Patents
Literature
126 results about "Material under test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
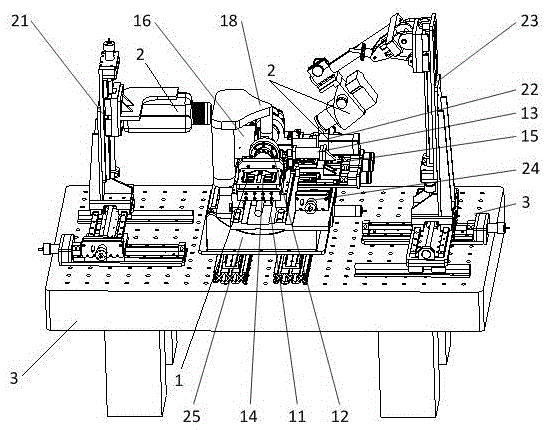
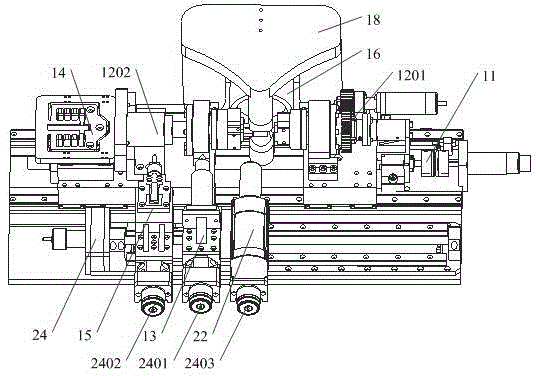
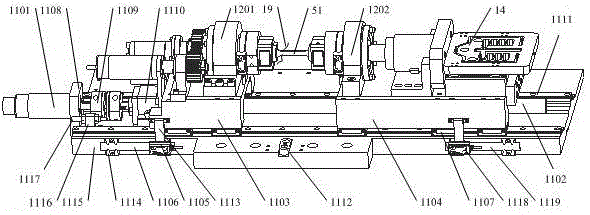
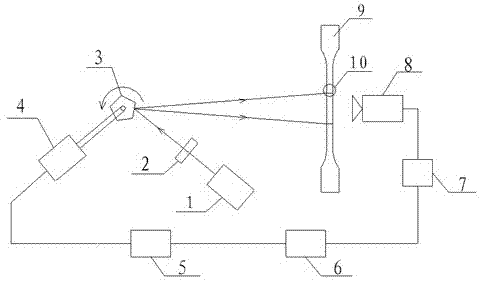
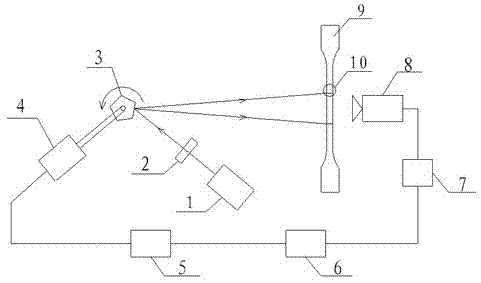
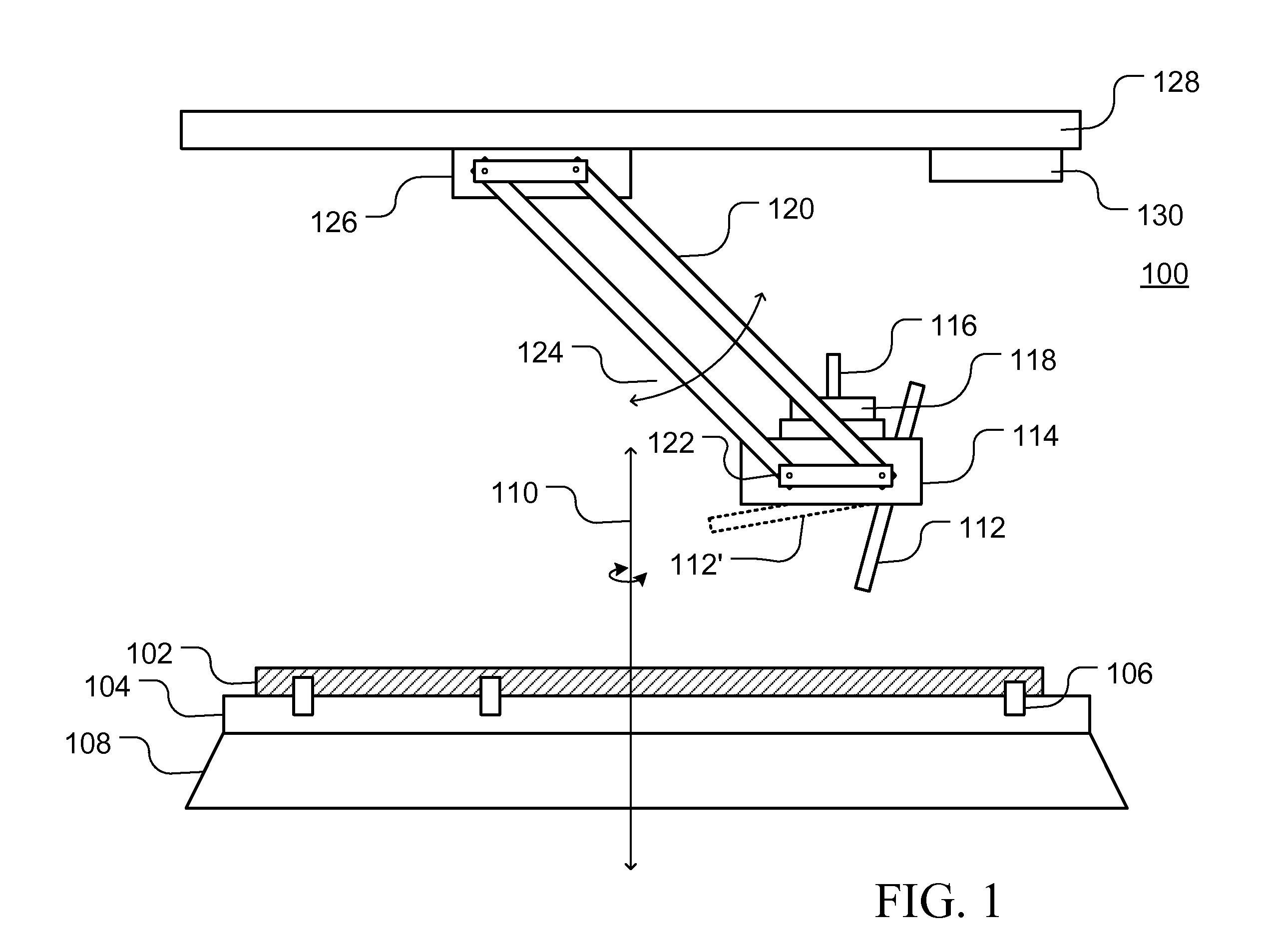
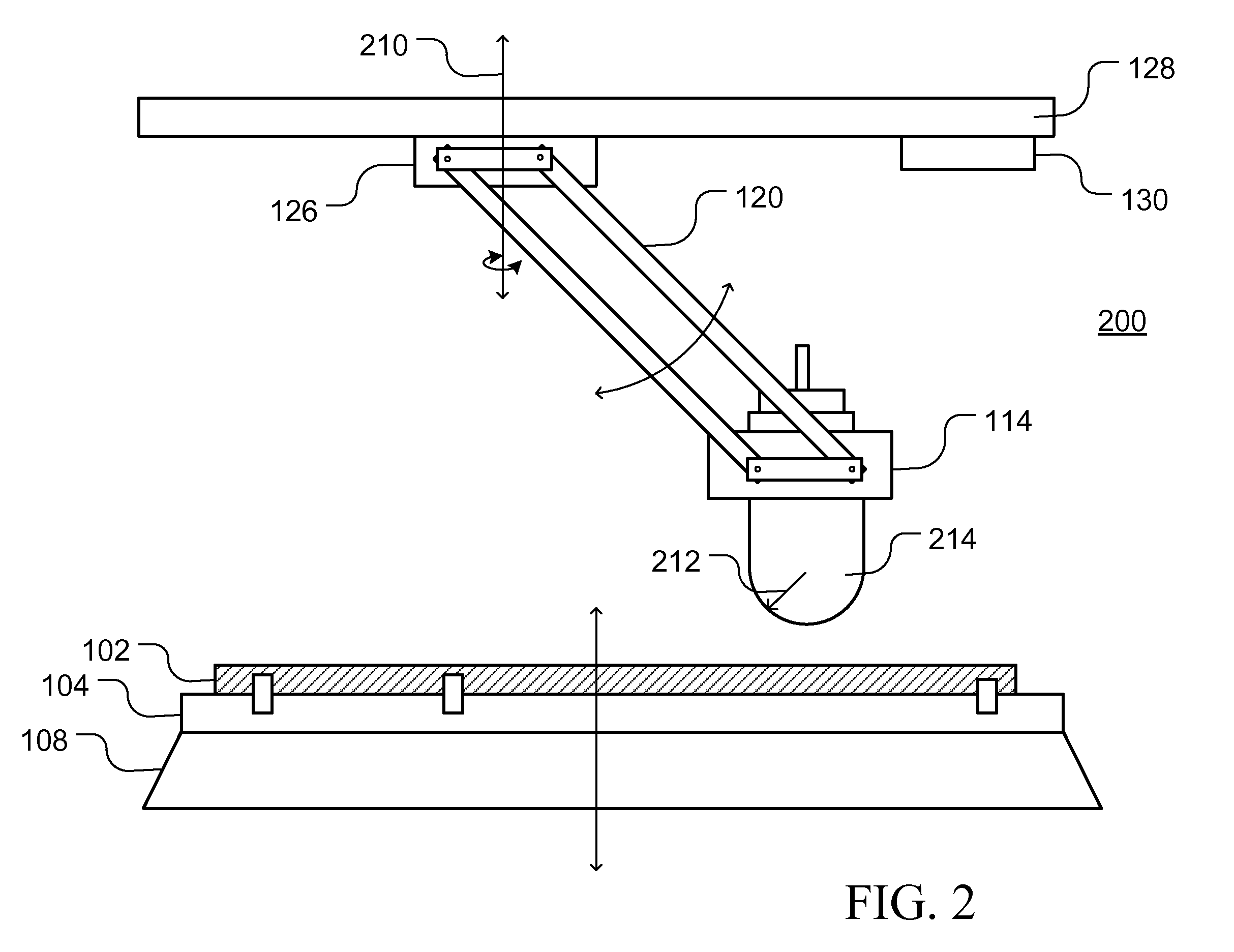
Combined load mode mechanical-electrical and thermal-magnetic coupling material performance in-situ test instrument and method
ActiveCN105628487ARich physical performance parametersRich performance parametersMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesCouplingPhysical field
The invention relates to a combined load mode mechanical-electrical and thermal-magnetic coupling material performance in-situ test instrument and method, and belongs to the field of precise scientific instruments. The test instrument comprises three parts: namely a combined load-multi-physical field loading test platform, an in-situ monitoring platform and a vibration-isolating base, wherein the vibration-isolating base is mainly used for supporting the combined load-multi-physical field loading test platform and the in-situ monitoring platform, and provides a positioning service for installation of the platforms and effective vibration isolating treatment for various precise driving loading elements, detecting elements and in-situ monitoring elements; the in-situ monitoring platform realizes real-time dynamic and in-situ monitoring on micro deformation, injury mechanism, microstructure changes and property evolution of a material sample under the combined load condition by precisely adjusting the position and posture of various monitoring modules. The combined load mode mechanical-electrical and thermal-magnetic coupling material performance in-situ test instrument has the following advantages: the structure is miniaturized and lightened in weight, and the instrument body can be placed in an optionally equipped vacuum cavity, so that testing environments like low pressure, vacuum and inert gases can be provided for the material sample to be tested, and the practicability is high.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
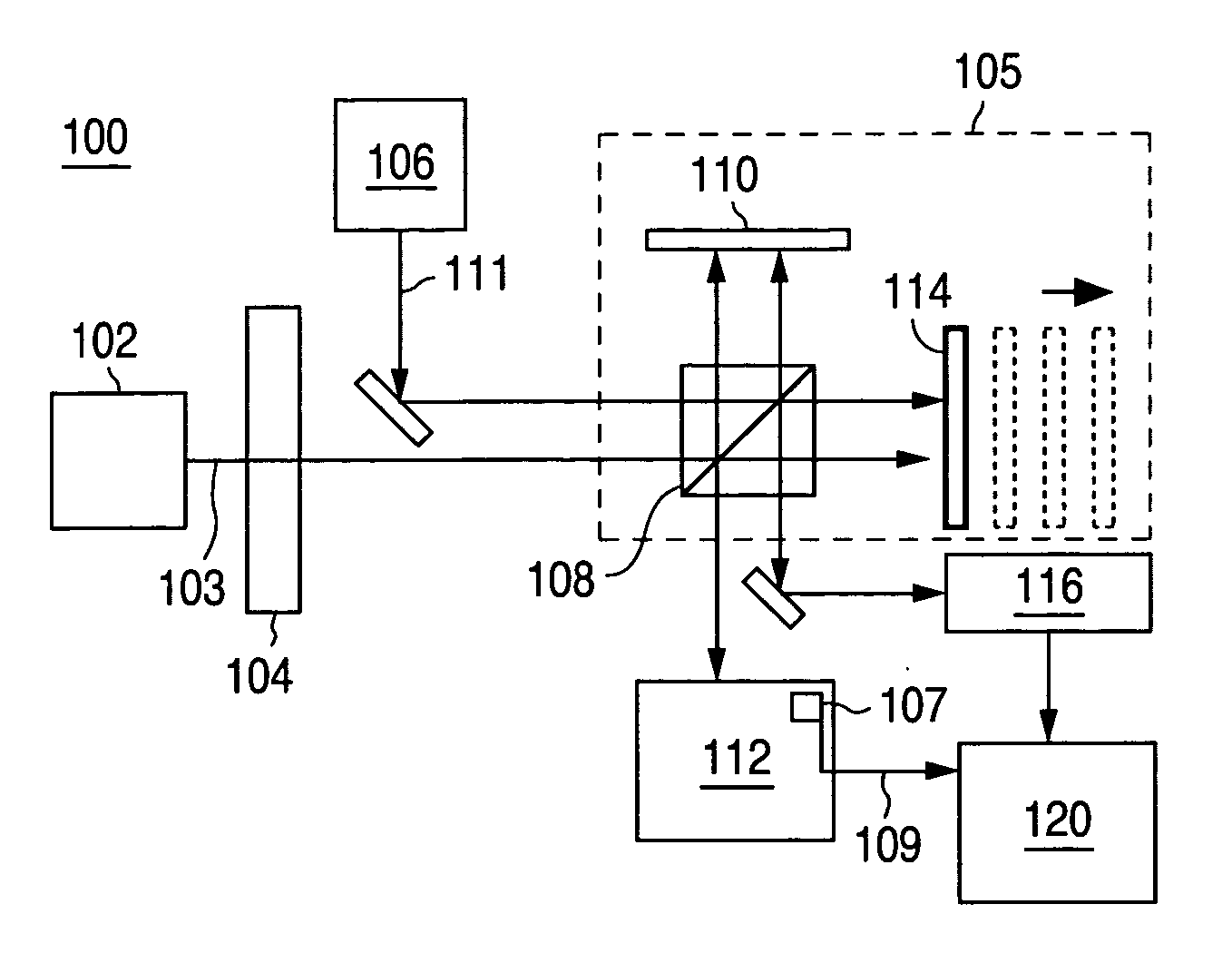
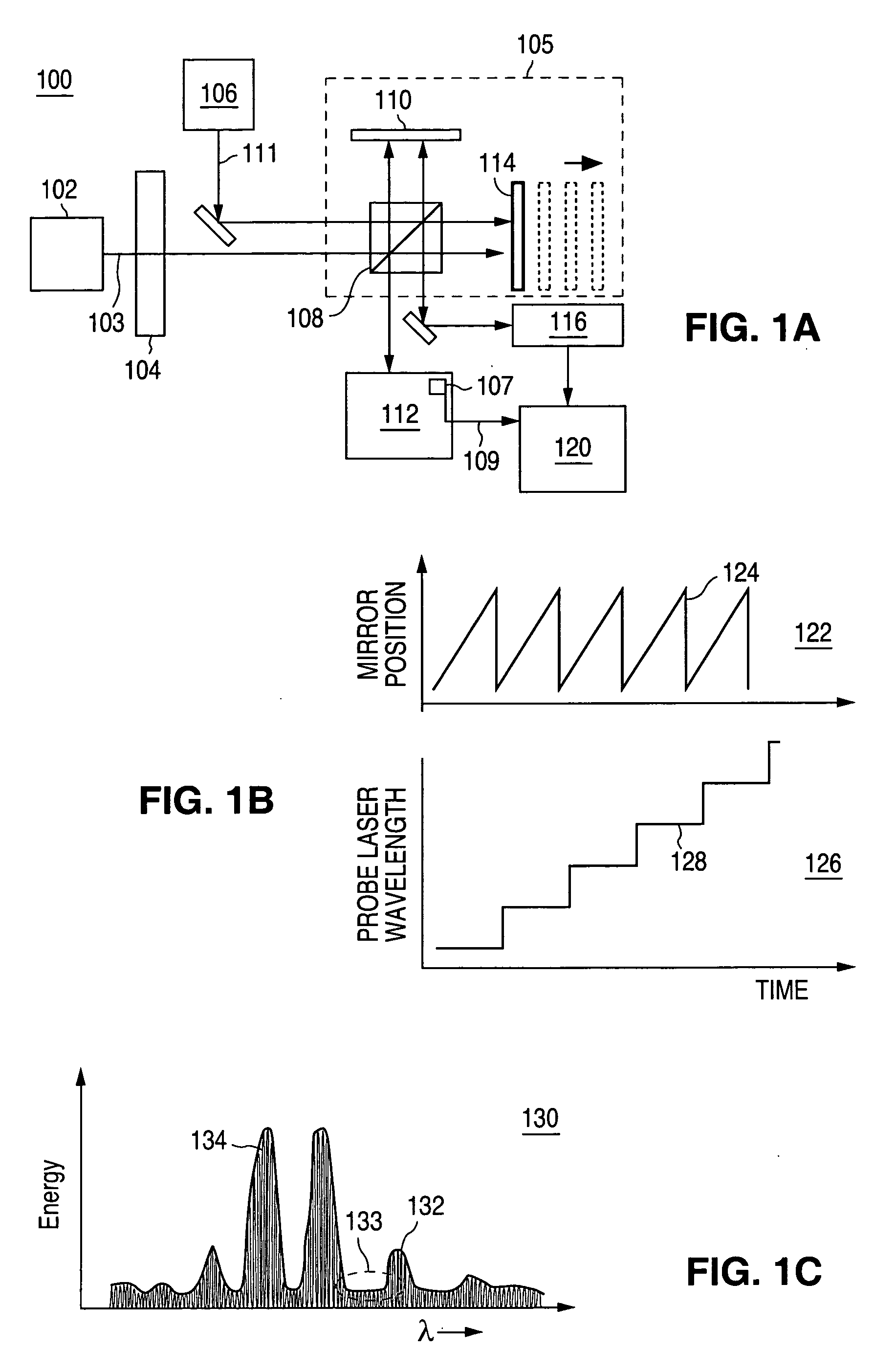
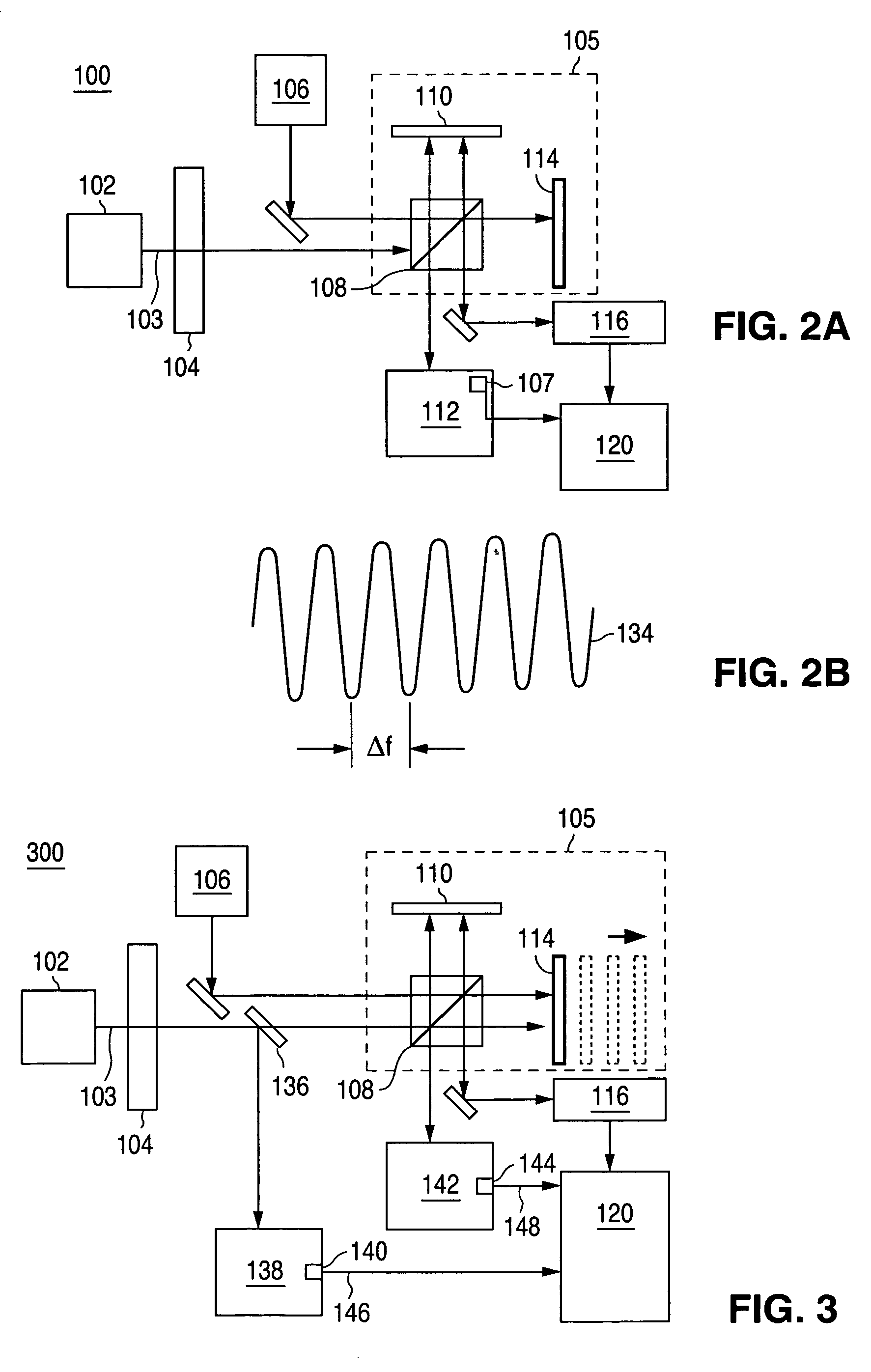
System and method for interferometric laser photoacoustic spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060262316A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryMaterial under testLength wave
A system of using an interferometer, in combination with a laser, and a detector to determine absorptive characteristics of a material under test. The operation of the interferometer allows for determination of the wavelength of the laser beam and for determining relative changes in the wavelength of the laser beam. A method for using a laser source and an interferometer to determine characteristics of a material under test in accordance with the present invention is also provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
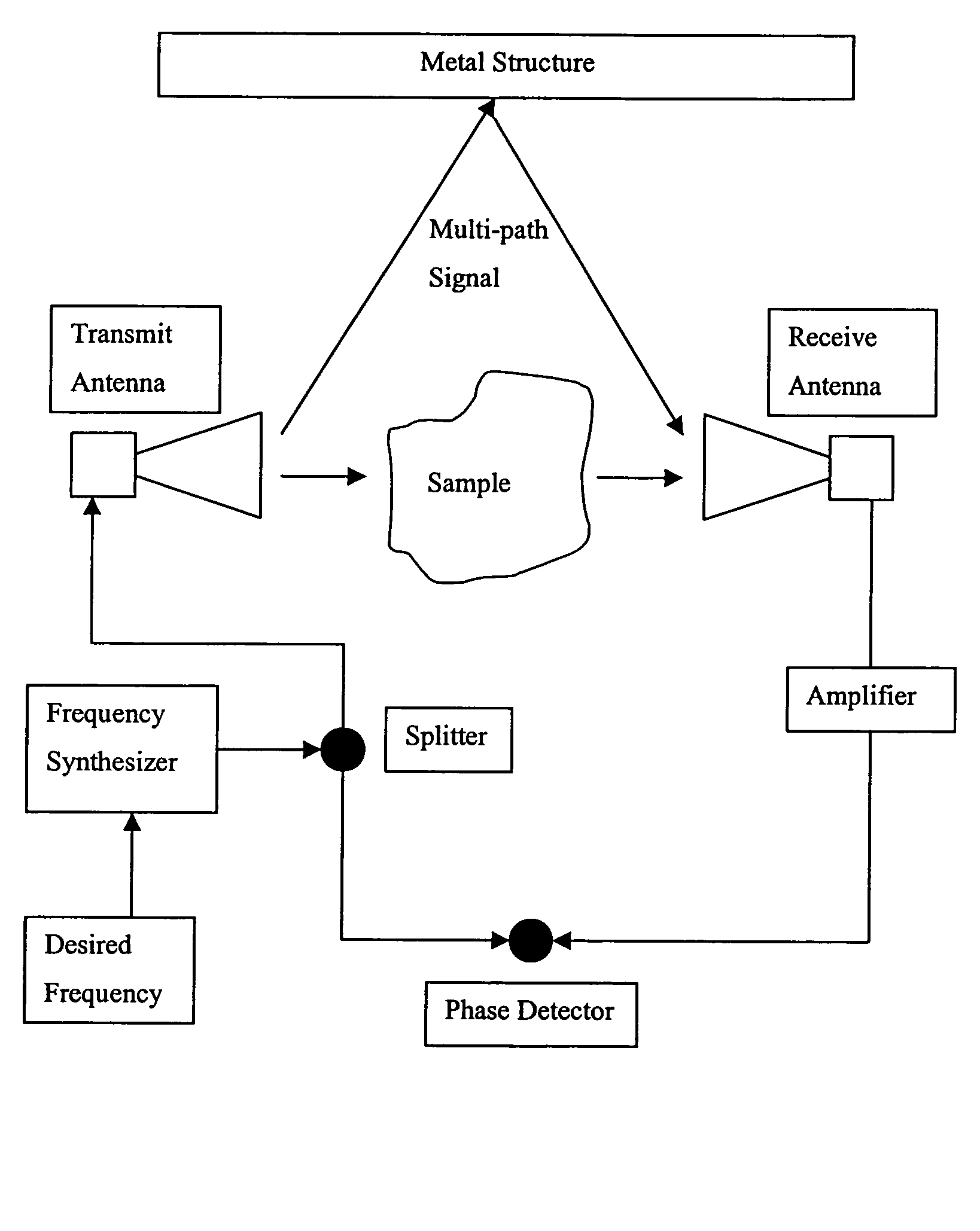
