Optical transceiver and fiber-optic gyro
An optical transceiver and light source technology, applied in the field of navigation systems, can solve the problems of complex and expensive technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
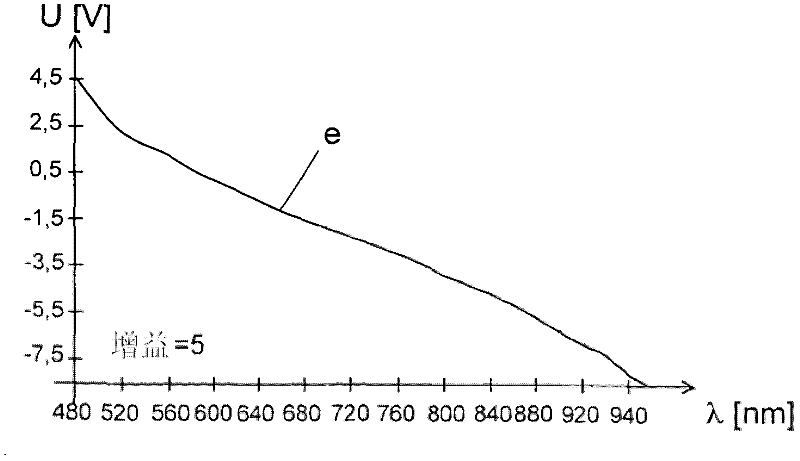
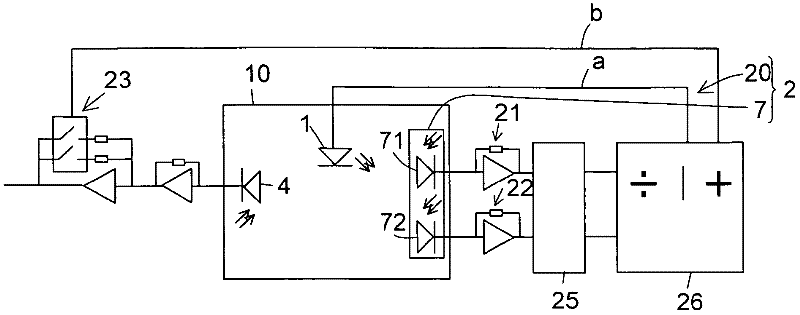
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
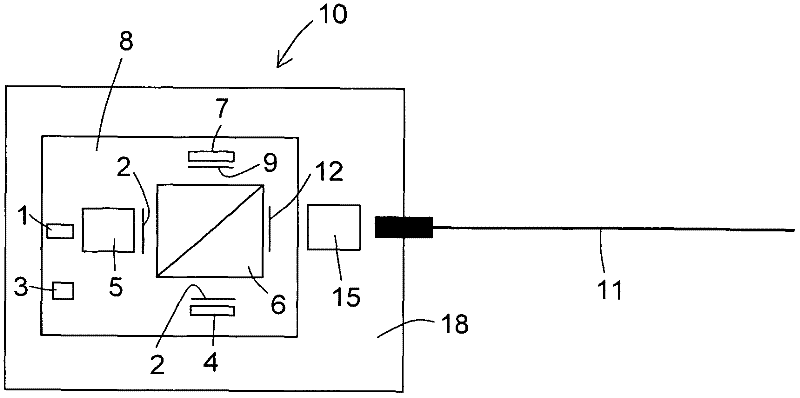
[0015] figure 1 An optical transceiver 10 is shown, wherein the optical and optoelectronic components of the optical transceiver 10 are arranged on a support. According to one embodiment, the optical transceiver 10 comprises a temperature regulation unit with a temperature sensor 3 and a thermoelectric cooling element 8 (TEC, Thermoelectric Cooler). In this embodiment, at least some optical components and optoelectronic components may be configured (integrated) on top of the TEC 8 . The TEC 8 is, for example, a Peltier element and may in turn be fastened to a carrier such as a substrate 18 comprising silicon, silicon dioxide, glass, ceramic or plastic, or comprising multilayer One or more of the above materials. According to another embodiment, the TEC 8 and the substrate 18 are arranged spatially apart from each other and the TEC 8 is thermally conductively connected to the substrate 18 or the light source 1 via a coupling element, i.e. the coupling element thermally couple...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com