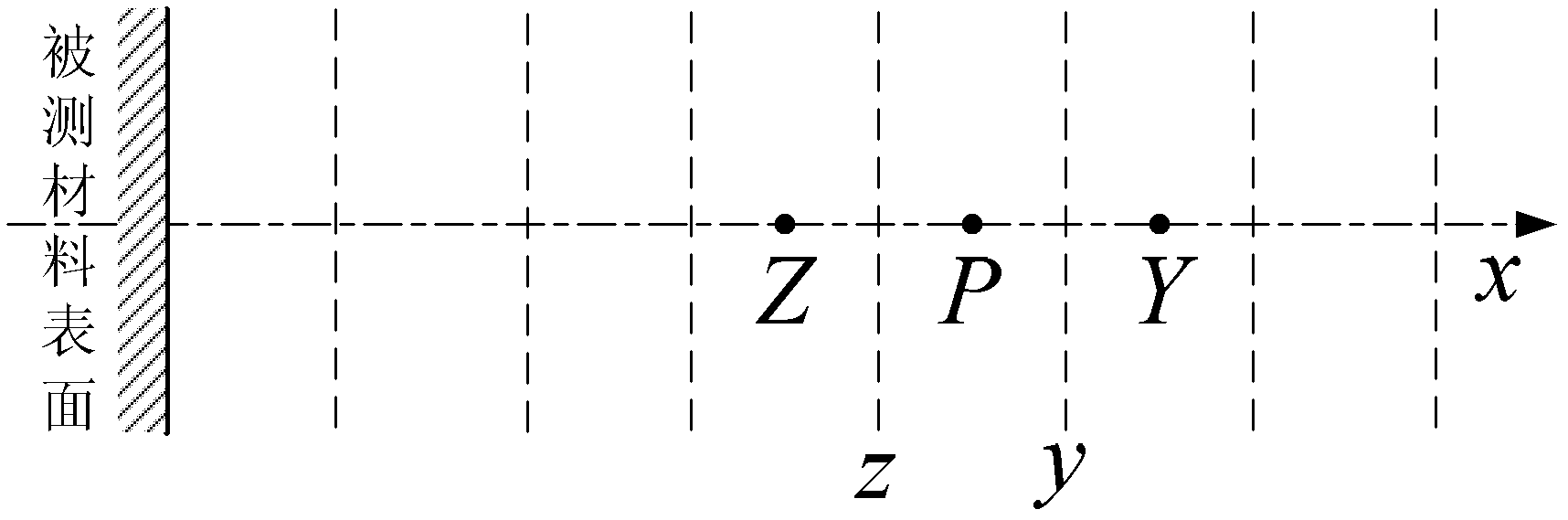Method of correction for non-contact thermometry in translucent medium environment
A translucent medium, non-contact temperature measurement technology, used in thermometer testing/calibration, thermometers, measuring devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
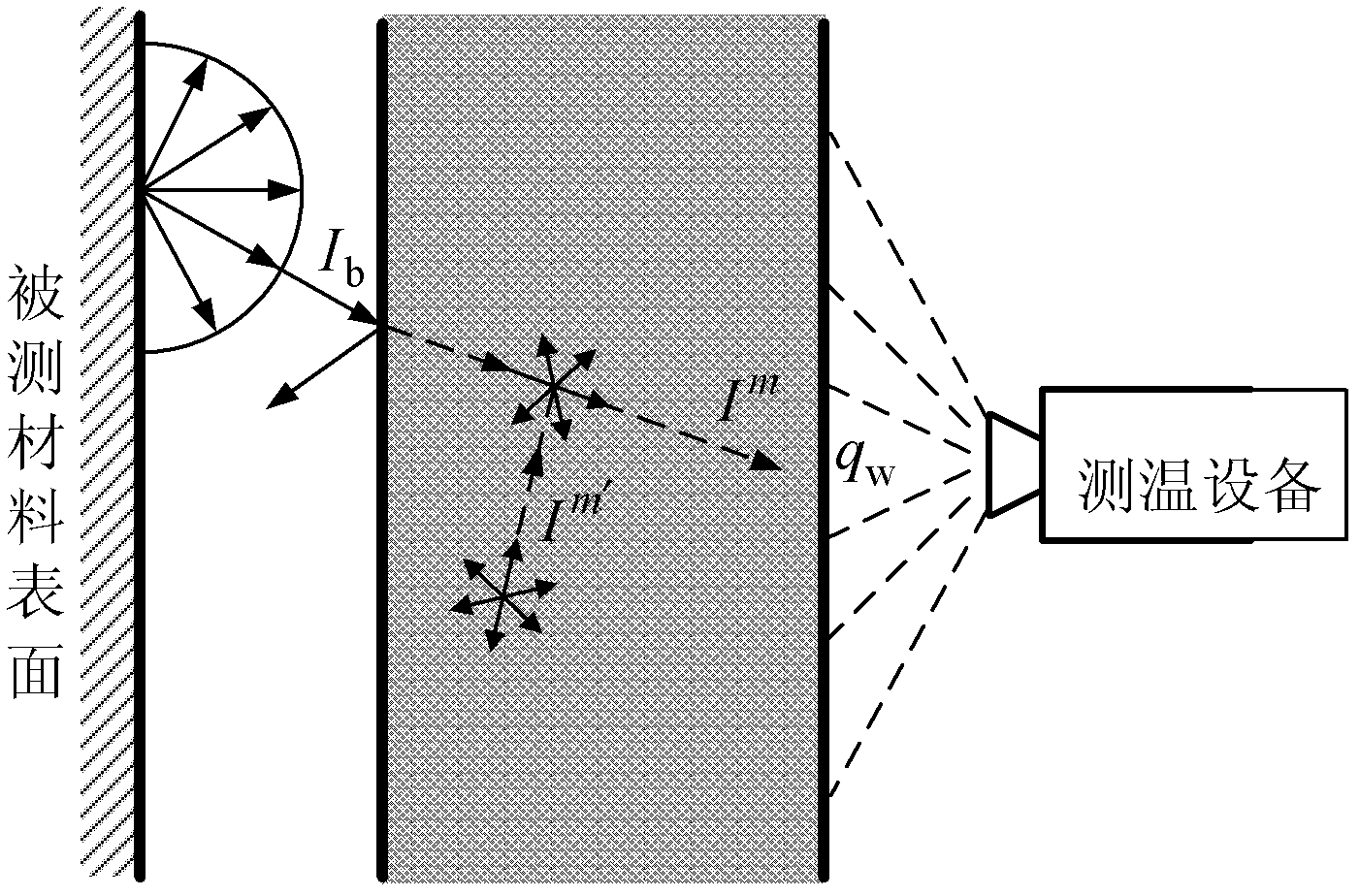
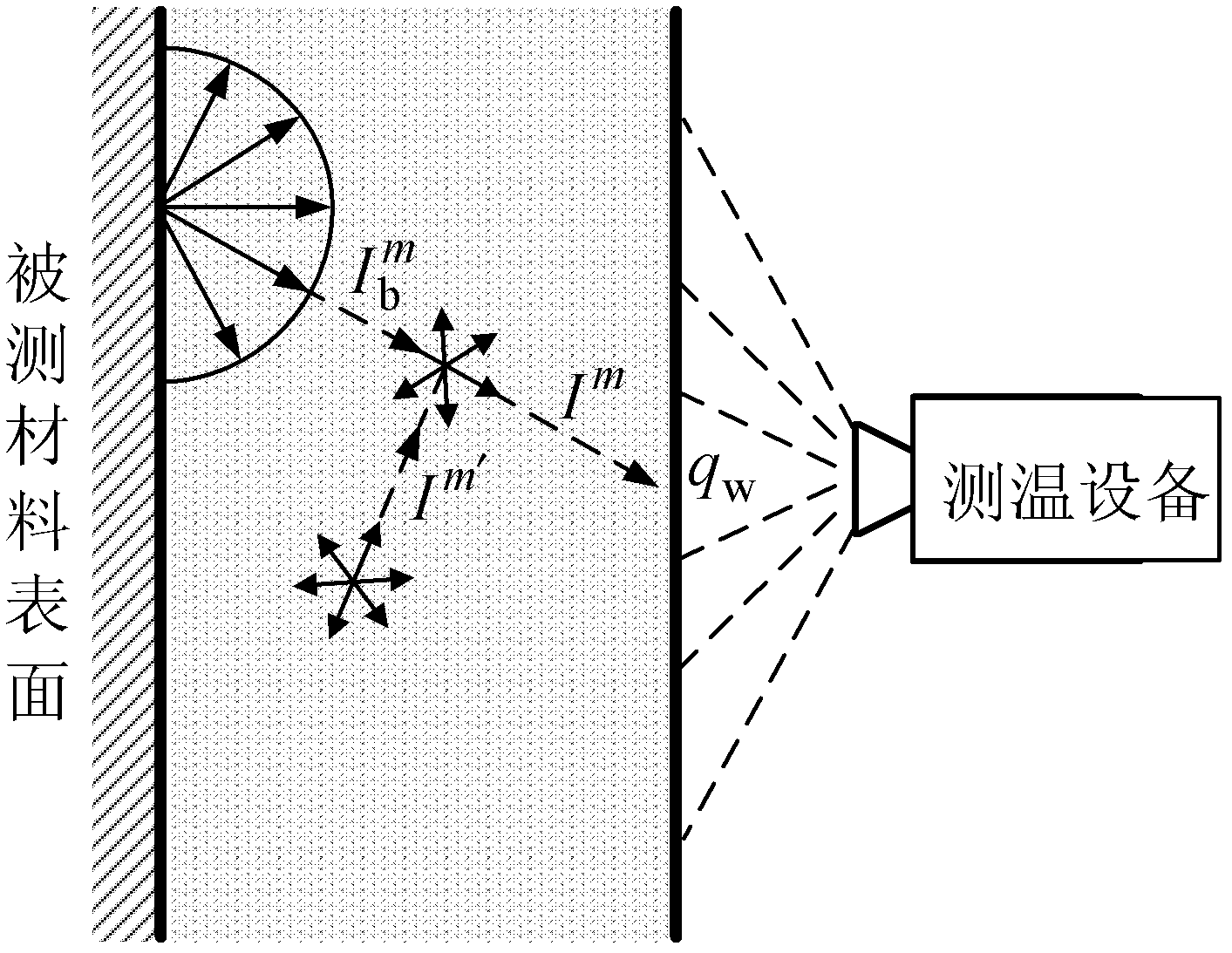
[0067] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 3 Describe this embodiment, the correction method for non-contact temperature measurement in a translucent medium environment described in this embodiment, it includes the following steps:
[0068] Step 1: Determine whether the translucent medium is in contact with the surface of the material to be tested, if so, perform step 2; otherwise, perform step 3;
[0069] Step 2: Select a one-dimensional coupled heat transfer model, use the finite volume method to calculate the forward model, and obtain the theoretical radiation energy value that the temperature measurement equipment can obtain, and then perform step 4;