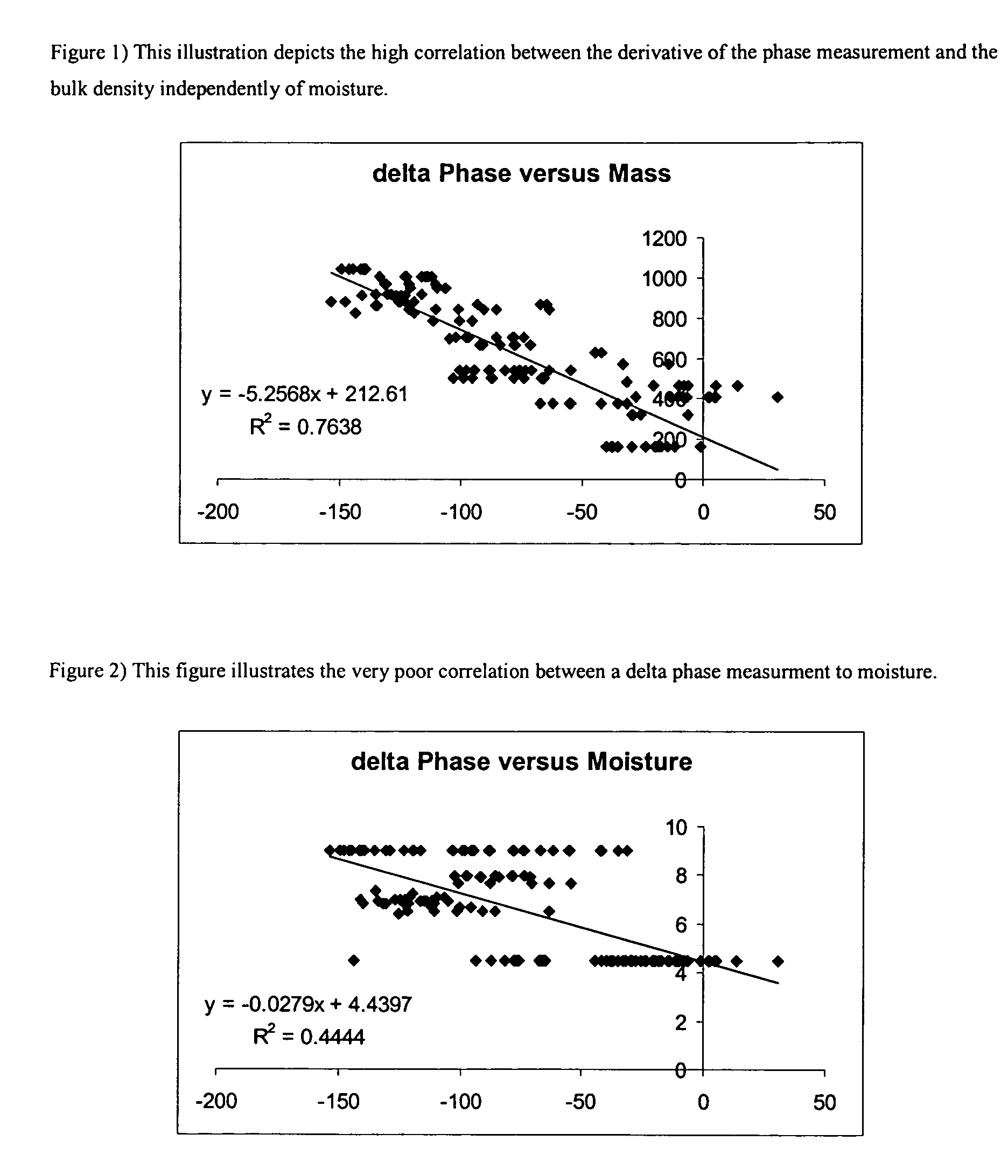
Moisture measurement system for seed cotton or lint
InactiveUS7330034B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMoisture content investigation using microwavesPhase detectorMaterial under test
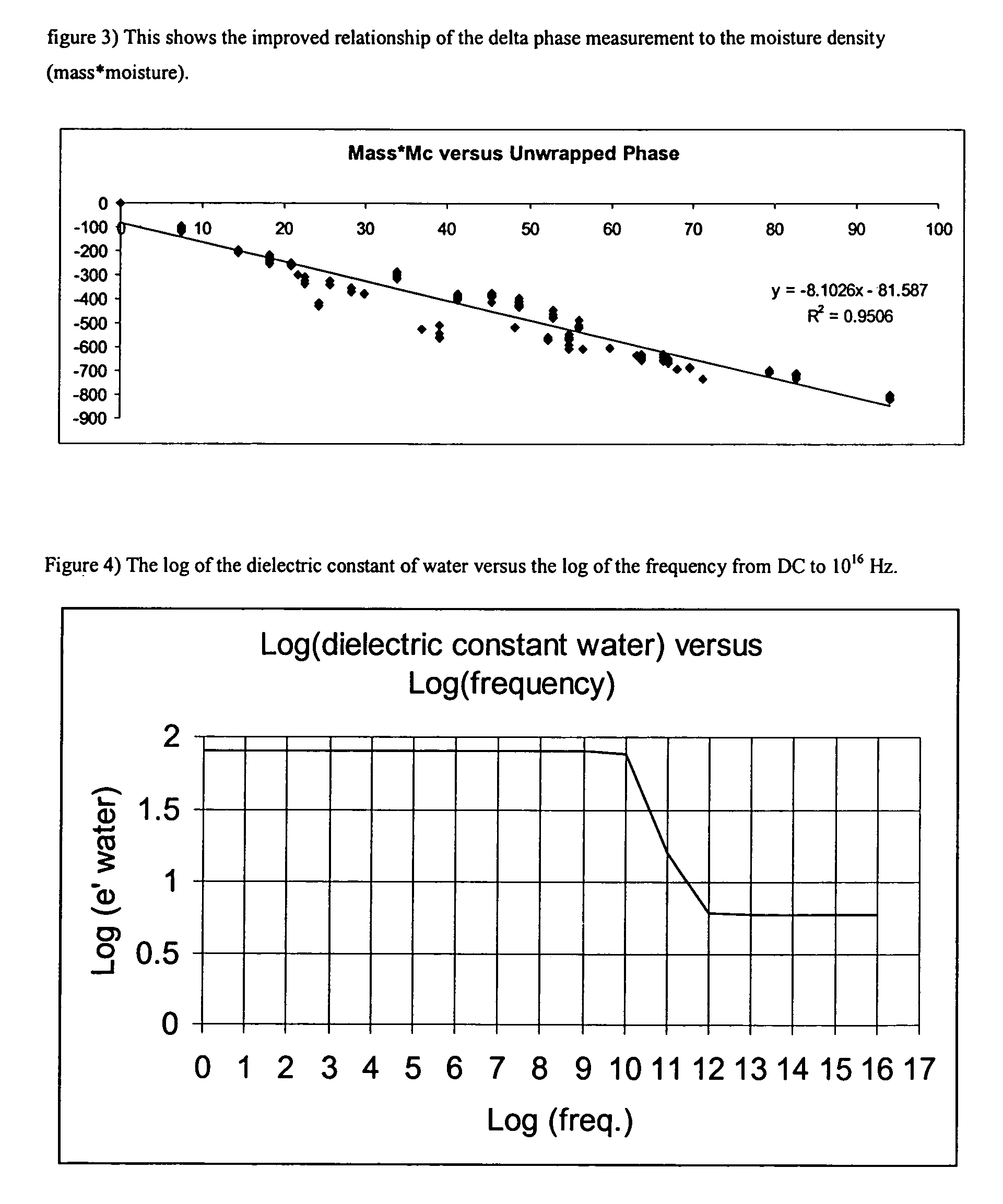
A process for measuring the moisture content and the mass-moisture content of materials is presented that requires no air reference or calibration sequence. A microwave signal is split into a reference and a transmission signal, and the reference signal is applied directly to the phase detector, whereas the transmission signal is first transmitted through the sample before being presented to the other side of the phase detector. This measurement provides a phase-constant measurement that is due to the dielectric characteristics of the material under test. The system measures the material's phase-constant across a band of frequencies. The slope of the phase-constant versus frequency is then utilized to predict the density of the material which is then combined with the corrected phase-constant measurement to calculate the moisture content of the material.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Thermal-force coupling fatigue test device and method
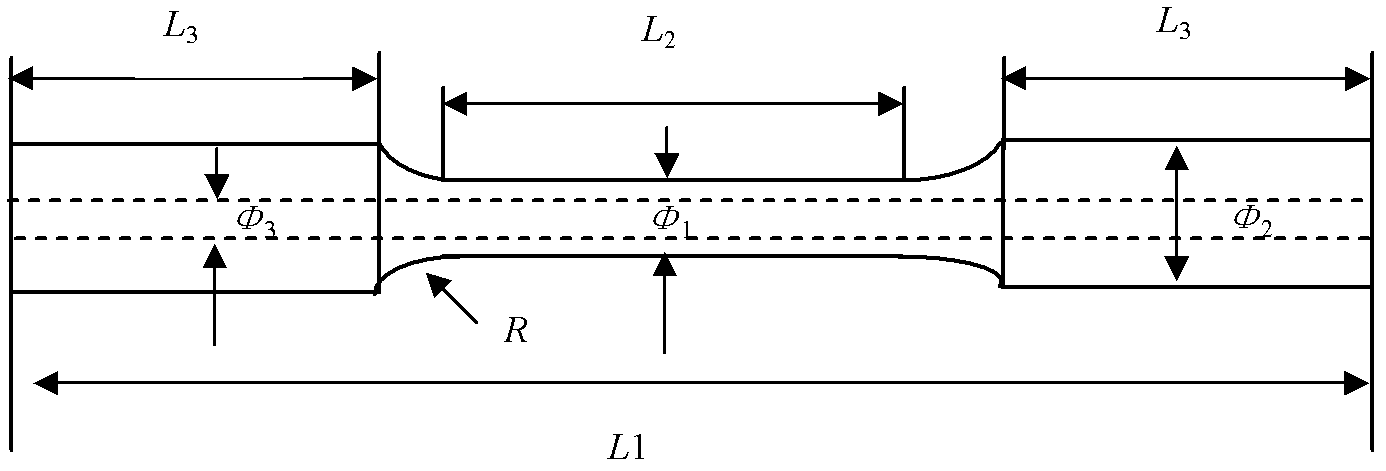
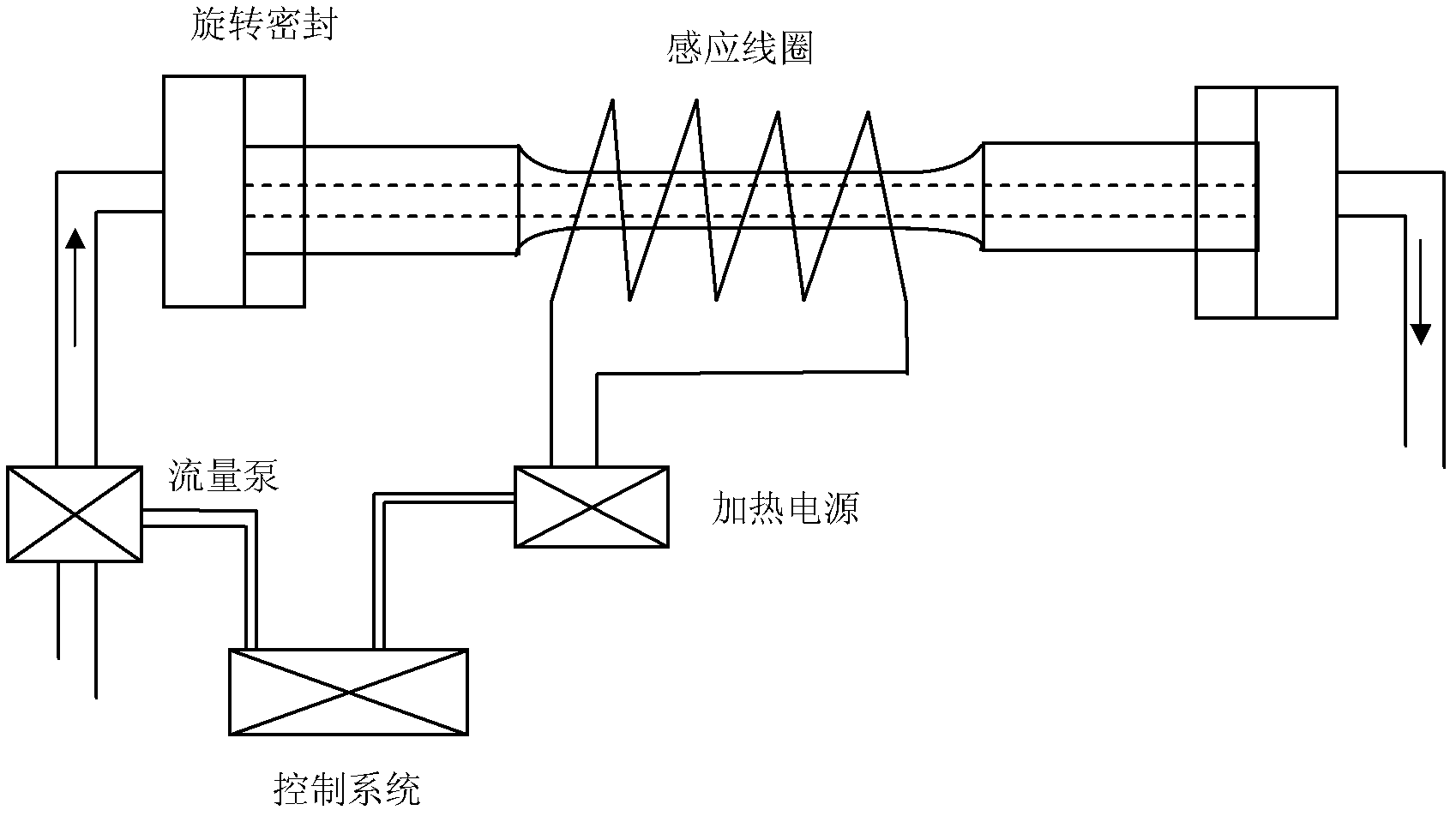
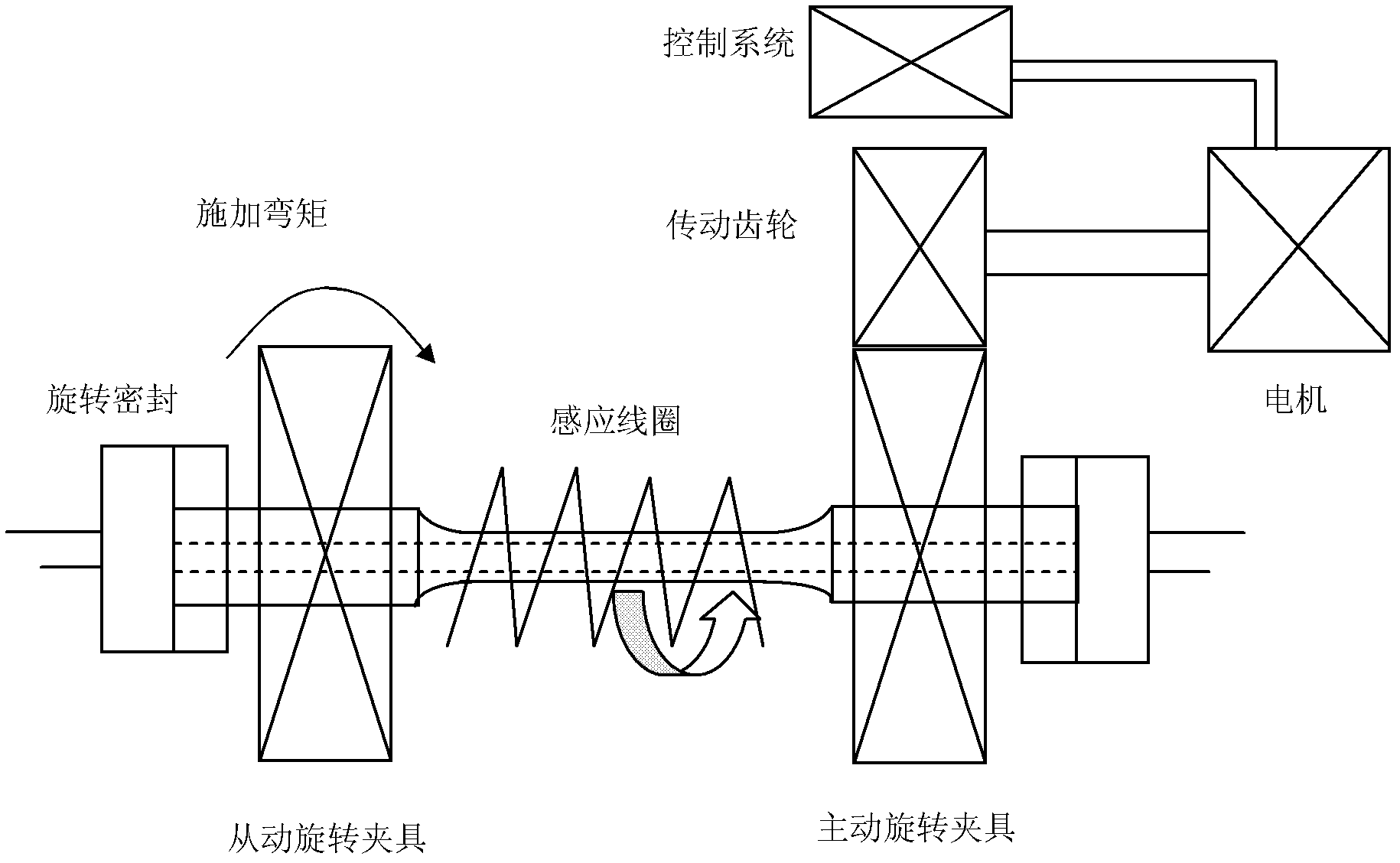
The invention relates to a thermal-force coupling fatigue test device and method, belonging to the field of metal material performance test and analysis. The device comprises a tested material test sample, a cold-thermal fatigue system and a stress fatigue system, wherein the test sample comprises a clamping section, a test section and a transition section; the cold-thermal fatigue system comprises a high frequency induction coil, a rotary seal device, a flow pump, a temperature sensor, a heating power supply, a cooling medium pipeline and a control system; and the stress fatigue system mainly comprises a driving rotating fixture, a driven rotating fixture, a transmission gear, a motor and a motor control system. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting and fixing the test sample with the cold-thermal fatigue system and the stress fatigue system, and carrying out cold-thermal fatigue while stress fatigues under different stresses are carried out to obtain a curve which shows variation of stress fatigue life along with cyclic stress; and adjusting parameters of the cold-thermal fatigue, thus influence of cold-thermal fatigue temperature to fatigue limit can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
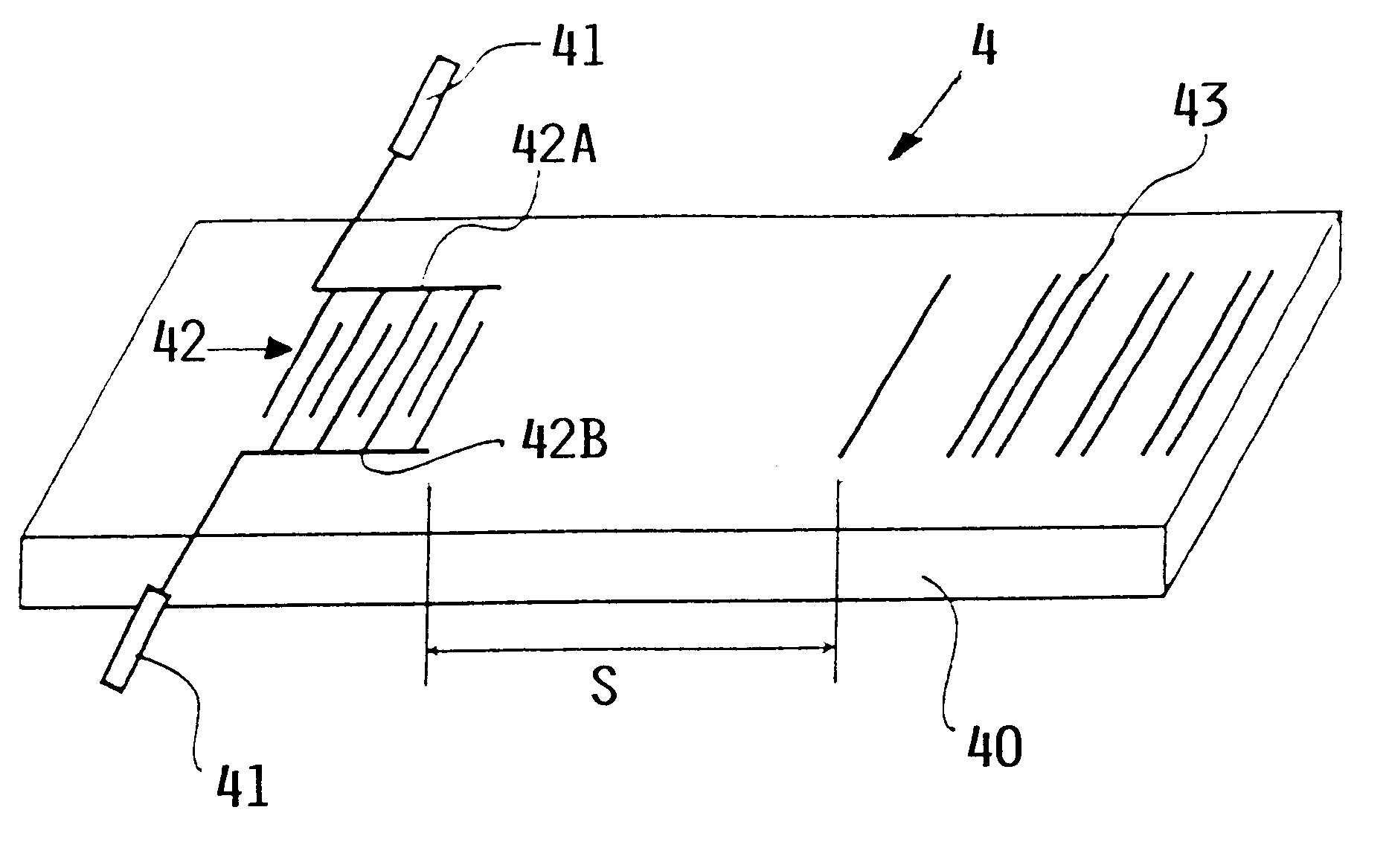
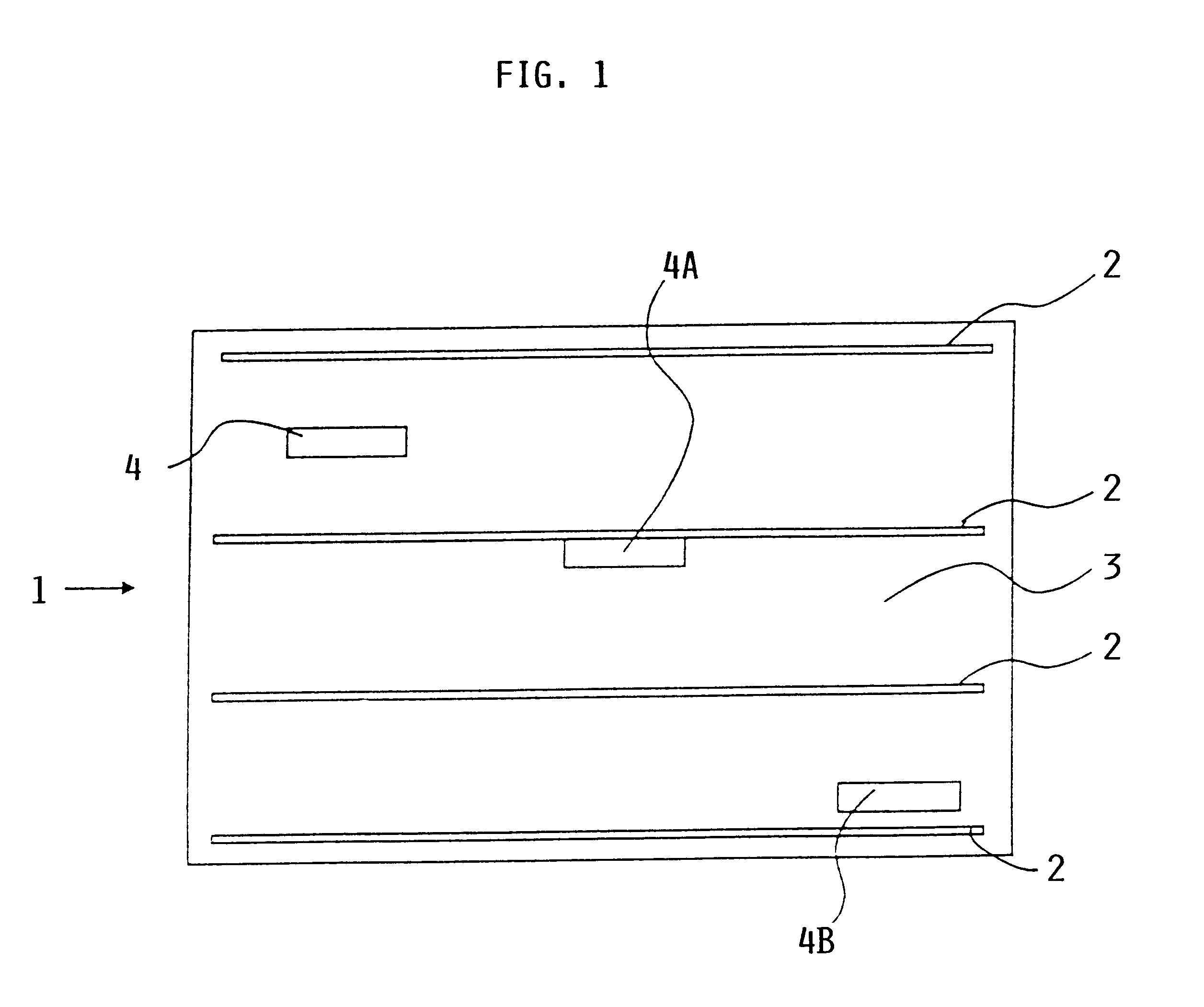
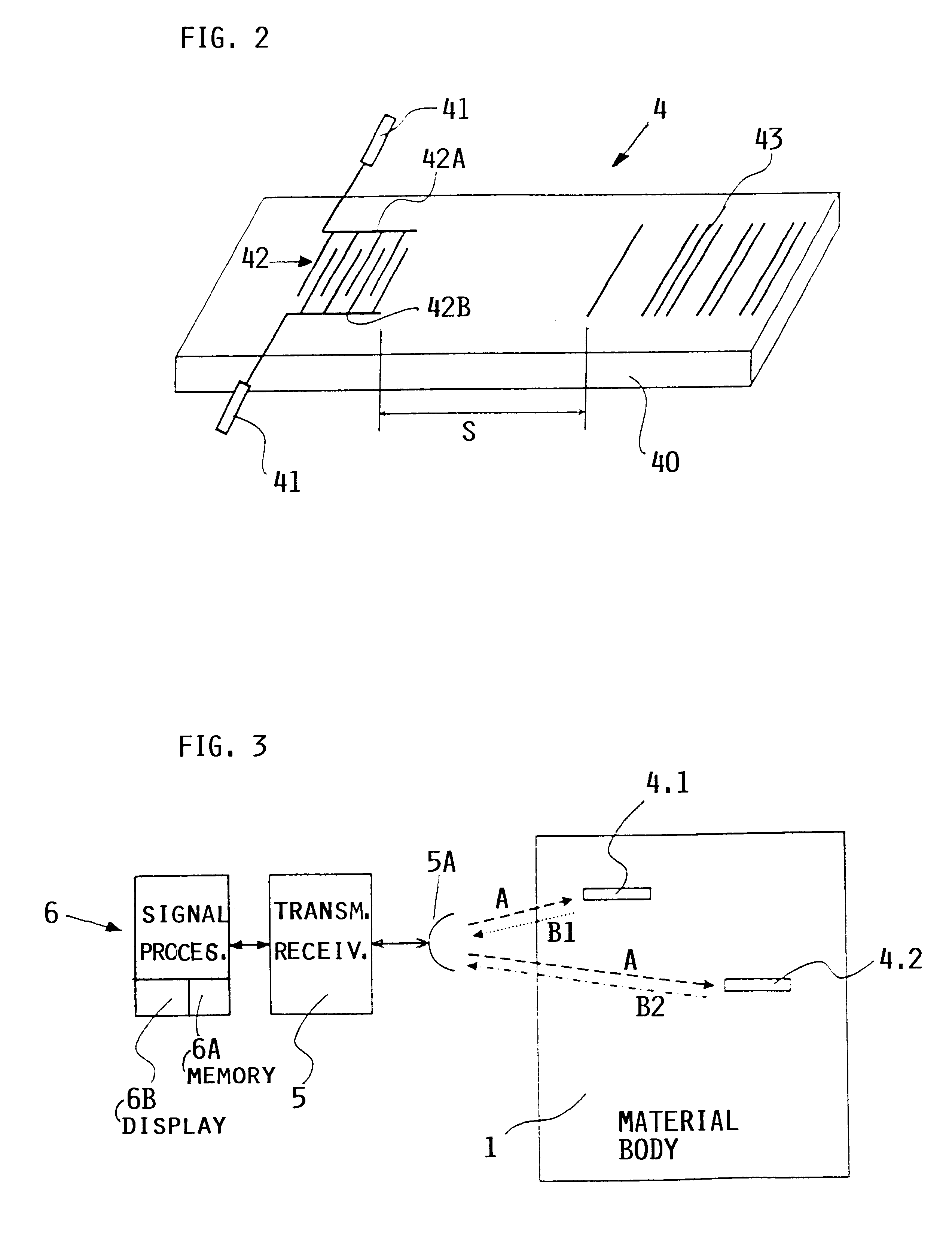
System and method for material testing, material suitable for such testing and method for producing such material
InactiveUS6260415B1Easy to testEasy assessment processAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesConverting sensor ouput using wave/particle radiationMaterial under testSurface acoustic wave
A material, such as a fiber composite material, has embedded inside at least one, preferably more, surface acoustic wave filters of piezoelectric material for receiving testing energy in a wireless manner and for retransmitting a material quality signal in a wireless manner which is evaluated in a system that has a wireless transmitter for sending testing energy into a material and a wireless receiver for receiving the material quality signal which is then processed and evaluated by a respective processor of the testing system. An output of the processor provides information regarding the nature and quality of the material tested and of the presence and location of any material faults that may be displayed on display screen.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Sound and ultrasonic nondestructive detection method
InactiveCN101413926AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationUltrasonic sensor
The invention discloses a sound and ultrasonic nondestructive detection method, In the method, the nondestructive detection is carried out on the performance (such as adhesion) of materials such as composites by sound and ultrasonic sensors (such as an electroacoustic transducer made of piezoelectric material, magnetostrictive material, and the like) in a way of direct contact coupling or coupling by a couplant, the single and dual electroacoustic transducers can be excited in the form of continuous waves such as variable sine, pulse or triangle wave, a Phase Sensitive Detection (DSD) technique is adopts to process the change of amplitude and phase of feedback echo, and the detection effect of removing certain interference signals (namely retaining the truth and clearing up the false) can be achieved especially by frequency mixing processing of signals which are collected by different frequencies. The application mechanism of the method adopts currently advanced multifrequency and frequency spectrum analysis technique used for eddy detection to process the information obtained by the electroacoustic transducer, thus obtaining all detection characteristics which the existing noise and vibration detecting does not have.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH
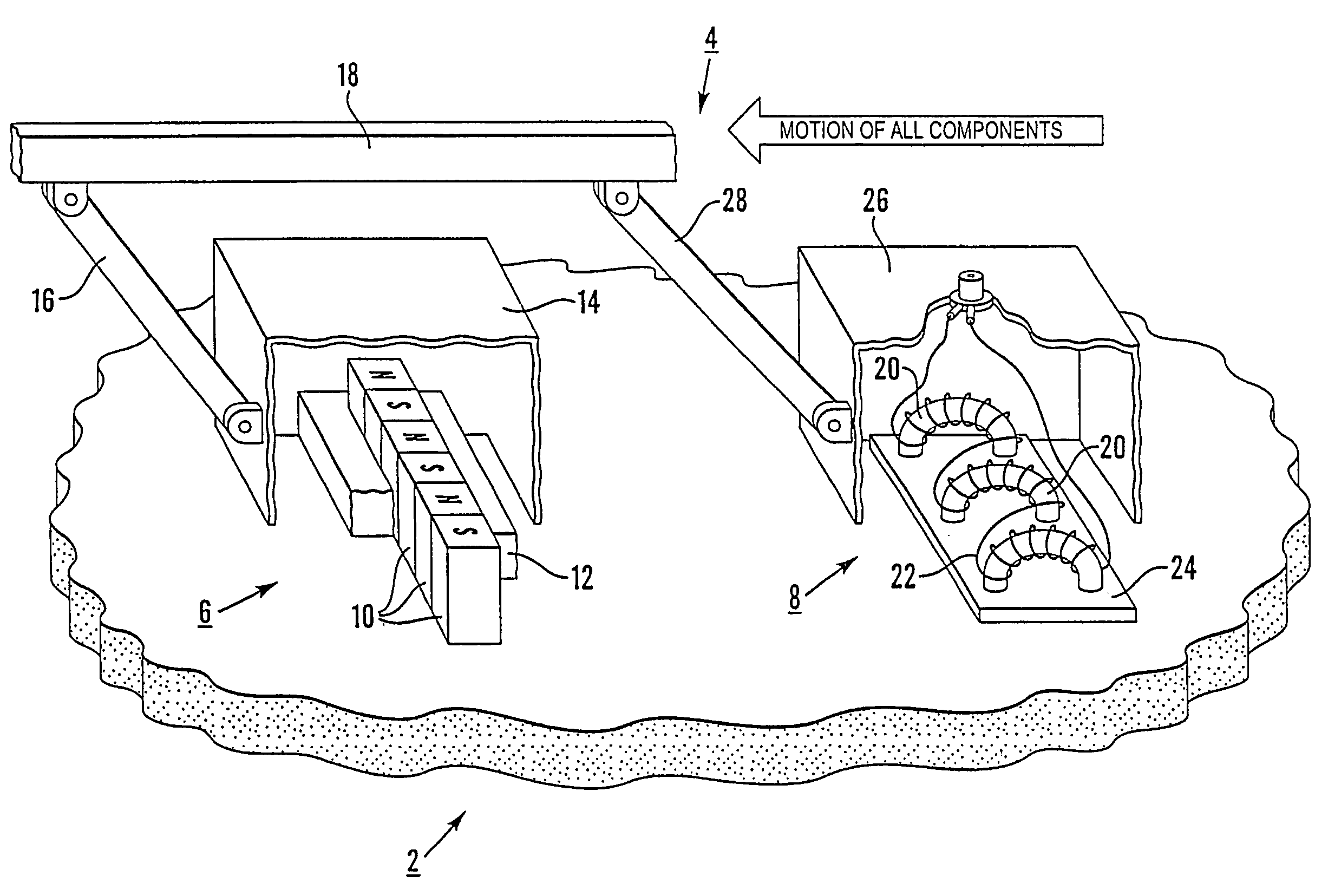
Electromagnetic acoustic transducers
InactiveUS7024935B2Design moreRemarkable effectAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSamplingElectricitySurface layer
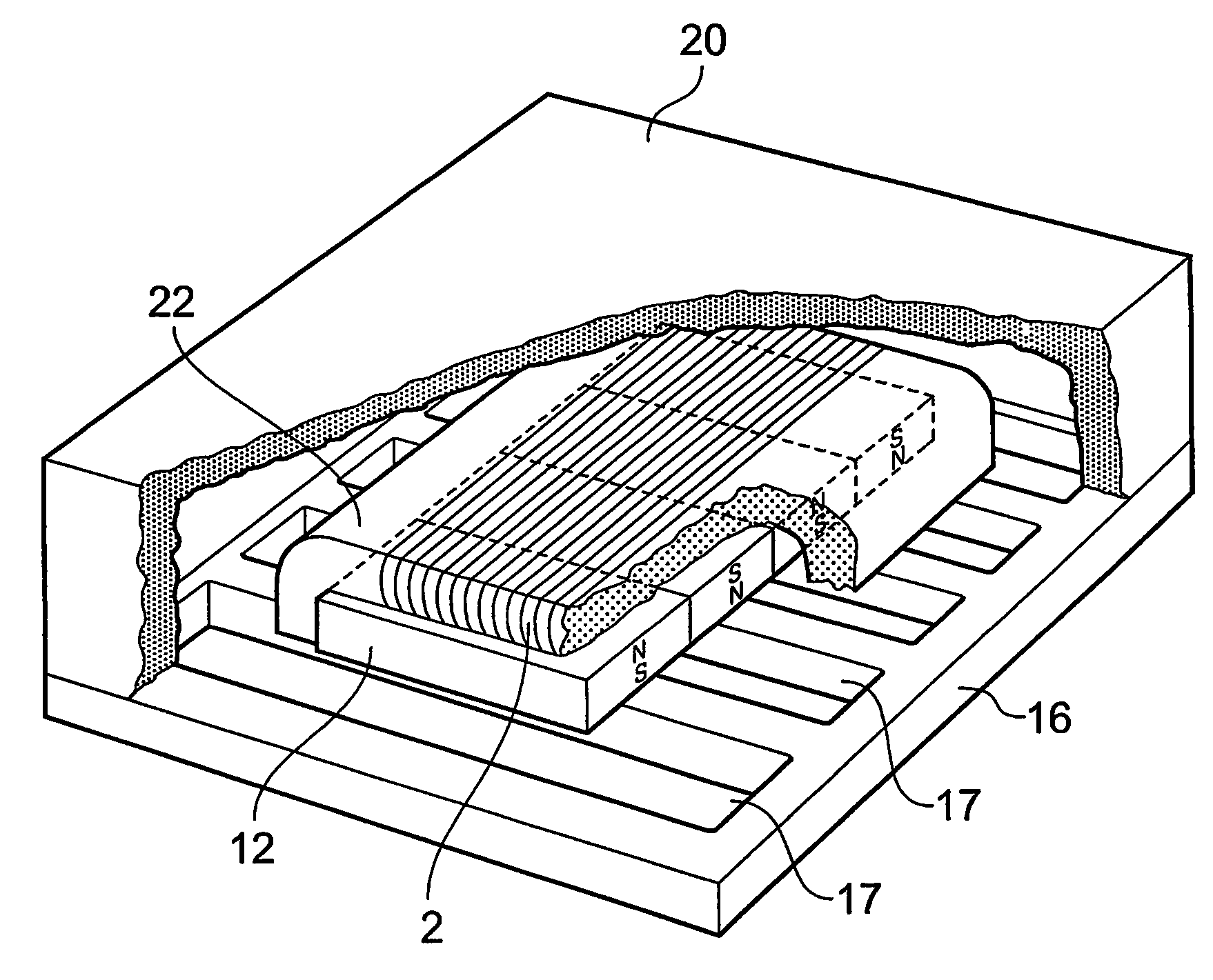
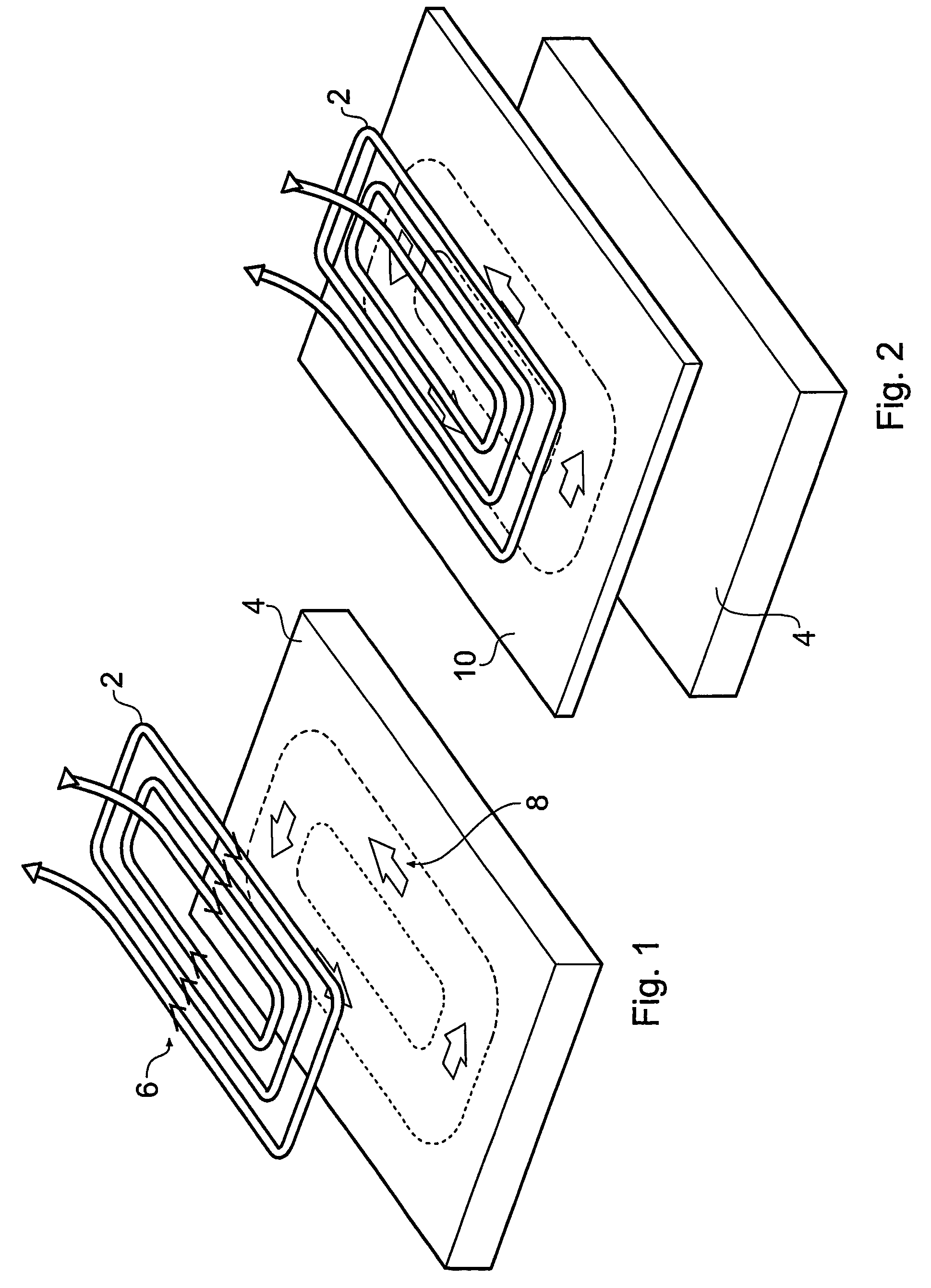
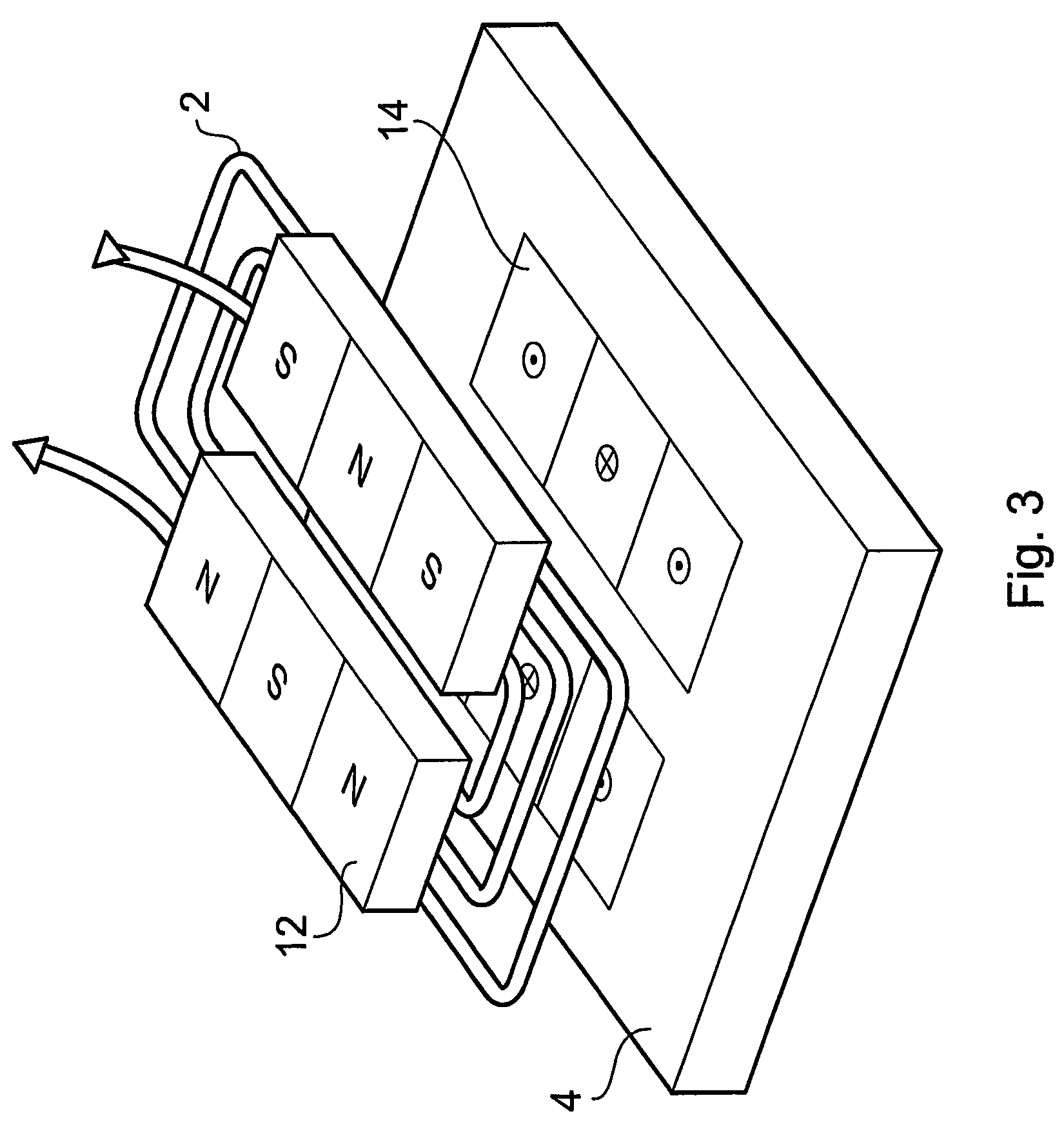
An electromagnetic acoustic transducer for exciting ultrasound in a ferromagnetic material under test (2), includes a magnetic unit (6) arranged to be moved relative to the material under test (2) to magnetize a surface layer of the material, and an electrical winding (8) supplied by an alternating current source, the magnetic unit (6) and the electric winding (8), in use, being applied in sequence to the material under test (2) whereby the electrical winding (8) is positioned adjacent the material subsequent to magnetization thereof by the magnetic unit (8), the alternating magnetic flux created by the winding (8) interacting with the remanent magnetization of the material to create ultrasonic vibration of the material.