[0070] Step 3: Select a one-dimensional pure radiation heat transfer model, use the finite volume method to calculate the forward model, obtain the theoretical radiation energy value that the temperature measuring equipment can obtain, and then perform step 4;
[0071] Step 4: Use...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0074] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 1 and image 3 This embodiment is described. This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. The specific method for obtaining the theoretical radiation energy value of the measuring device in step 2 is:
[0075] Choose a one-dimensional coupled heat transfer model, and divide the interior of the translucent medium into grids along the direction perpendicular to the surface of the material to be tested according to the calculation accuracy requirements, and divide them into multiple grid units evenly, and use the zenith angle and horizontal angle to evenly divide The method discretely divides the solid angle of the internal space of the translucent medium into N Ω , the grid unit is parallel to the surface of the measured material; set the radiation source term q R The initial value of is 0, using the energy conservation equation of the one-dimensional coupled heat transfer model and the coup...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0105] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination figure 1 with figure 2 This embodiment is described. This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. The specific method for obtaining the theoretical radiation energy value of the temperature measuring device in step 3 is:
[0106] Suppose the temperature of the surface of the material to be measured is T w , according to the spectral emissivity ε of the surface of the measured material k Calculation of the outgoing radiation intensity from the surface of the material under test
[0107] I 0 , k m = ϵ k σT w 4 π , - - - ( 10 )
[0108] will emit ra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com