Owner:PII LIMITED
Ultrasonic flaw detection method and ultrasonic flaw detection equipment
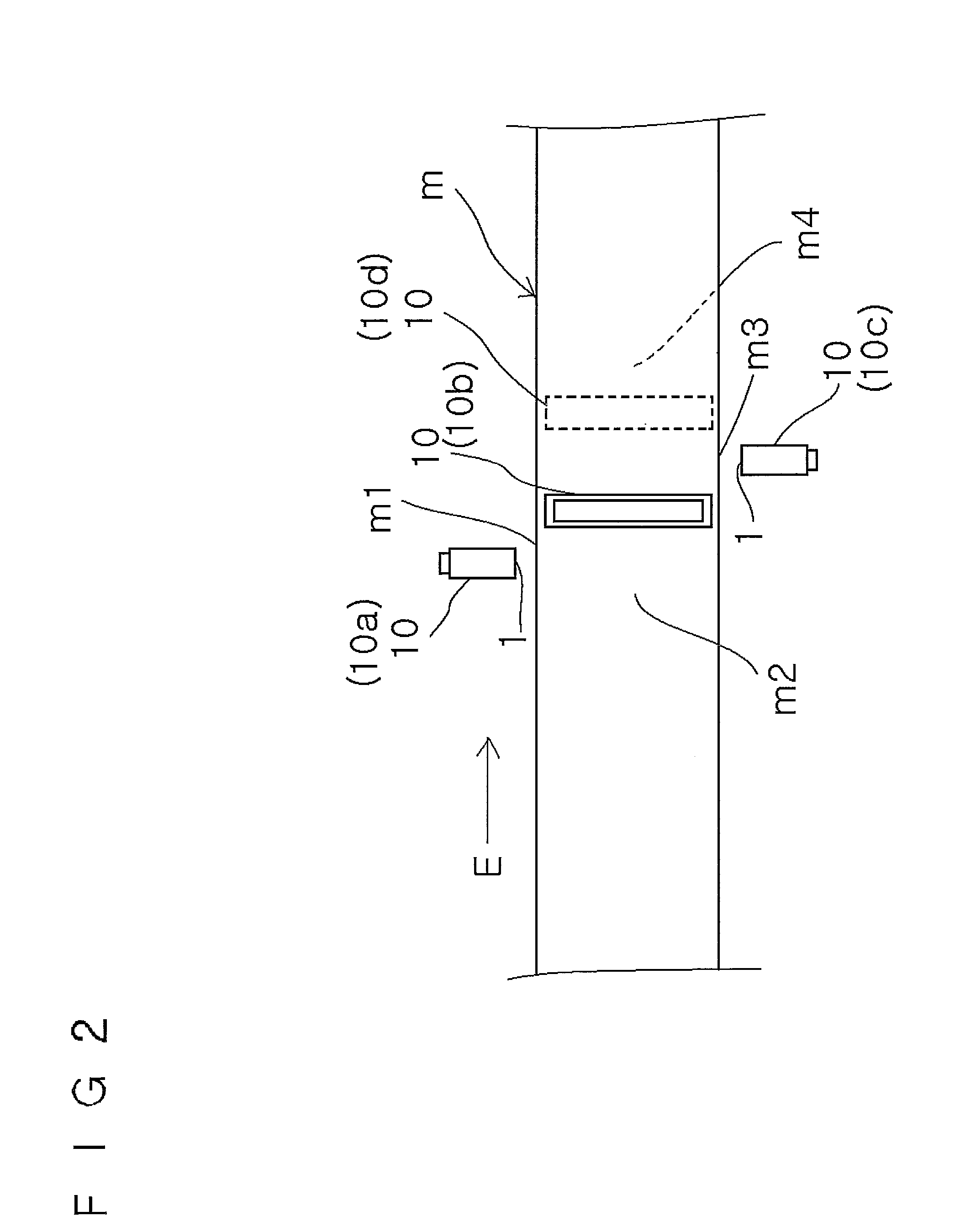
ActiveUS20100212430A1Reduce dead zoneReliable detectionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansTransducerUltrasound
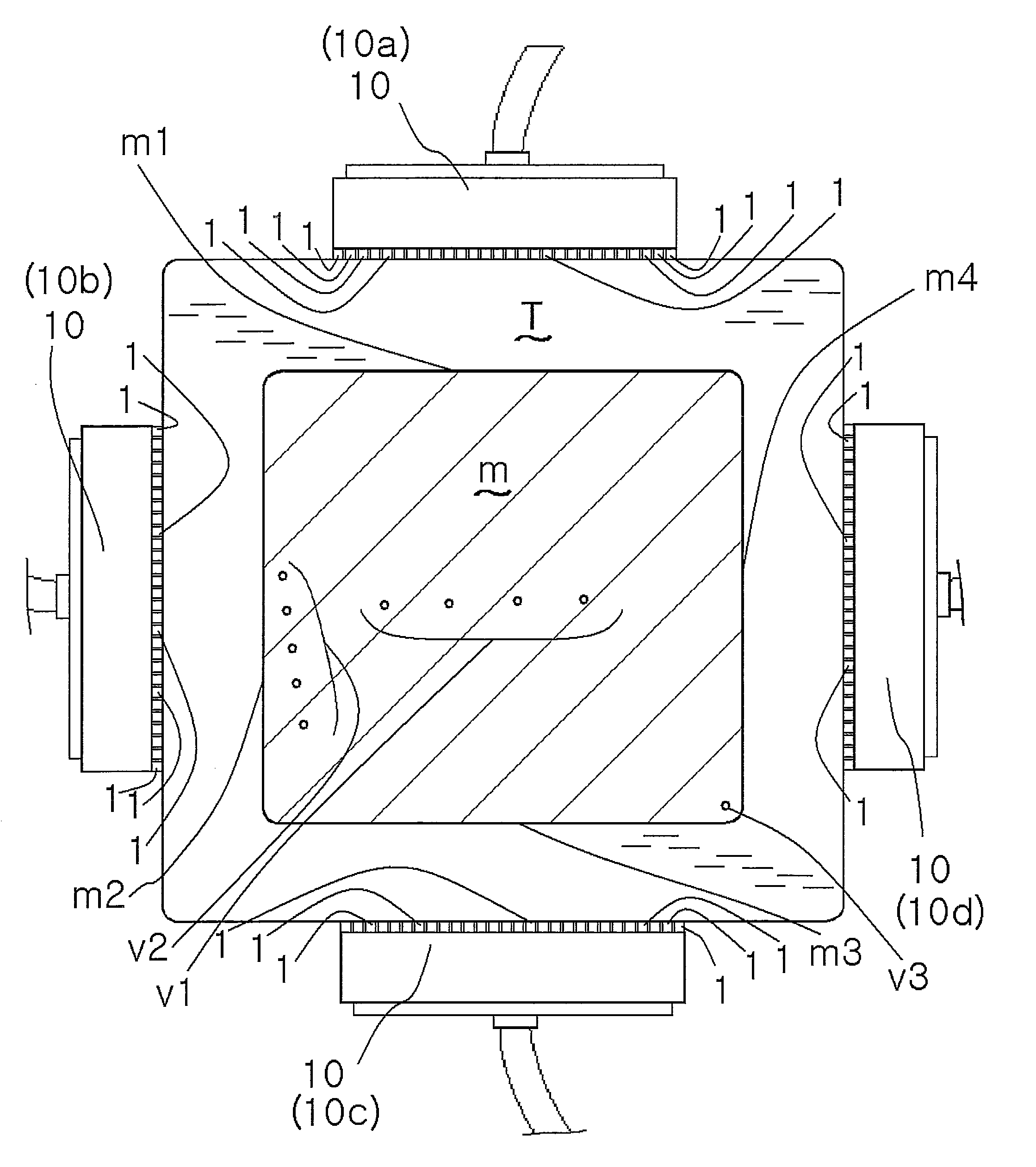
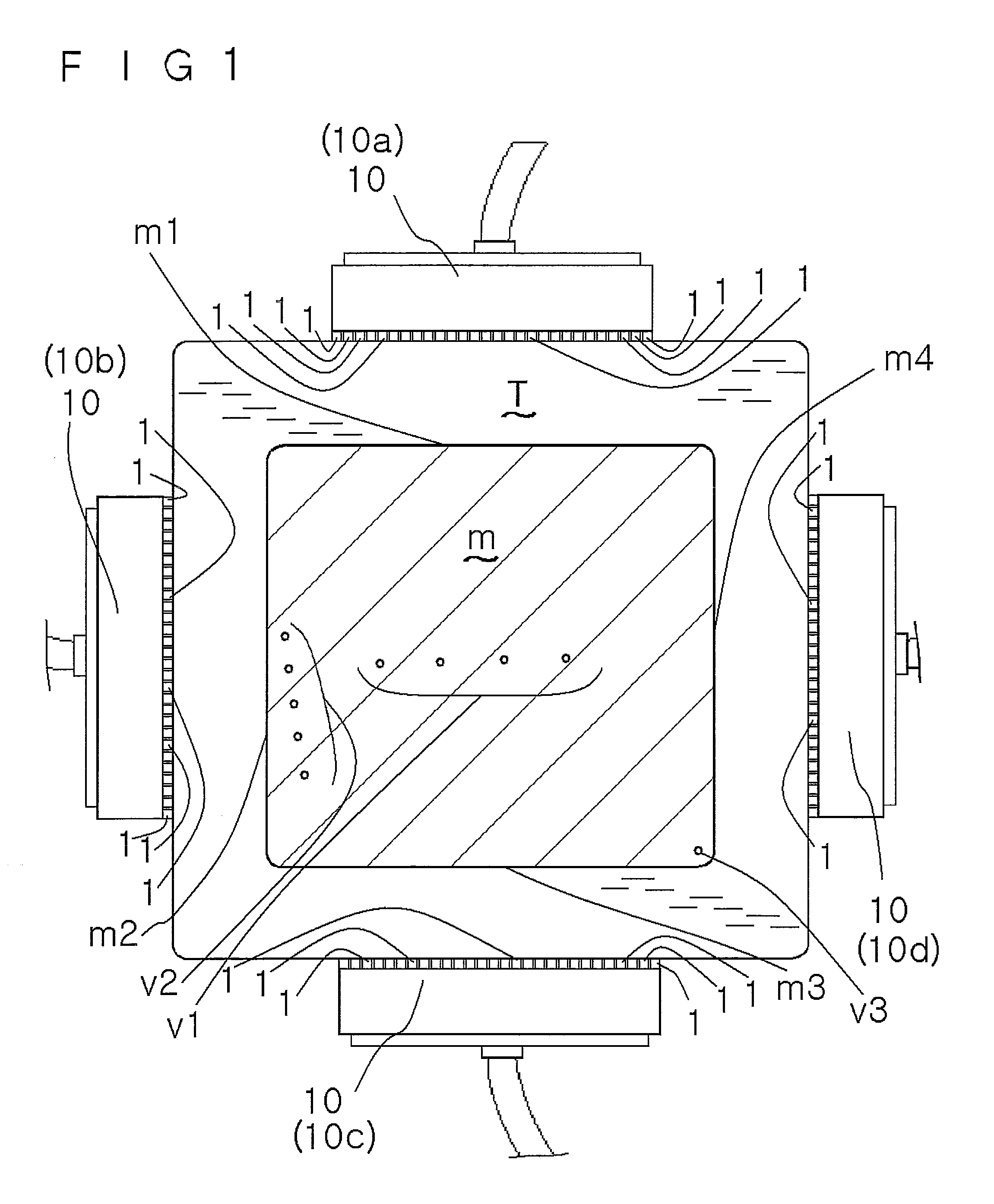
Equipment of the invention uses a volume focusing flaw detection method. In a sectional view of a material m being tested, a plurality of transducers 1 . . . 1 of one of array probes 10 are arranged along one side of a rectangular shape of the material being tested, and a plurality of transducers 1 . . . 1 of the other of the array probes 10 are arranged along one of sides adjacent to the one side. An exciting unit makes each array probe emit ultrasonic waves by a vertical flaw detection method and an oblique flaw detection method in such a way as to allow the ultrasonic waves to enter the material being tested from each position on an incident side, which is a side along which the array is placed, as a result of the plurality of transducers being vibrated once, makes the ultrasonic waves allowed to enter by the vertical flaw detection method reach a counter side facing the incident side, and makes the ultrasonic waves allowed to enter by the oblique flaw detection method reach one of adjacent sides adjacent to the incident side, and the exciting unit sets no actual focus of the ultrasonic waves in the material being tested.
Owner:KRAUTKRAMER JAPAN
Method of inspecting food stuffs and/or associated packaging
InactiveUS7107852B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationMaterial under test
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
Method for inspecting a channel using a flexible sensor
InactiveUS7183764B2Easy to insertReduce mechanical stressMagnetic property measurementsFluid pressure measurementLimited accessMaterial under test
Described are methods for pressurizing elastic support structures or balloons in sensor probes used for the inspection of components having areas of limited access. When inflated, the balloons press flexible sensors against the surface of the material under test. When deflated, the balloons permit easier insertion of the probes into the component and reduce the mechanical stresses on the sensors, thereby extending the sensor lifetime. By sequentially partially inserting the sensor into a limited access area from either side of the limited access area and scanning in opposite directions, the entire surface of the test material can be inspected.
Owner:JENTEK SENSORS
Nondestructive testing method for metal material fracture toughness
InactiveCN103063508ANo damageThe detection process is fastStrength propertiesMaterial under testMetallic materials
The present invention discloses a nondestructive testing method for metal material fracture toughness, and the method mainly includes: performing Charpy impact tests to samples of different damage degrees to obtain the brittle transition temperatures of the samples; performing ultrasonic secondary harmonic measurement to the samples of each type of the damage degrees to obtain the second harmonic ultrasound nonlinearity parameter normalized value of the samples of the type of the damage degree; obtaining the fracture strength factor of the samples of each type of the damage degrees via the fracture toughness tests or by reference of fracture empirical formulas, and making a calibration curve for nondestructive testing fracture toughness; performing ultrasonic secondary harmonic measurement to a metal material under test to obtain the second harmonic ultrasound nonlinearity parameter normalized value of the metal material under test; and obtaining the fracture toughness value of the metal material under test by using the calibration curve. The nondestructive testing method for metal material fracture toughness of the invention is capable of performing testing and evaluation of material fracture toughness of in-service metallic components, and providing a reliable basis for the security service of the metal materials.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
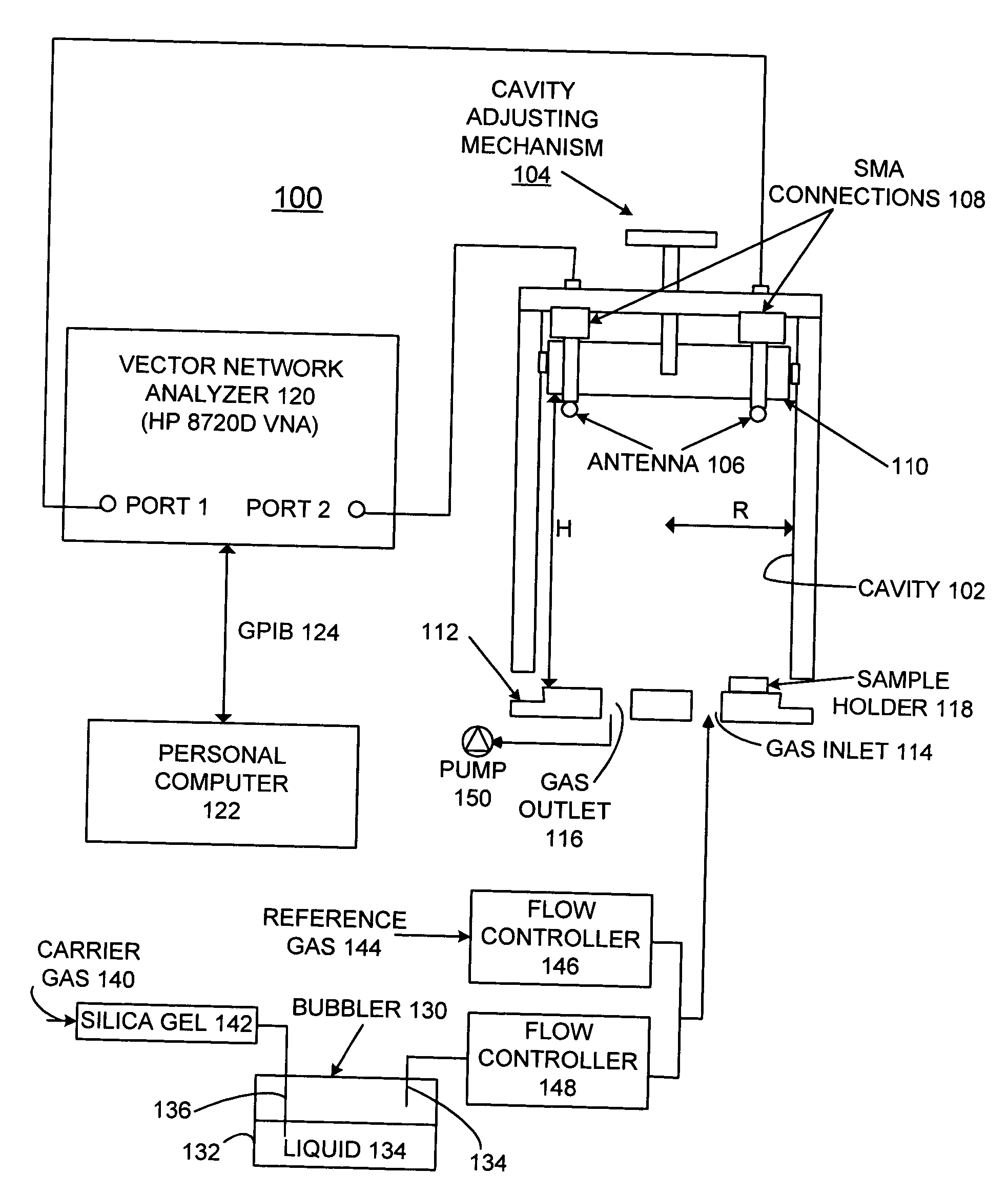
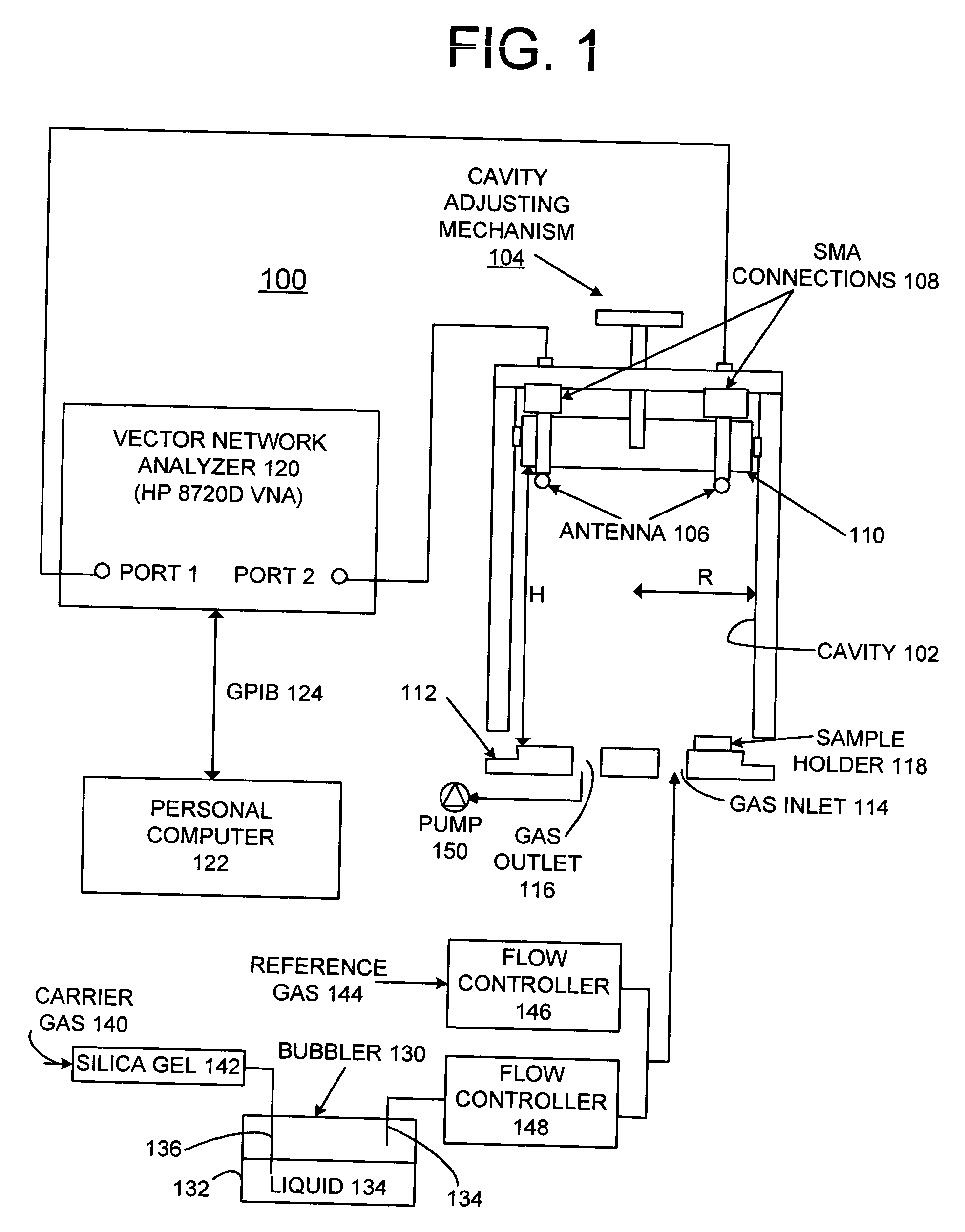
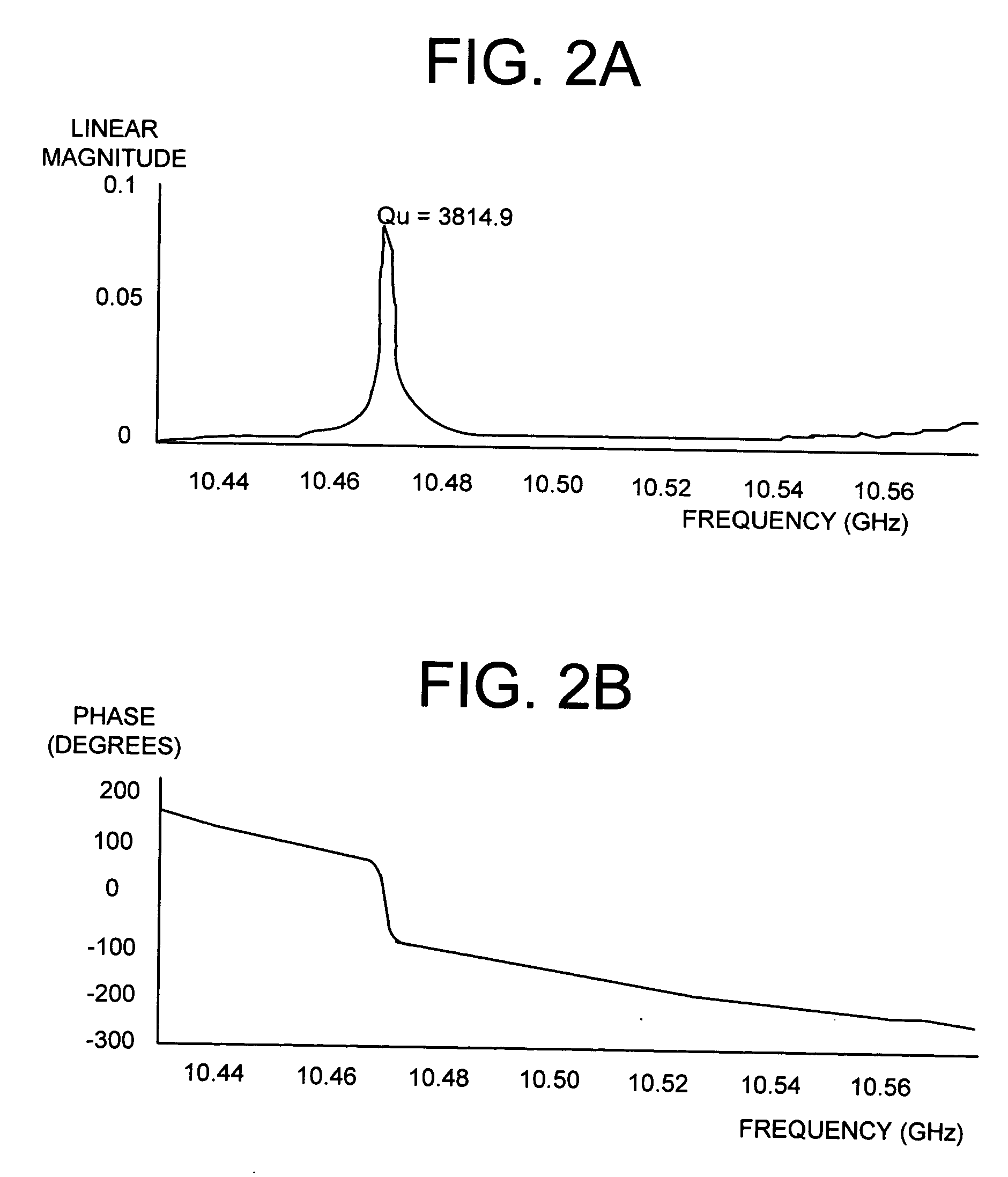
System and method of testing complex dielectric constant of material based on gradient coaxial resonator
ActiveCN108594023AReduce sizeSave materialDielectric property measurementsResonant cavityCoaxial resonators
The invention provides a system and method of testing complex dielectric constant of a material based on a gradient coaxial resonator. The system comprises the gradient coaxial resonator and a coupling device. The method comprises the steps: 1) testing and recording resonant frequency f0 and quality factor Q0 in a corresponding cavity working mode when no sample is loaded; 2) measuring diameter DSand thickness dS of a sample under test, placing the sample in a sample area, and testing and recording resonant frequency fS and quality factor QS in the corresponding cavity working mode when the sample is loaded; 3) using resonator perturbation theory to calculate complex dielectric constant of the material under test. The system and method have the advantages that high-precision testing of complex dielectric constant at normal temperature is achieved for a microwave dielectric material, required cavity size and sample size for low frequency testing can be reduced, a sealed-bottom tube clamp can also be used to test the complex dielectric constant of liquid and powdery materials.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
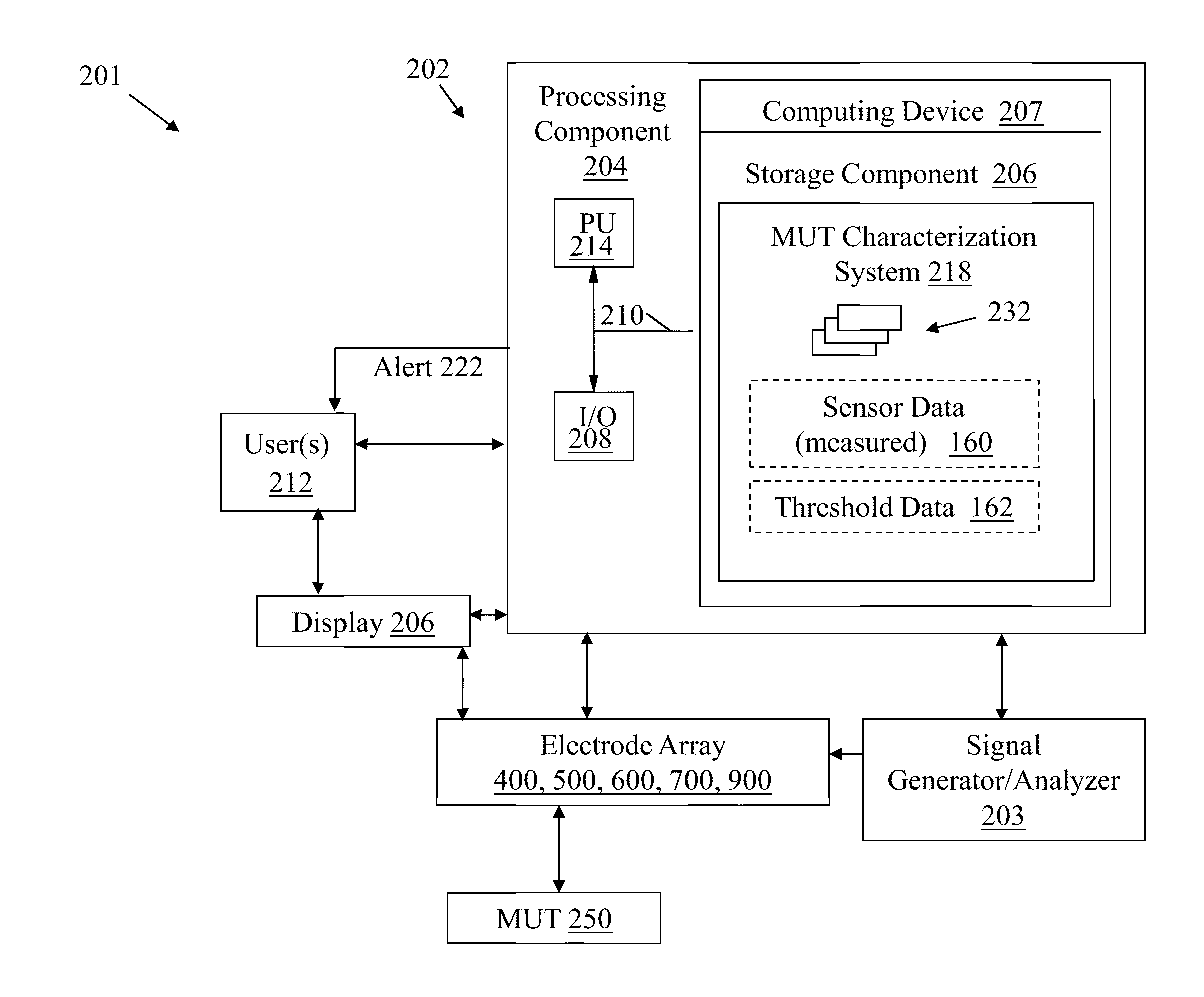
In-process material characterization
ActiveUS20130307564A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis using microwave meansMaterial under testElectromagnetic field
Various embodiments include solutions for in-process material characterization. Various particular embodiments include a computer-implemented method including: providing instructions for transmitting oscillating electromagnetic field signals to a material under test (MUT); obtaining a return signal associated with the transmitted oscillating electromagnetic field signals; comparing the return signal with the oscillating electromagnetic field signals to determine a difference in an aspect of the return signal and the aspect of the oscillating electromagnetic field signals; comparing the difference in the aspect to a predetermined threshold; and determining a characteristic of the MUT based upon the compared difference.
Owner:TRANSTECH SYST
Material deformation measurement method and device based on laser marking automatic tracking
InactiveCN102261894AOvercoming fragileOvercome the reverse phenomenonUsing optical meansMaterial under testMotor controller
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method of inspecting food stuffs and/or associated packaging
InactiveUS20050155430A1Vibration measurement in fluidMagnetic property measurementsSonificationMaterial under test
A system to perform measurements on liquids, meat, viscous sugar or starch-based materials, and other foodstuffs using air-coupled ultrasound is provided. The technique uses ultrasonic transducers (advantageously capacitive transducers with polymer membranes), to generate ultrasonic signals in air, and to receive these signals after they have passed through the material under test. An ultrasonic pulse-compression process is then applied to increase the sensitivity of signals transmitted through the materials.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK
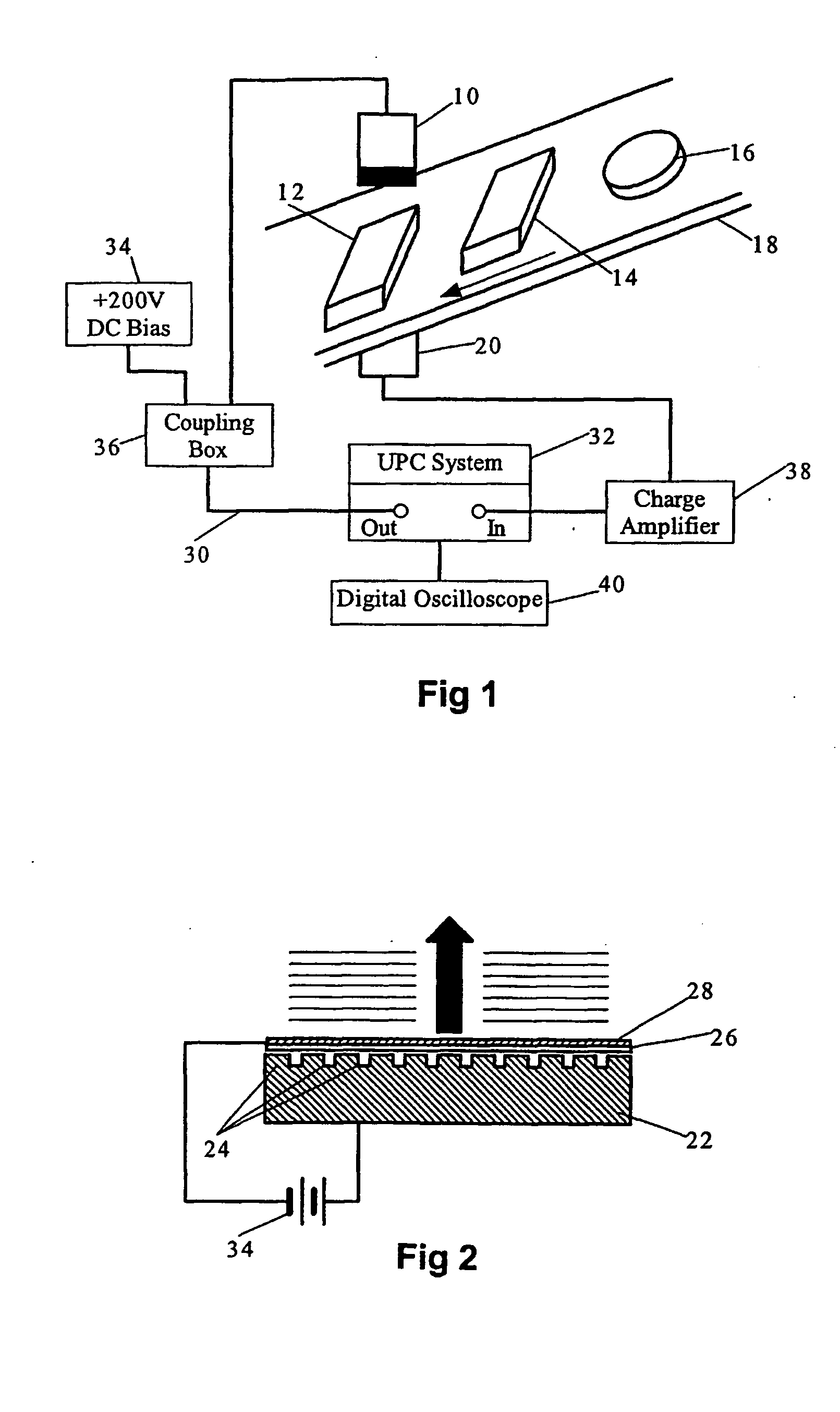
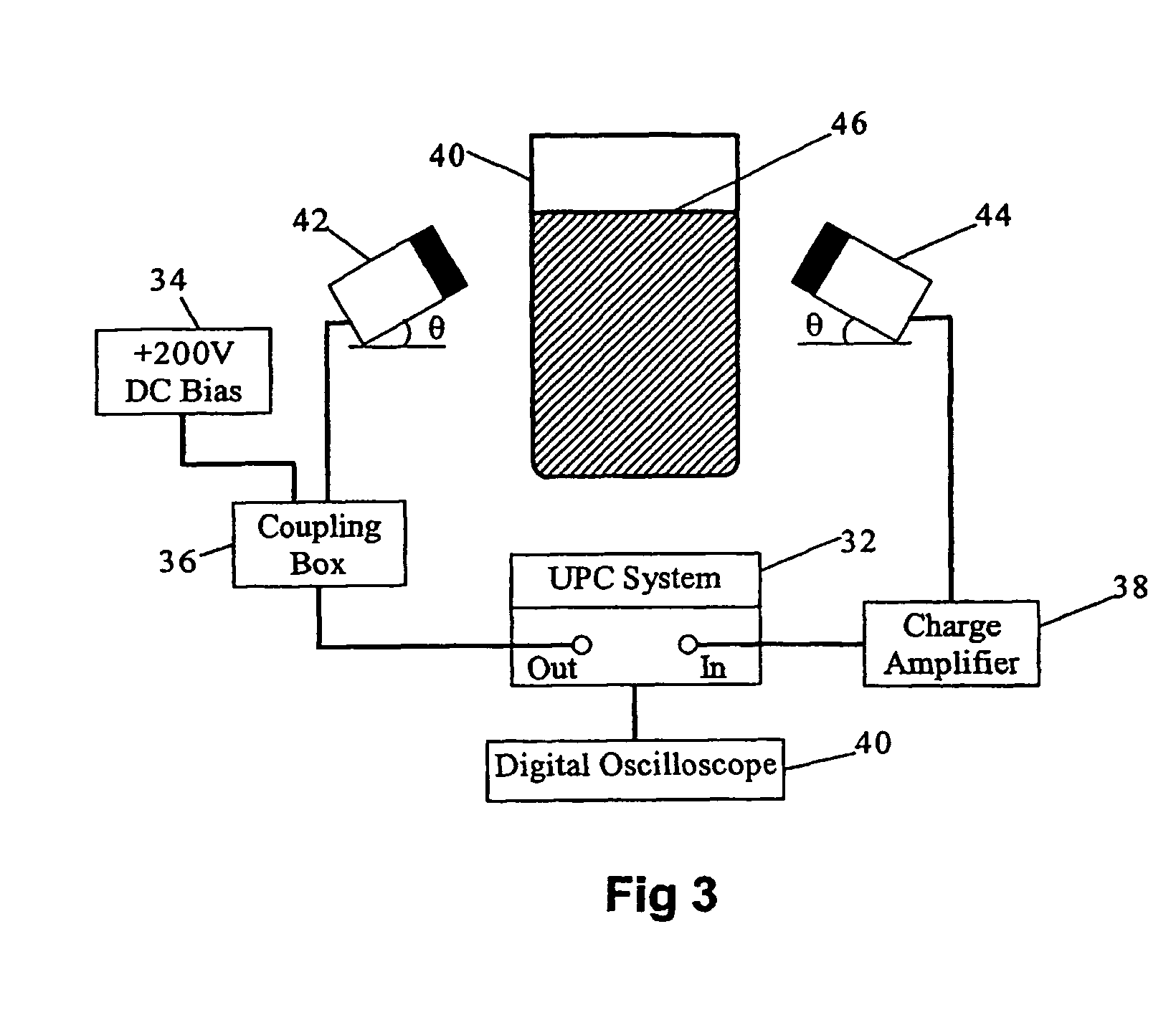
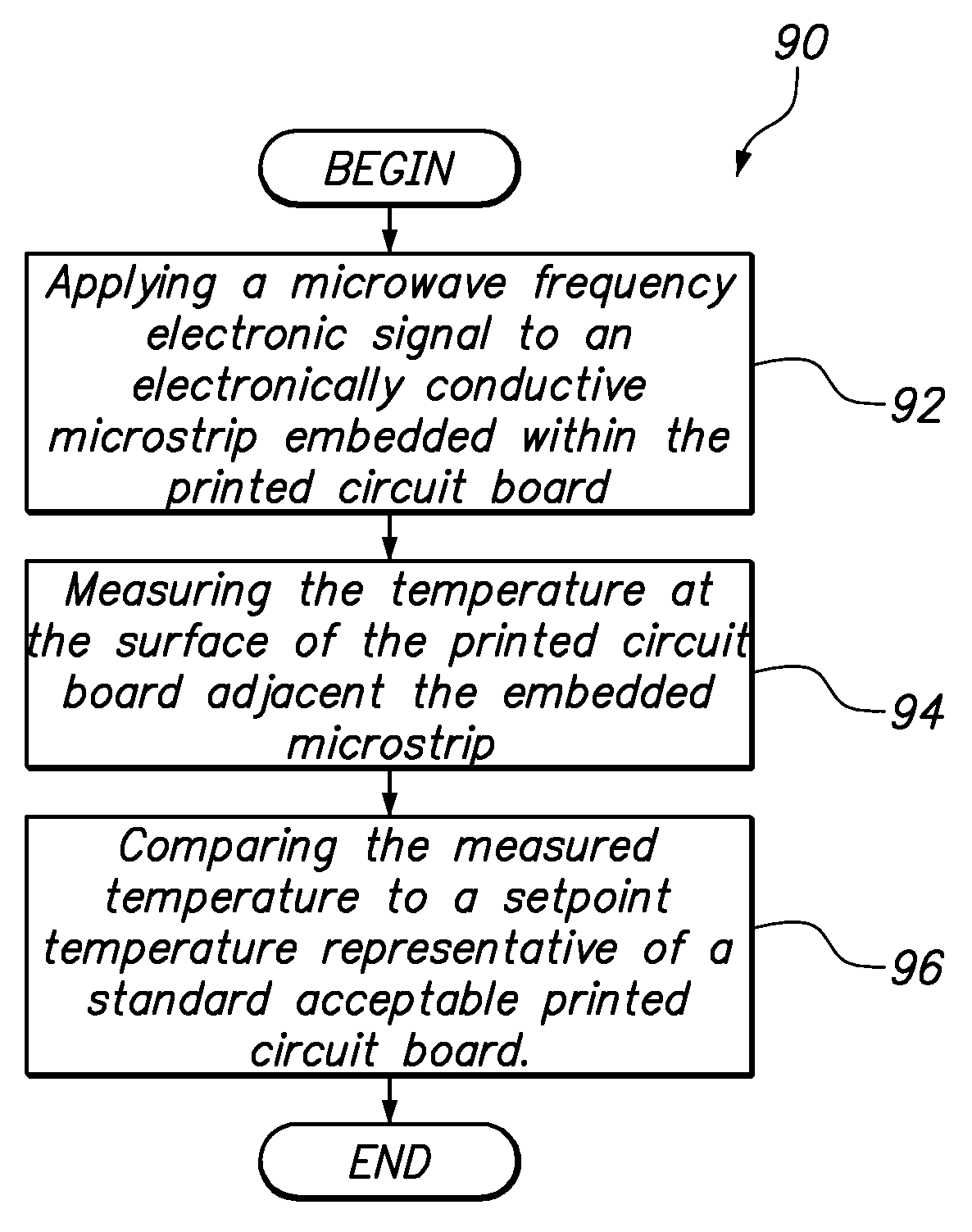
Method for Validating Printed Circuit Board Materials for High Speed Applications
InactiveUS20090102487A1Radiation pyrometryResistance/reactance/impedenceValidation methodsMaterial under test
A method for testing a printed circuit board to determining the dielectric loss associated with the circuit board material relative to a standard. Dielectric losses in the material generate heat when a high frequency electronic signal, such as a microwave frequency signal, is communicated through a microstrip that is embedded within the printed circuit board. The temperature or spectrum at the surface of printed circuit board is measured and compared against the temperature or spectrum of the standard to determine whether the material under test is acceptable. While various temperature measurement devices may be used, the temperature is preferably measured without contacting the surface, such as using an infrared radiation probe.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electromagnetic acoustic transducer
ActiveUS7406873B2Wide choiceThickness wideAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationSonificationMaterial under test
Owner:PII LIMITED
High speed analyzer using near infrared radiation transmitted through thick samples of optically dense materials
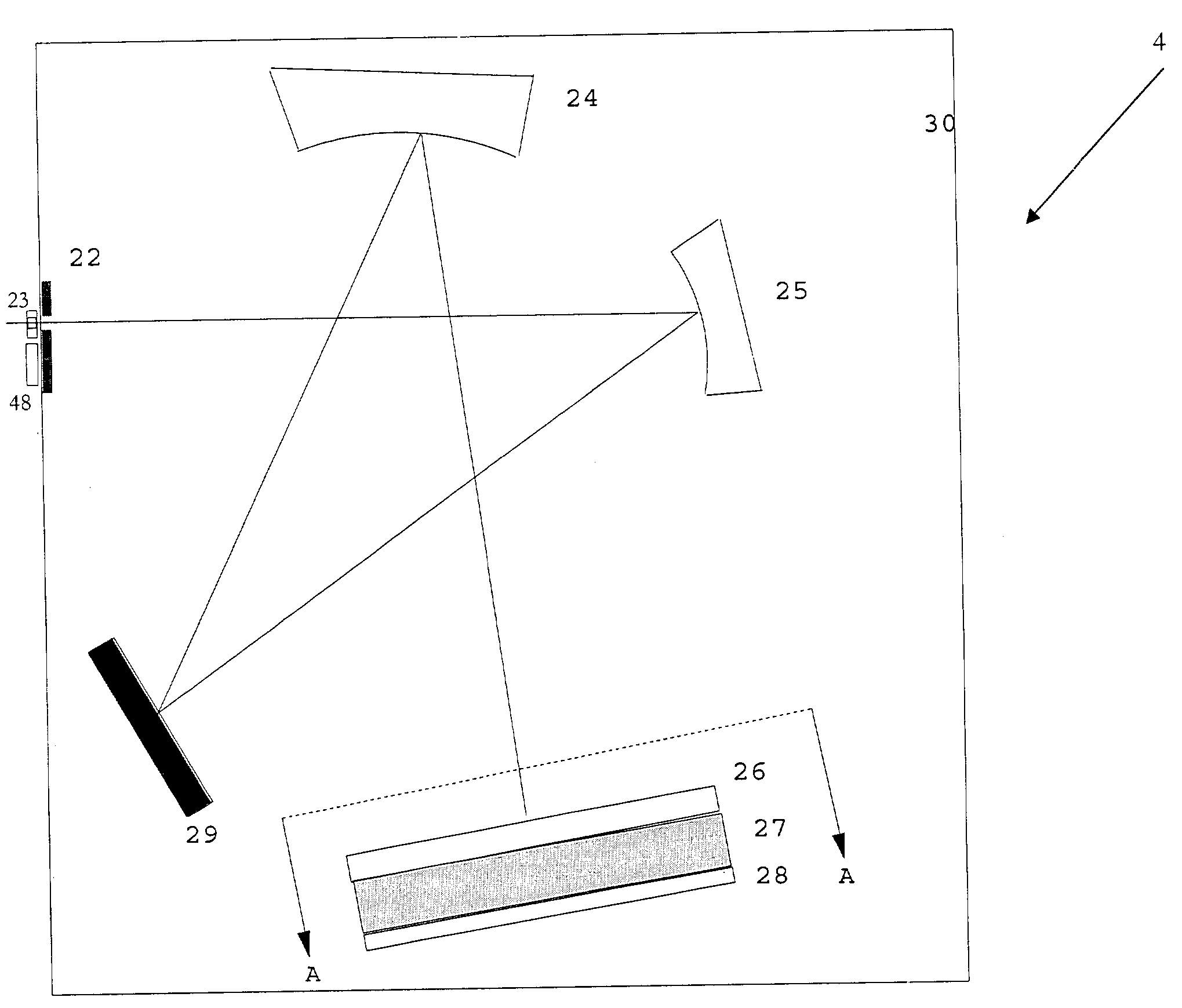
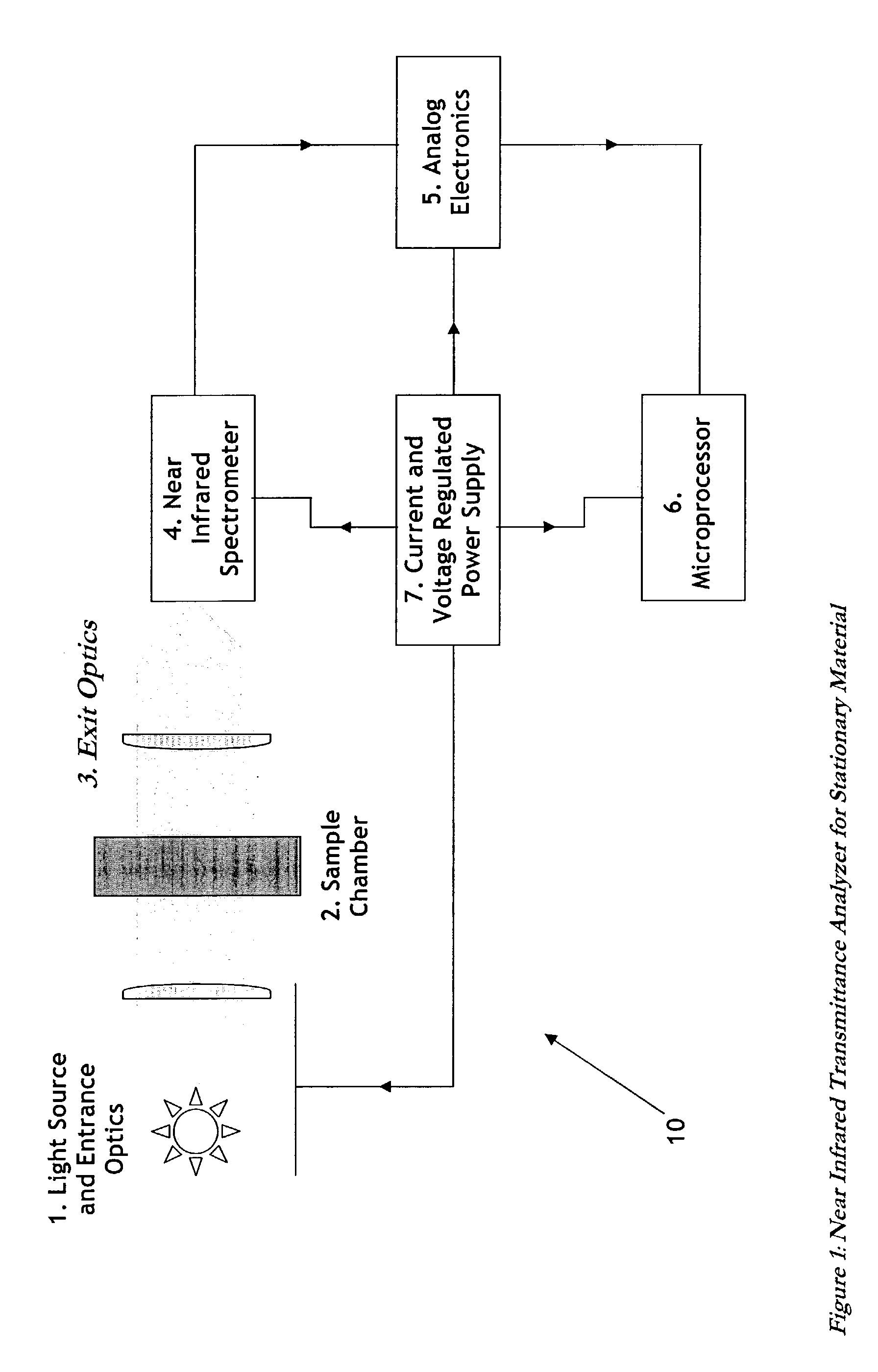
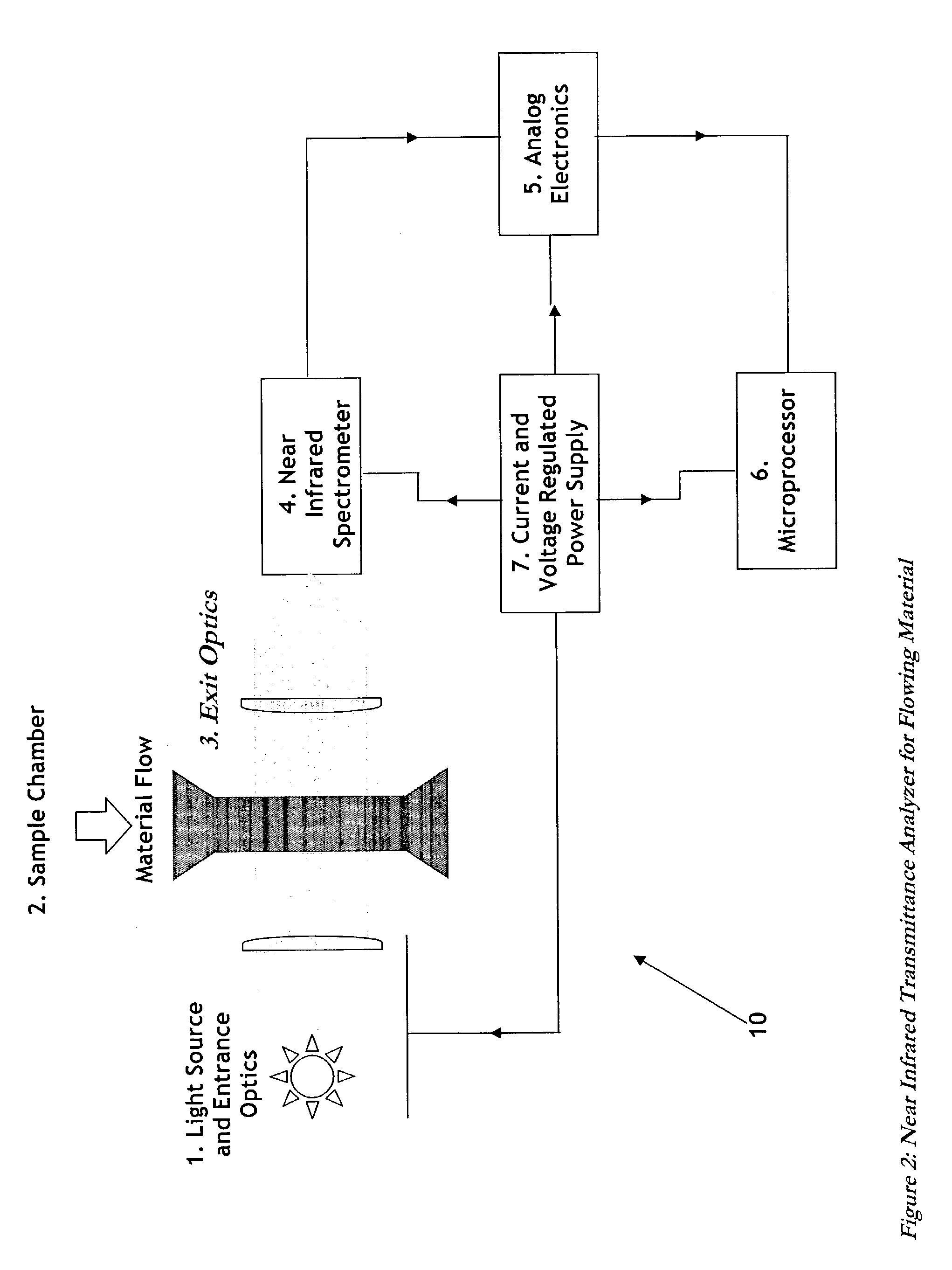
InactiveUS7087901B2Shorten the timeHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMaterial under testLight spectrum
The present invention relates to an instrument for measuring in relatively short periods of time concentrations of constituents in optically dense materials using the spectra near infrared radiation transmitted through thick samples of the material while the material is either stationary or flowing. The invention uses a broadband incandescent intensity stabilized light source combined with collimating optics to transmit a parallel beam of light through the material under test. The light transmitted through the material is then collected by a focusing lens and imaged onto a rectangular entrance slit of a special purpose spectrometer. This spectrometer has no moving parts and employs a fixed diffraction grating to physically spread the image of the entrance slit into a continuous range of wavelengths. A portion of the diffracted slit images covering the selected portion of the near infrared range is focused onto an array of individual rectangular photodiodes. By using relatively large area photodiodes and a relatively small number of photodiodes, high sensitivity is achieved and low intensity radiation levels can be measured quickly. By using a relatively narrow spectral range, medium resolution can be achieved. The outputs of each photodiode, or the outputs of a selected number of the photodiodes, are fed into current to voltage converters: either resistive (instantaneous) or preferred capacitive (integrating). Thus the outputs of all photodiodes are measured in parallel, which reduces the time to acquire the spectra. The gain of these current to voltage converters is programmable so that both high intensity and low intensity near infrared radiation levels can be measured without reducing the intensity of the radiation incident on the material under test and thereby eliminating the need for moving parts in the spectrometer. After the spectra are acquired, they are operated on by models developed to predict the percentages of various constituents in the material. These models are pre-calibrated using spectra obtained from materials of known concentrations and developed using chemometric, neural net, and / or genetic algorithms.
Owner:LEADER TECH
Fluorescence emissions detector
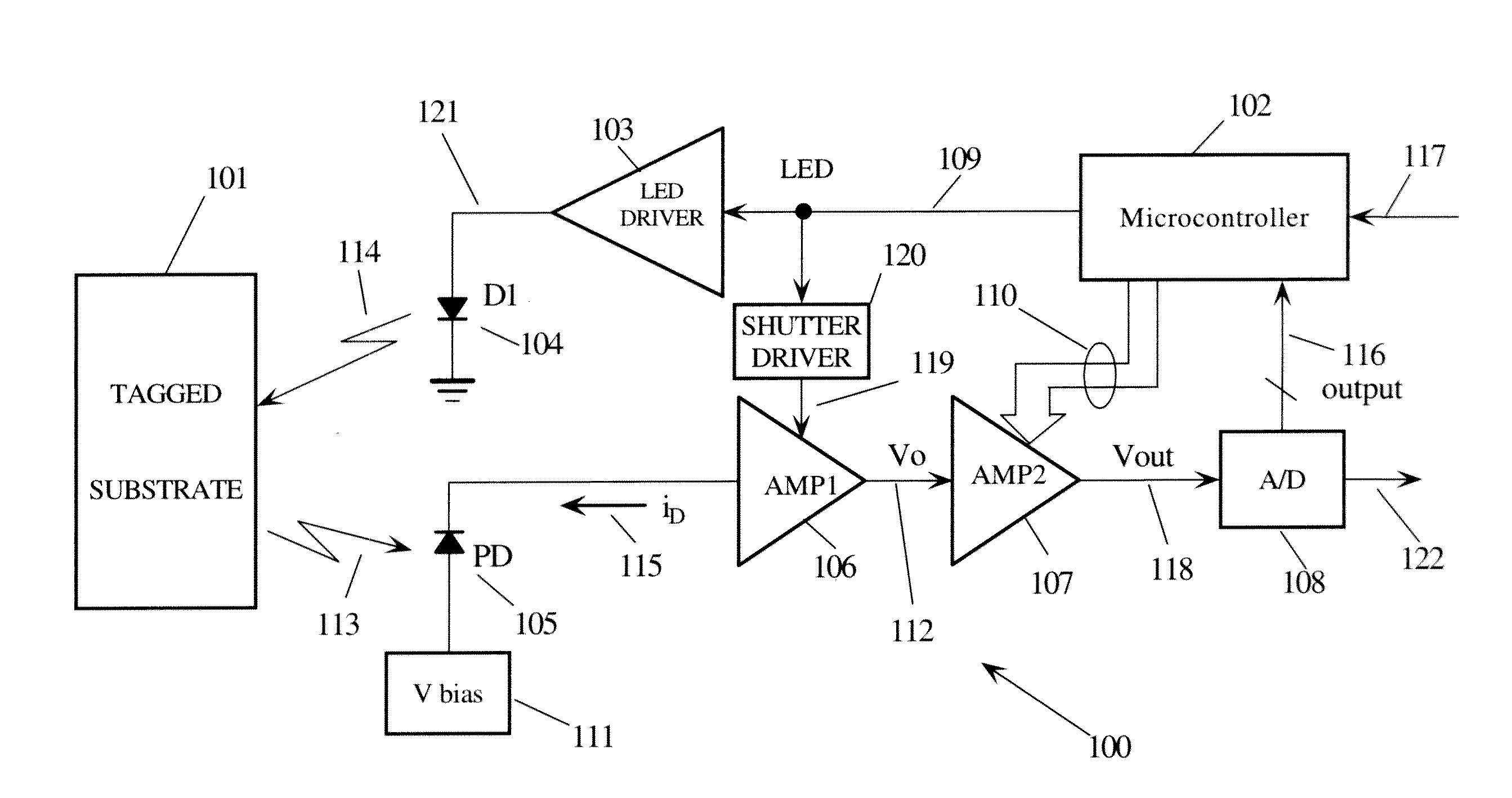
ActiveUS20120145924A1Minimize impactEffective capacitanceRaman/scattering spectroscopyBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPulse controlPower flow
A light source is gated ON and OFF in response to a pulsed signal. Photo emissions from the light source are coupled to a material under test. Resonant fluorescent emissions from the material are coupled to a photodiode. Current from the photodiode is coupled into an amplifier system comprising a first and second amplifier stages. The first amplifier stage is gated to a low gain when the light source is turned ON and the gain is increased when the light source goes from ON to OFF. The second amplifier stage has digitally programmable offset and gain settings in response to control signals. The output of the second amplifier stage is digitized by an analog to digital converter. A controller generates the pulse control signal and the control signals.
Owner:AUTHENTIX INC
Material failure prediction/stress/strain detection method and system using deformation luminescence
InactiveUS20080236294A1Expanded indicationsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationUsing optical meansPhoton emissionReal time analysis
A method and apparatus are provided for detecting strain, stress, fatigue and incipient failure in materials. A detector (e.g., a photomultiplier tube) is used to detect photonic emissions from a material under test. Data based on the detected photonic emissions is displayed in real time so as to enable real time analysis of the data in determining strain, stress, fatigue and / or incipient failure.
Owner:WOO GEOFFREY
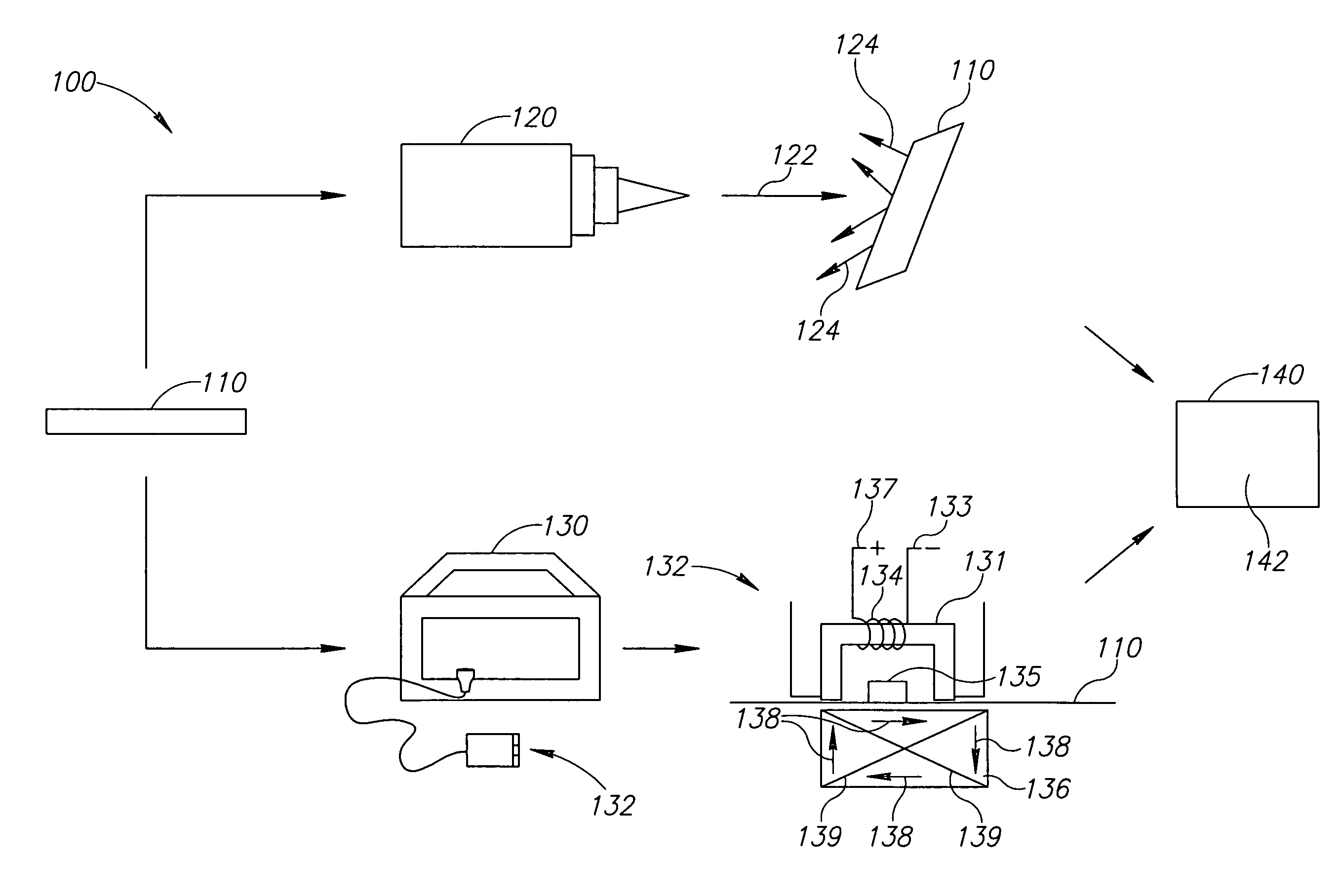
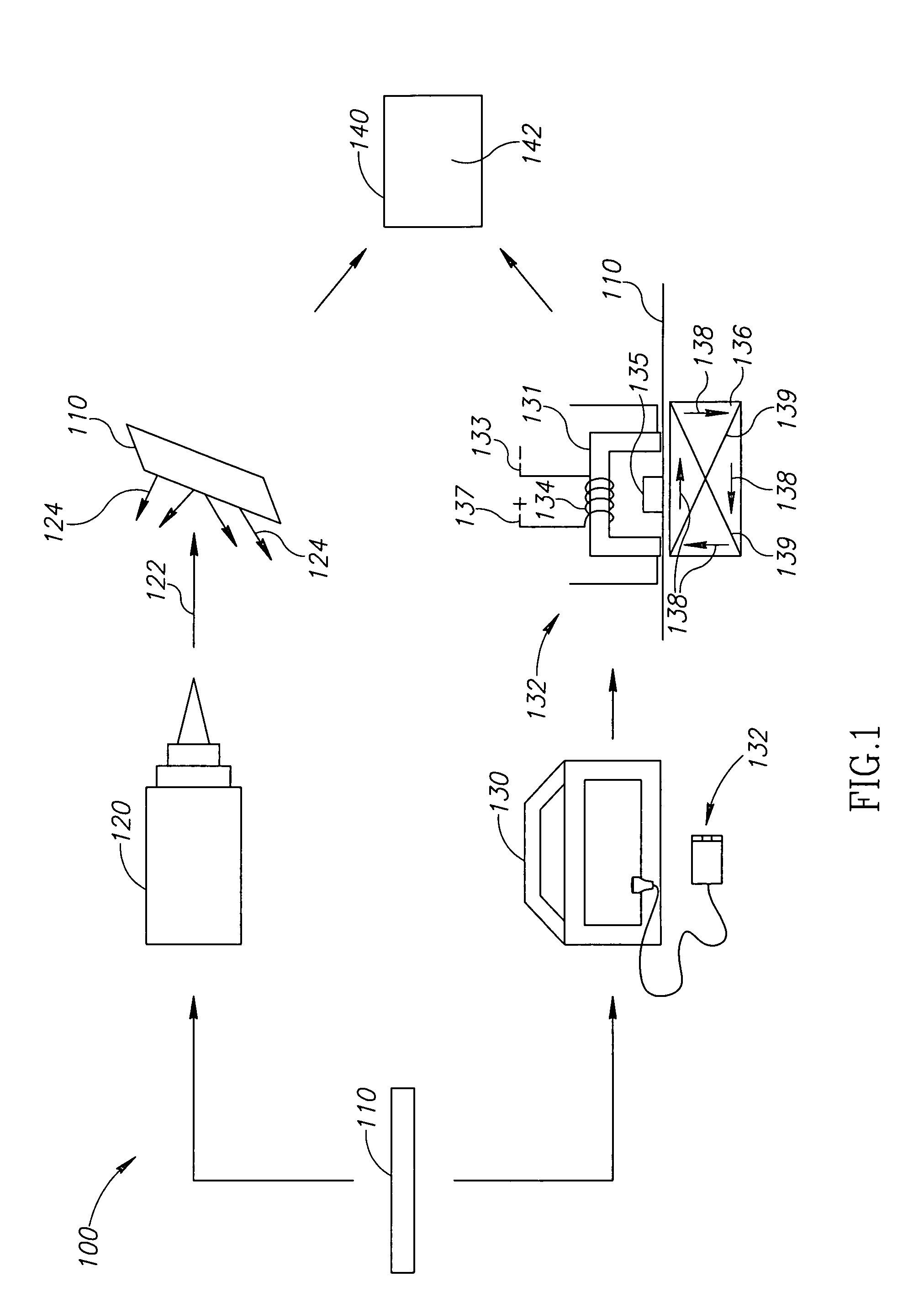
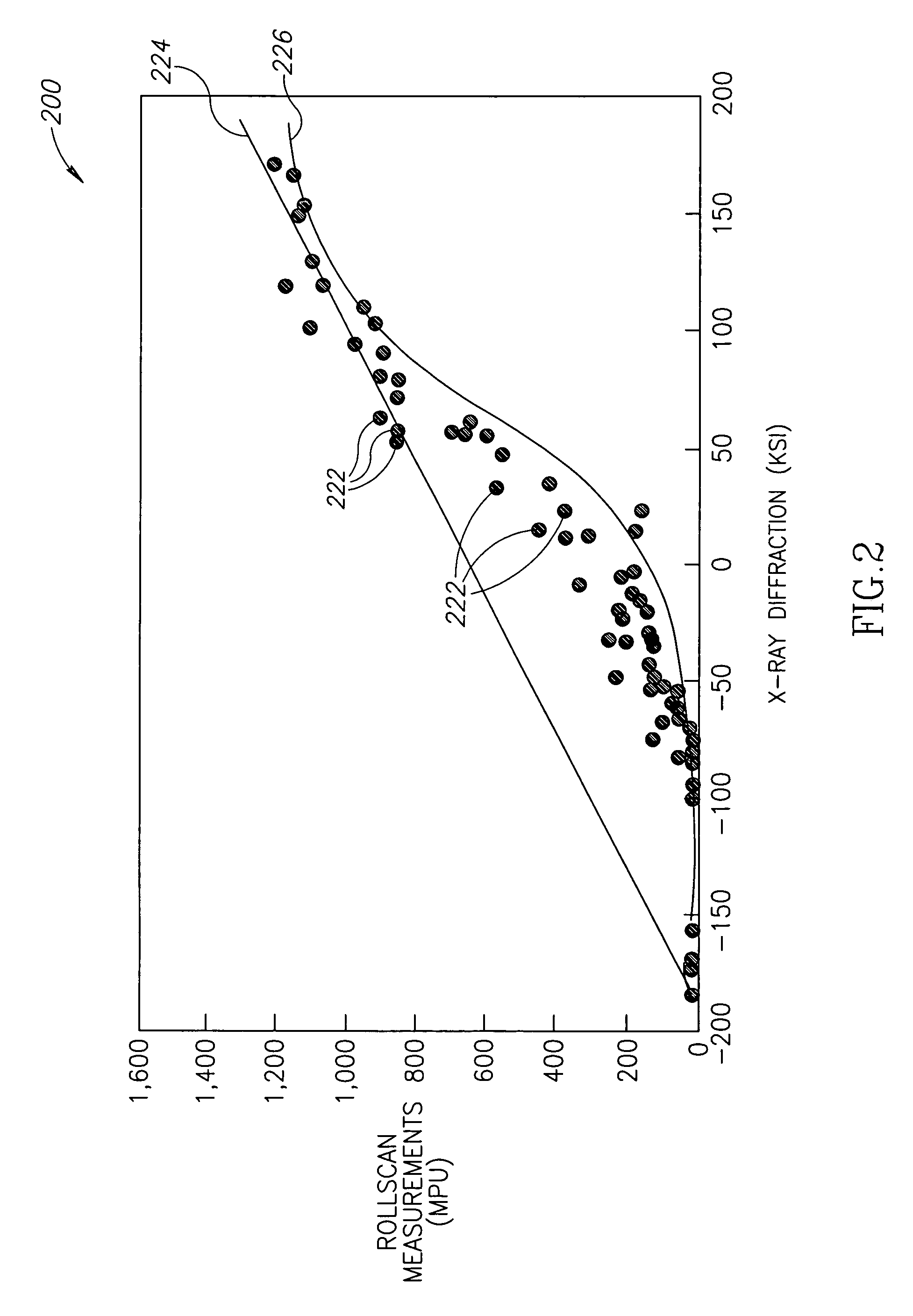
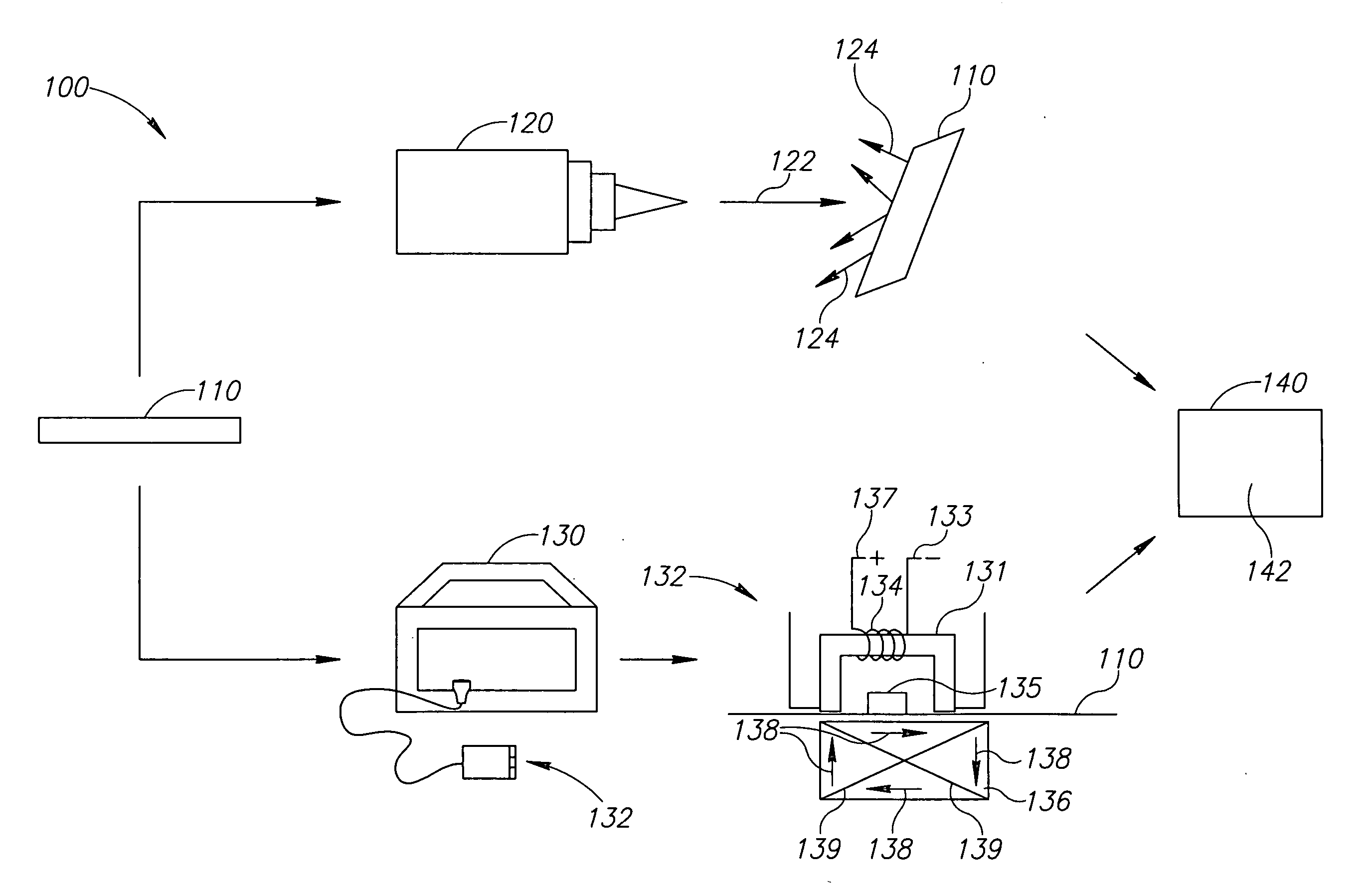
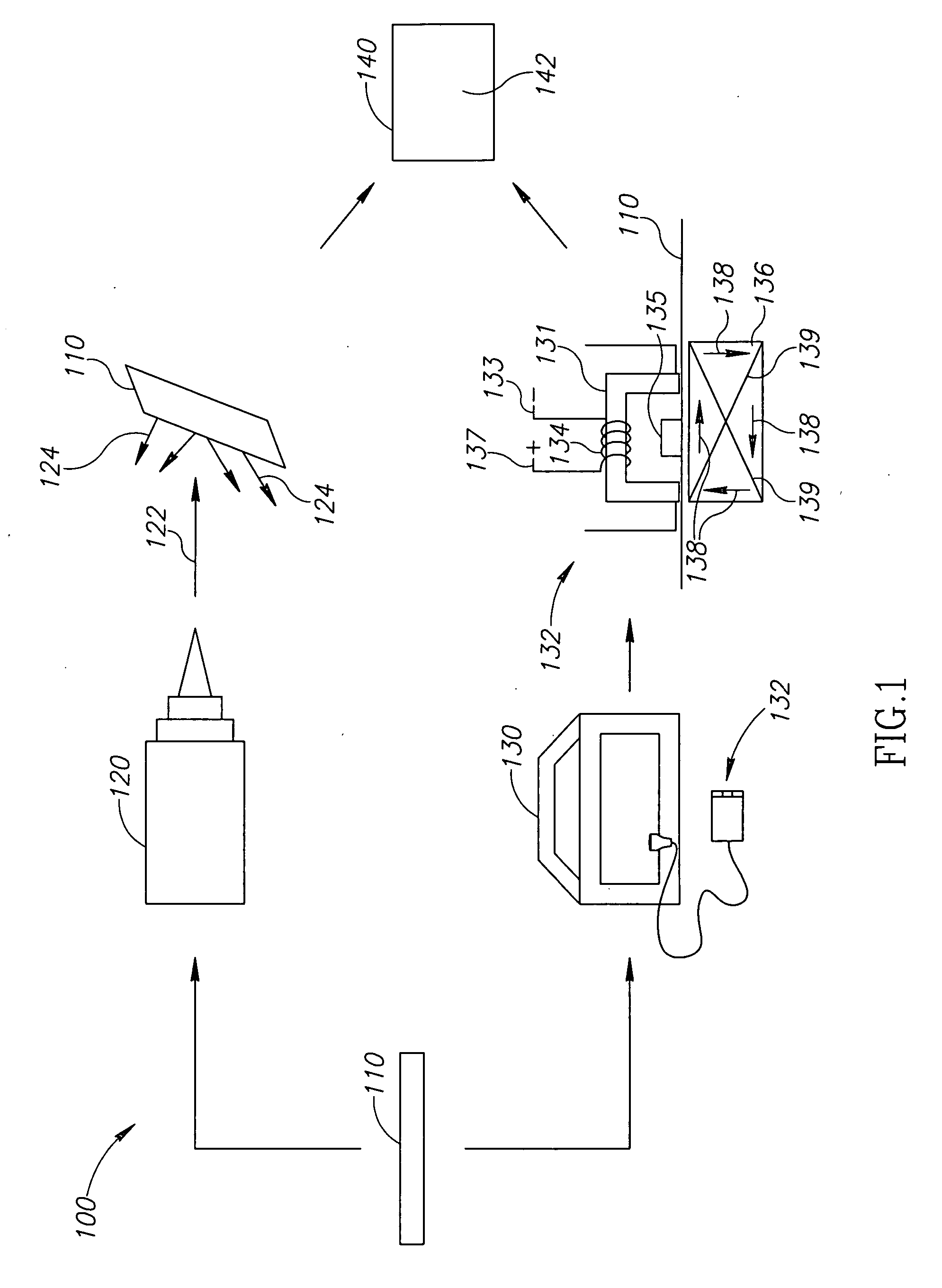
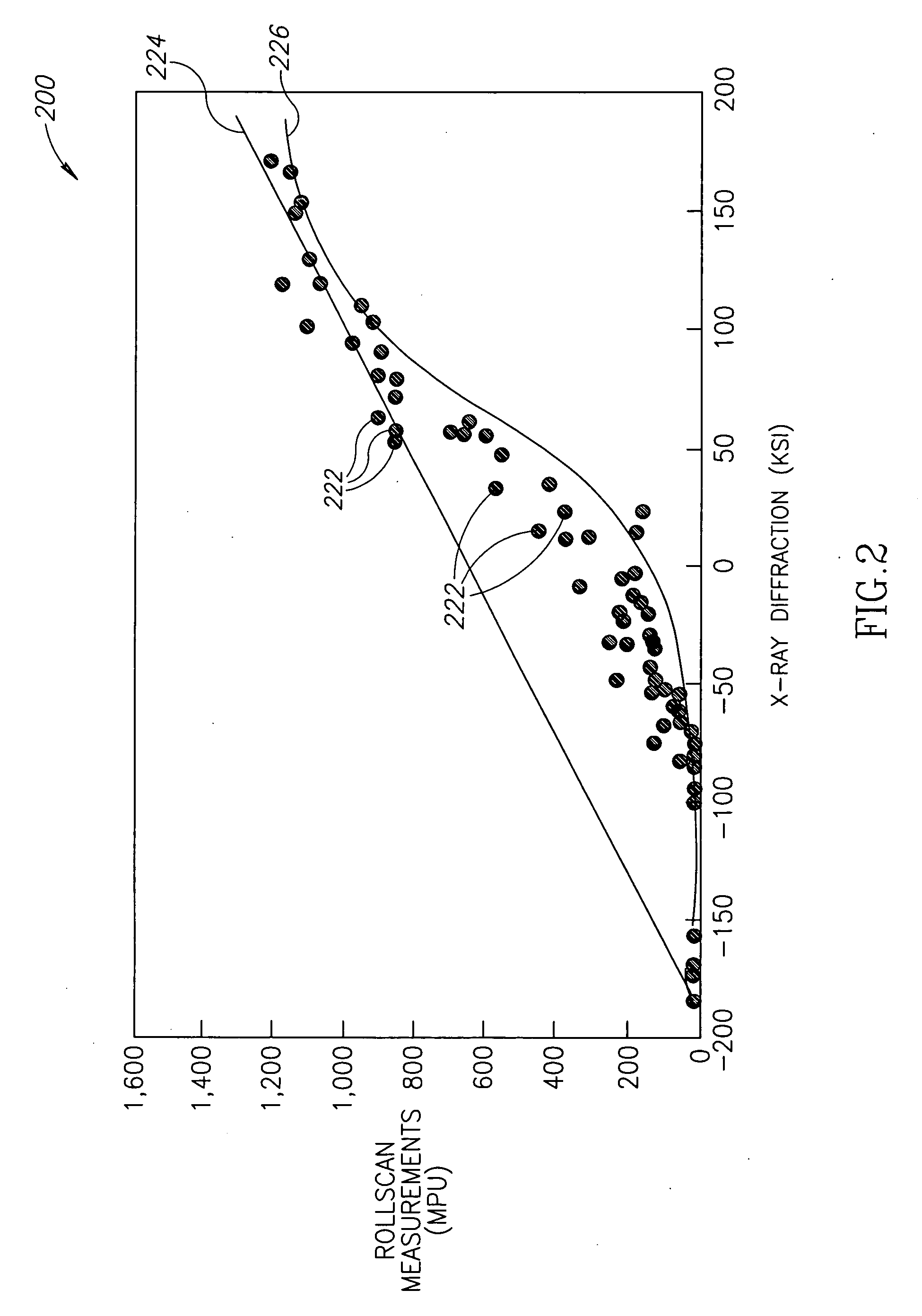
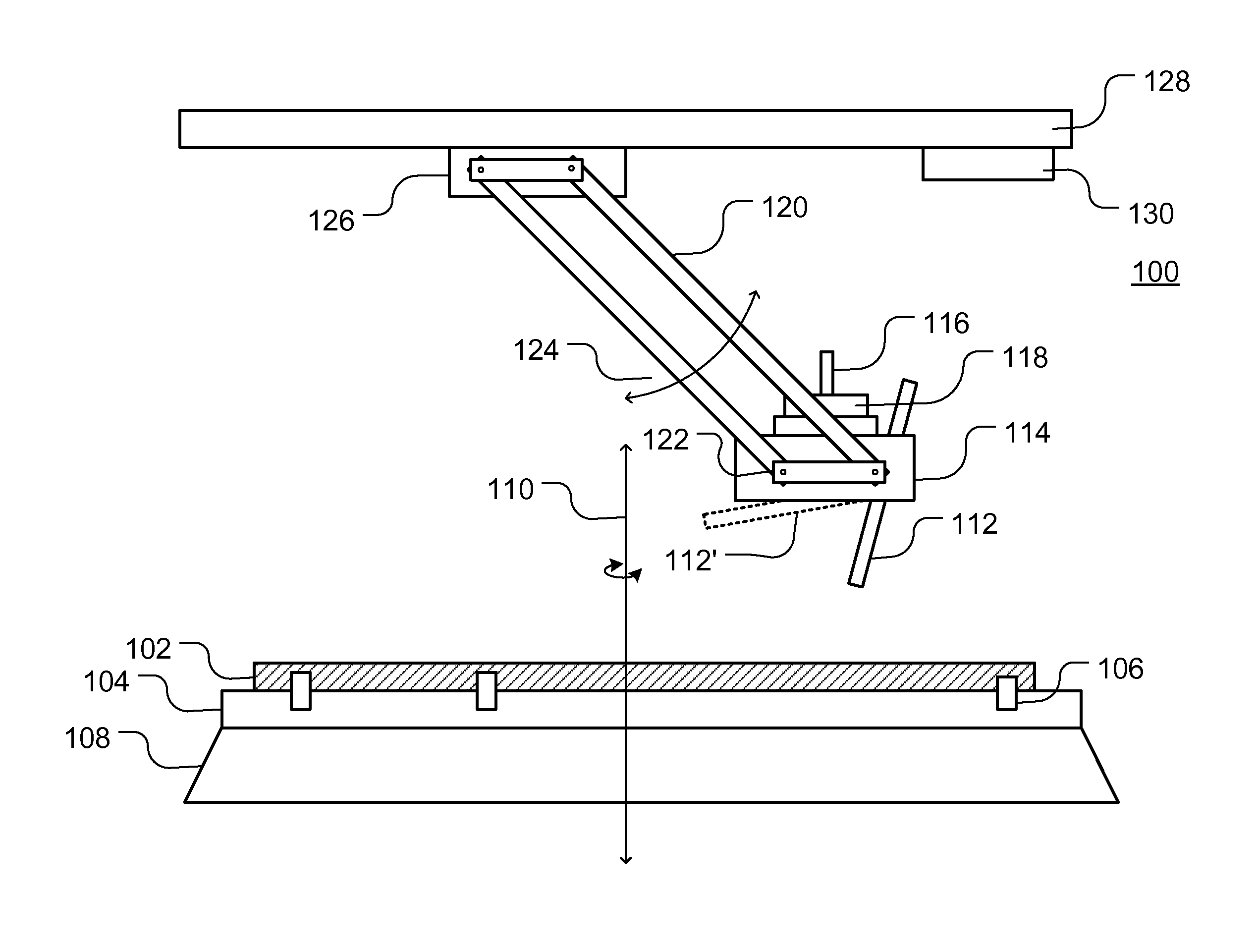
Systems and methods of measuring residual stress in metallic materials
ActiveUS7159470B2Accurate and meaningful measurement of residual stressReduce exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationForce measurementControl specimenMaterial under test
Systems and methods of measuring residual stress are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of measuring residual stress in a material under test includes directing radiation onto a stressed material and detecting the resulting diffraction peaks to measure known residual stress of a control specimen, inducing and sensing magnetoelastic interactions onto the control specimen, developing an empirical database of the diffraction and magnetoelastic interaction measurements of the control specimen, inducing and measuring magnetoelastic interactions on a material under test, and correlating the empirical database to the magnetoelastic interaction outputs from the material under test.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Planar sensor array for non-destructive evaluation of material using electromagnetic impedance
ActiveUS20150212026A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase angleSensor arrayNon destructive
Various embodiments include planar sensor arrays for use in determining characteristics of a material under test (MUT). The planar sensor arrays can include a set of electrodes positioned to enhance a depth and clarity of detection into the material under test. Some embodiments include an electromagnetic sensor array having: a first set of two rectilinear electrodes, positioned opposed to one another across a space; and a second set of two rectilinear electrodes, positioned opposed to one another across the space, the second set being off-set from the first set, wherein the first set and the second set are configured to detect an electromagnetic impedance of the MUT.
Owner:TRANSTECH SYST
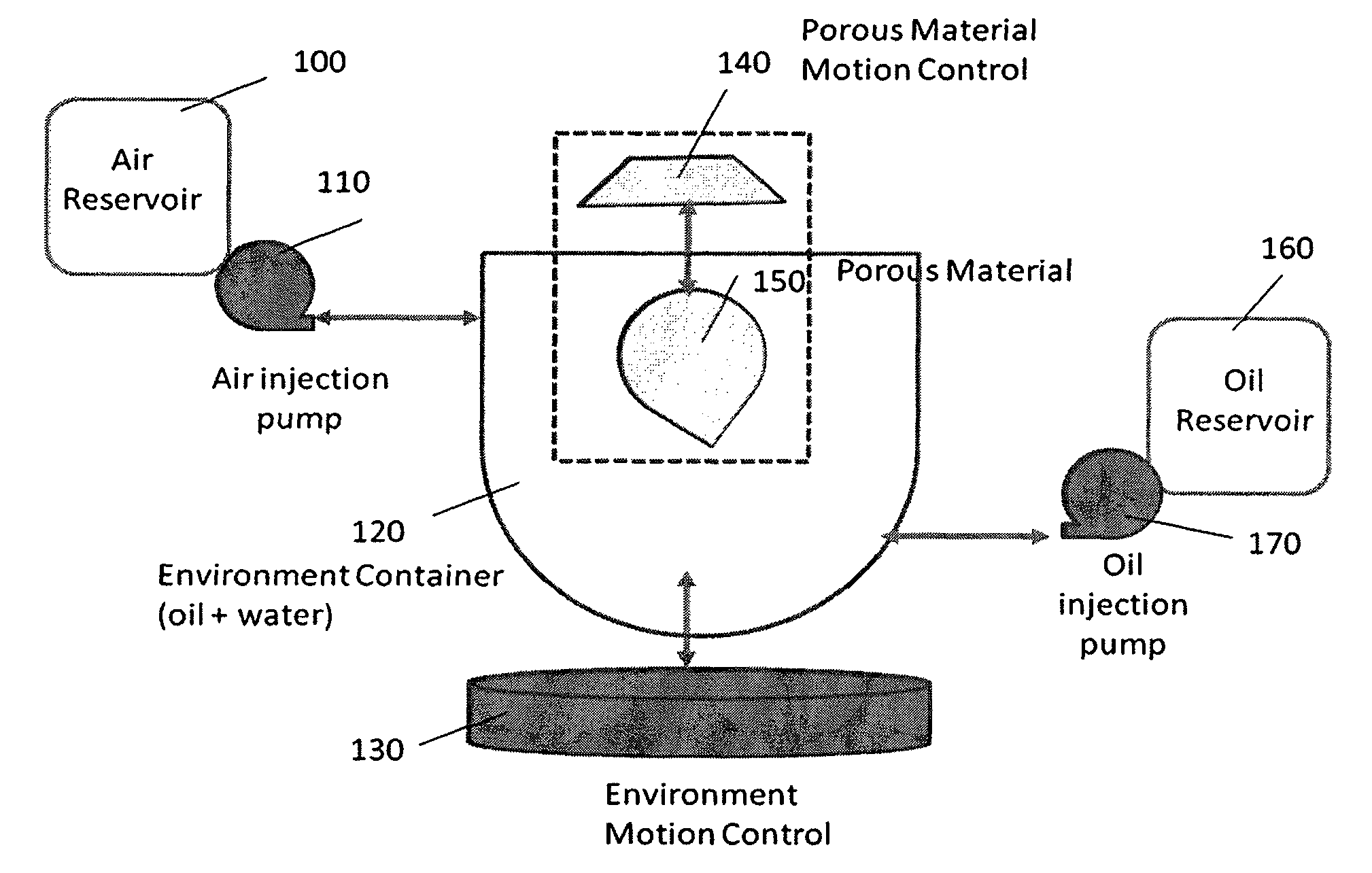
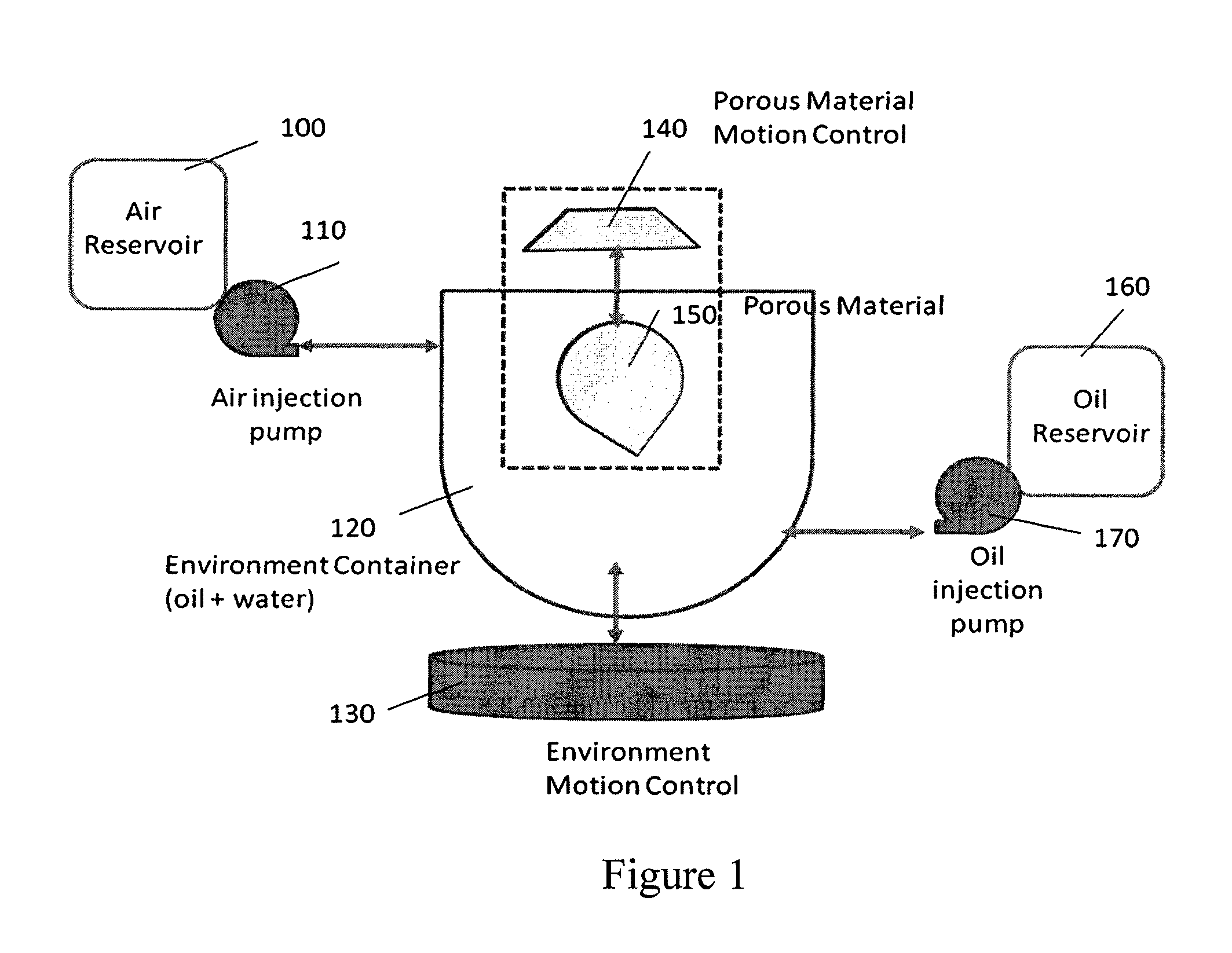
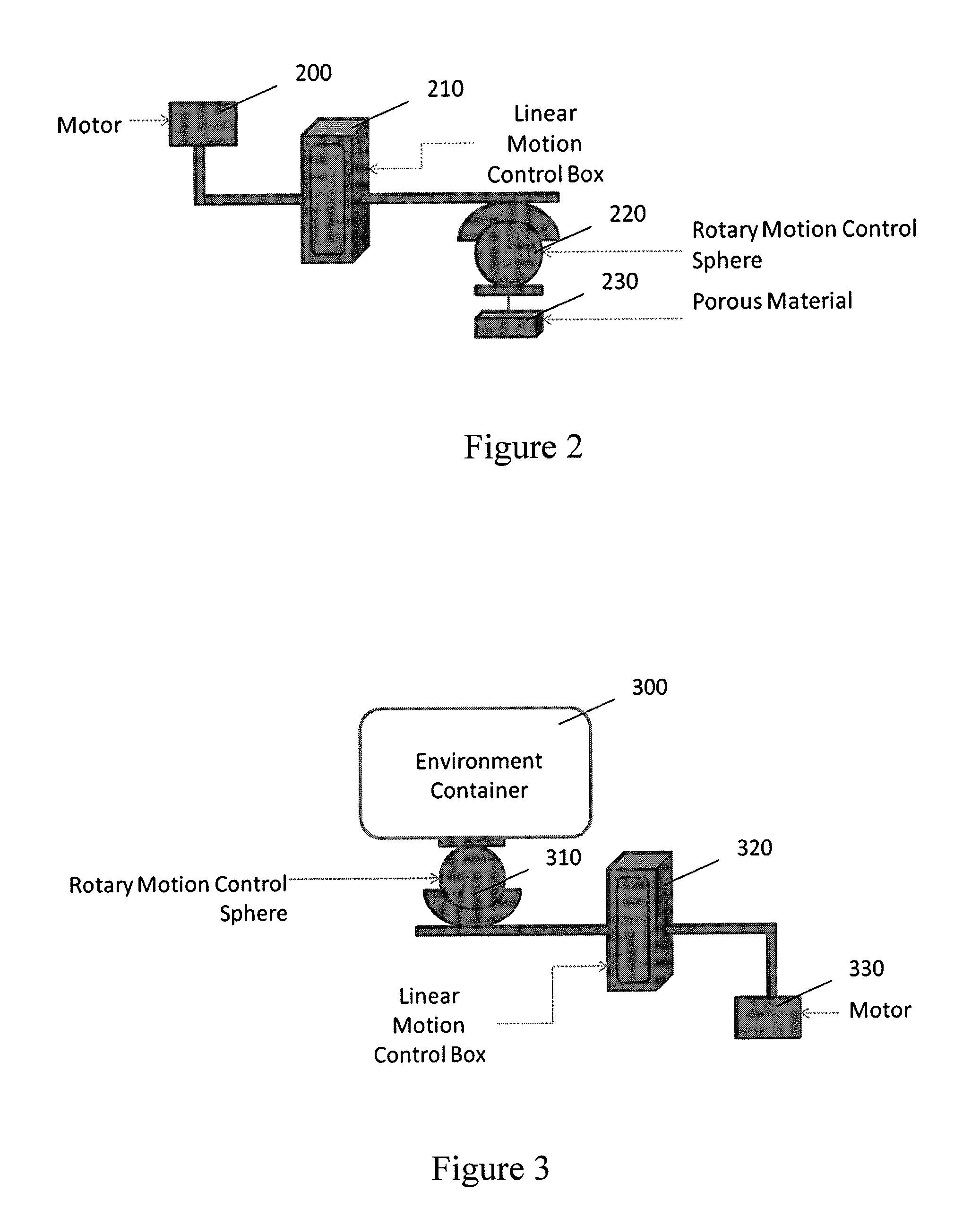
System to measure the absorptive capabilities of porous materials used in oil spill remediation
InactiveUS8631686B2Quick identificationConstructionsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceAbsorption capacityMaterial under test
Traditional porous material testing does not provide a measure of how well the porous material will perform in oil spill conditions. We disclose a new system that can analyze and determine the absorptive capability and oil-selectivity of a porous material in a moving mixture of oil and water, under different environmental conditions of pressure and wind. Our system allows the porous material under test and the mixture of oil and water to experience complex motion trajectories, and we measure the absorption capacity as well as the rate of oil absorption under different environmental conditions.
Owner:CHAKRADHAR VINEEL
Method for detecting air-out pollution constituent of non-metal material for space application
InactiveCN101271074AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationWithdrawing sample devicesSpace environmentMaterial under test
The invention discloses a detection method of the components of the gassing pollution of a non-metallic material used in a satellite, which is characterized in that the invention designs a sampling and sample storing system that can effectively detect the components of the gassing pollution of the non-metallic material used in the satellite under the simulated space environment. When in testing process, a sample is put in the sampling system, and the material under test completely generates gassing release action as fully as possible by the sample storing system, thus the detection system can fully detect the components of the gassing pollution. The detection method realizes the analysis of the gassing pollution from the qualitative aspect, overcomes single analyzing the gassing pollution from the quantitative pollution aspect in existence, effectively and deeply analyzes the gassing pollution of the non-metallic material used in the satellite and provides reference data for screening and processing the non-metallic material used in the satellite and carries out control and protection of satellite pollution from the aspect of pollution source.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
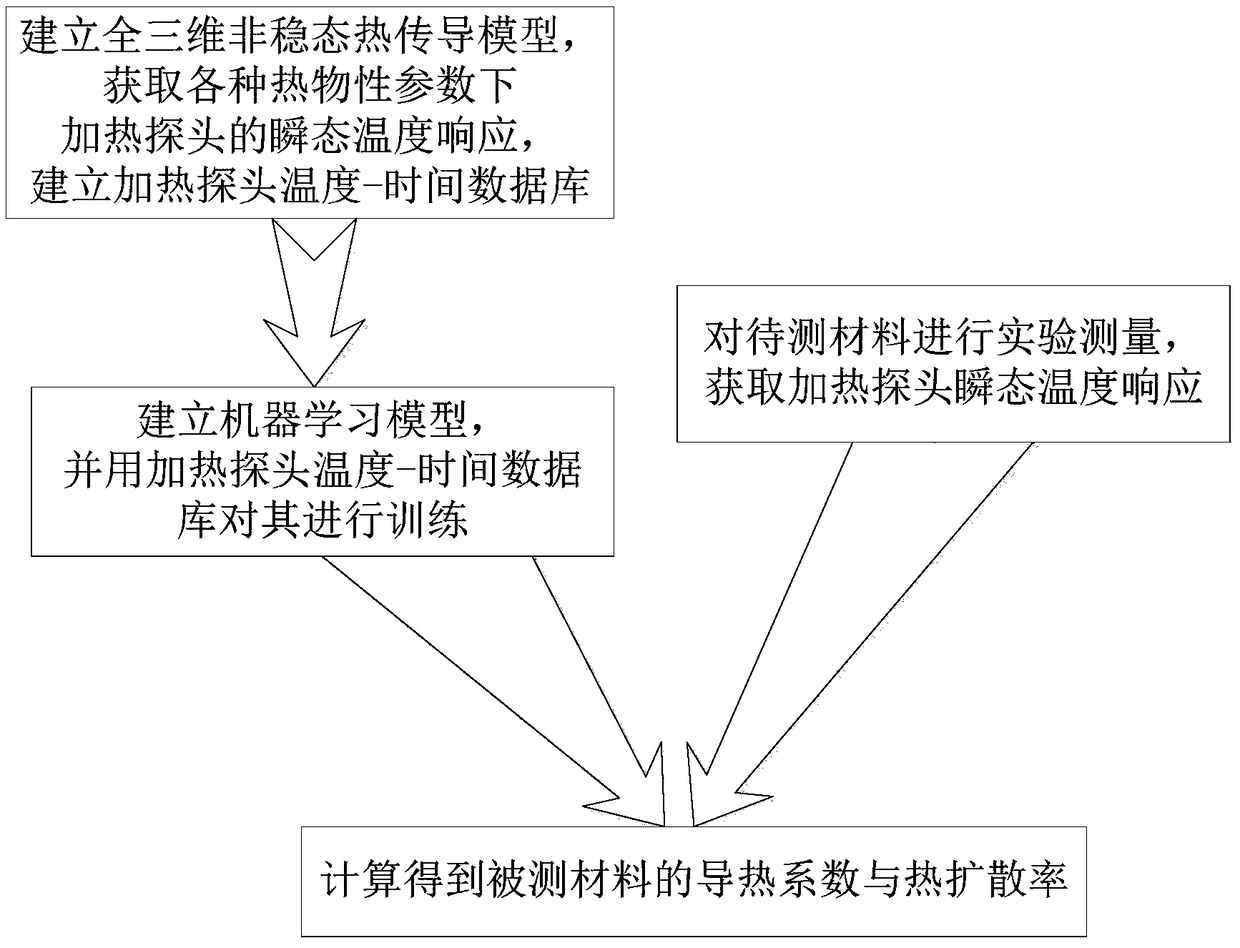
Heat conductivity coefficient and heat diffusivity transient body heat source measuring method
ActiveCN109142434AEasy to buildReduce measurement errorMaterial heat developmentTemporal databaseObservational error
The invention relates to a heat conductivity coefficient and heat diffusivity transient body heat source measuring method, and aims to solve the problems that an existing steady-state method needs addition of a heat protection structure, consequently, a device is complicated in structure and large in size, the shape and the volume effect of a heating probe cannot be accurately considered in a measuring model of non-steady state methods such as a planar heat source method, and measuring errors are large. The measuring method particularly includes the steps: first, building an excess temperature-time database of the heating probe with different thermophysical parameters; second, building a machine learning model of the thermophysical parameters and transient temperature rise of the heating probe based on the database built in the first step; third, acquiring change data of temperature rise of the heating probe with the passage of time by experimental measurement; fourth, calculating theheat conductivity coefficient and the heat diffusivity of a measured material according to the machine learning model built in the second step and the change data of temperature rise of the heating probe with the passage of time. The measuring method is used for the field of thermophysical parameter measurement of the material.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
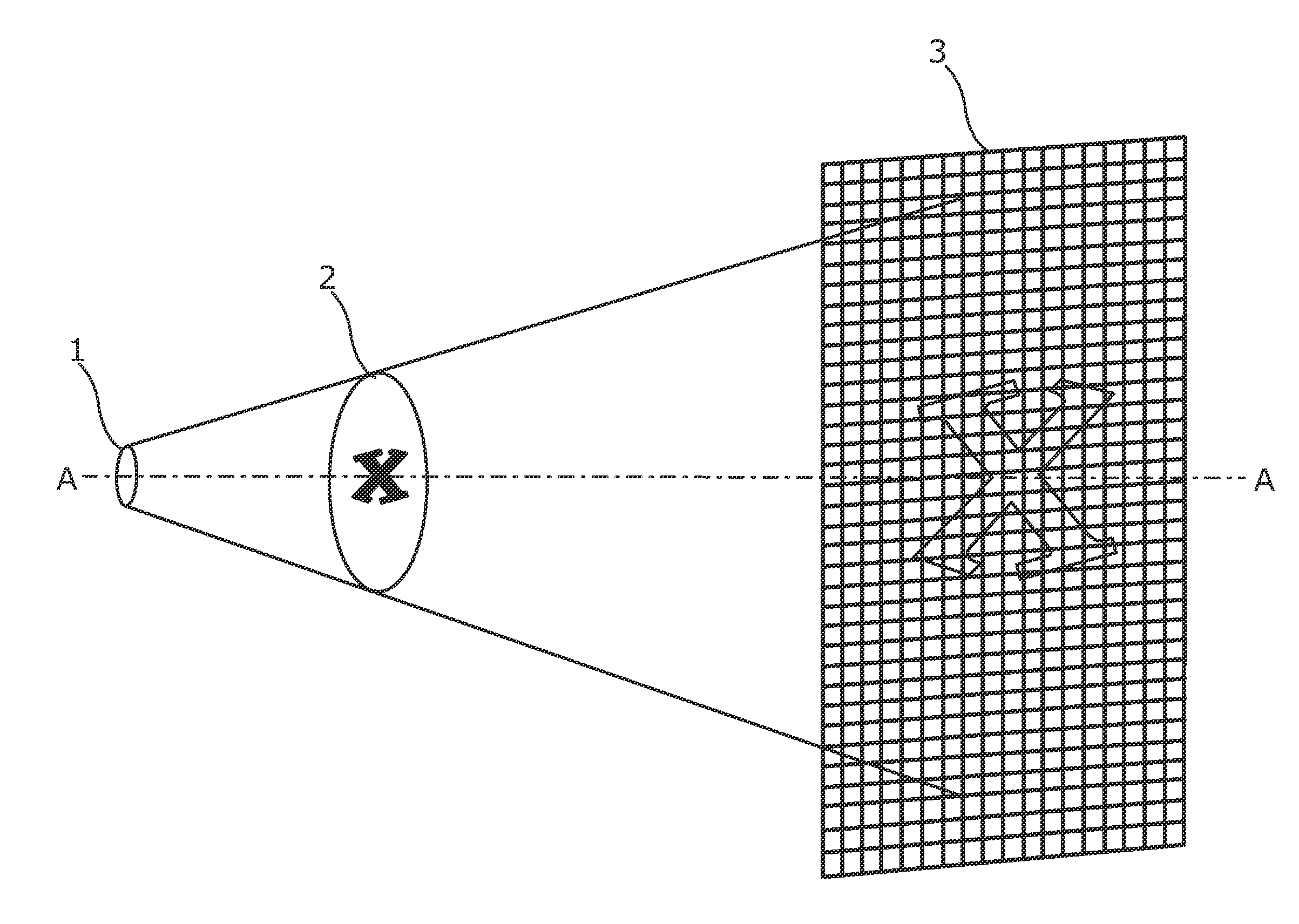
X-Ray Detection Apparatus
InactiveUS20140321616A1Small sizeHigh resolutionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementSoft x rayMaterial under test
X-ray imaging apparatus,which includes an x-ray detector. The x-ray detector comprises a member configured to convert incident x-ray wavelength photons into emitted visible wavelength photons, a position for a material under test, an x-ray source, and a structure configured to perturb an x-ray energy spectrum, each lying on a common axis. The x-ray source is arranged to direct an x-ray energy spectrum along the common axis to impinge upon the member, the structure configured to perturb the x-ray energy spectrum, and positioned material under test. The structure lies between the x-ray source and the member to one side of the position for material under test intersecting the common axis, and the said structure comprises at least three adjacent regions, each region different to immediately adjacent regions and configured to perturb the x-ray energy spectrum differently.
Owner:IBEX INNOVATIONS
Method for validating printed circuit board materials for high speed applications
InactiveUS7701222B2Radiation pyrometryResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial under testDielectric loss
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Resonance-enhanced dielectric sensing of chemical and biological species
InactiveUS20050032233A1Degree of selectivity enhancedHigh sensitivityMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial analysis using microwave meansDielectricElectricity
A dielectric sensing method and apparatus are provided for detection and classification of chemical and biological materials. Resonance patterns of a sample within a resonator are detected for identifying a shift in resonance frequency and a change of line width before and after introduction of the sample. The identified shift in resonance frequency and change of line width are used for determining a complex dielectric constant of the sample for the material detection and classification. A degree of selectivity at any excitation frequency is enabled for the dielectric sensing method from the manner in which the complex dielectric constant of a material affects the resonance pattern of the resonator with respect to shift in resonance frequency and the change in line width. By selecting the excitation frequencies to generally correspond to one of the resonance frequencies of the sample material under test, the degree of selectivity and the sensitivity of detection are enhanced.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Systems and methods of measuring residual stress in metallic materials
ActiveUS20060260412A1Accurate and meaningful measurement of residual stressReduce exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationForce measurementControl specimenMaterial under test
Systems and methods of measuring residual stress are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method of measuring residual stress in a material under test includes directing radiation onto a stressed material and detecting the resulting diffraction peaks to measure known residual stress of a control specimen, inducing and sensing magnetoelastic interactions onto the control specimen, developing an empirical database of the diffraction and magnetoelastic interaction measurements of the control specimen, inducing and measuring magnetoelastic interactions on a material under test, and correlating the empirical database to the magnetoelastic interaction outputs from the material under test.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Scratch Resistance Test Methods and Apparatus
InactiveUS20120103055A1Using mechanical meansInvestigating material hardnessMaterial under testEngineering
The apparatus and methods disclosed may be utilized for the scratch / mar testing of various materials and components that provide improved correlation between the simulated damage modes and those reasonably expected to be encountered by the final components. The apparatus includes both a fixture configured for receiving and holding the material under test (MUT) and a tool holder that is arranged and configured for supporting and holding a variety of test tools in one or more orientations relative to the MUT. The tool holder and / or the fixture are, in turn, supported by one or more assemblies arranged and configured for bringing the tool into contact with the MUT and providing for movement of the tool relative to the MUT. The apparatus is then used for collecting data from a series of tests that can be used to compare the performance of different MUT compositions and configurations.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com