Low voc solvent-borne printing inks
A solvent and dispersant technology for low VOC solvent-based printing inks to address issues such as health effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
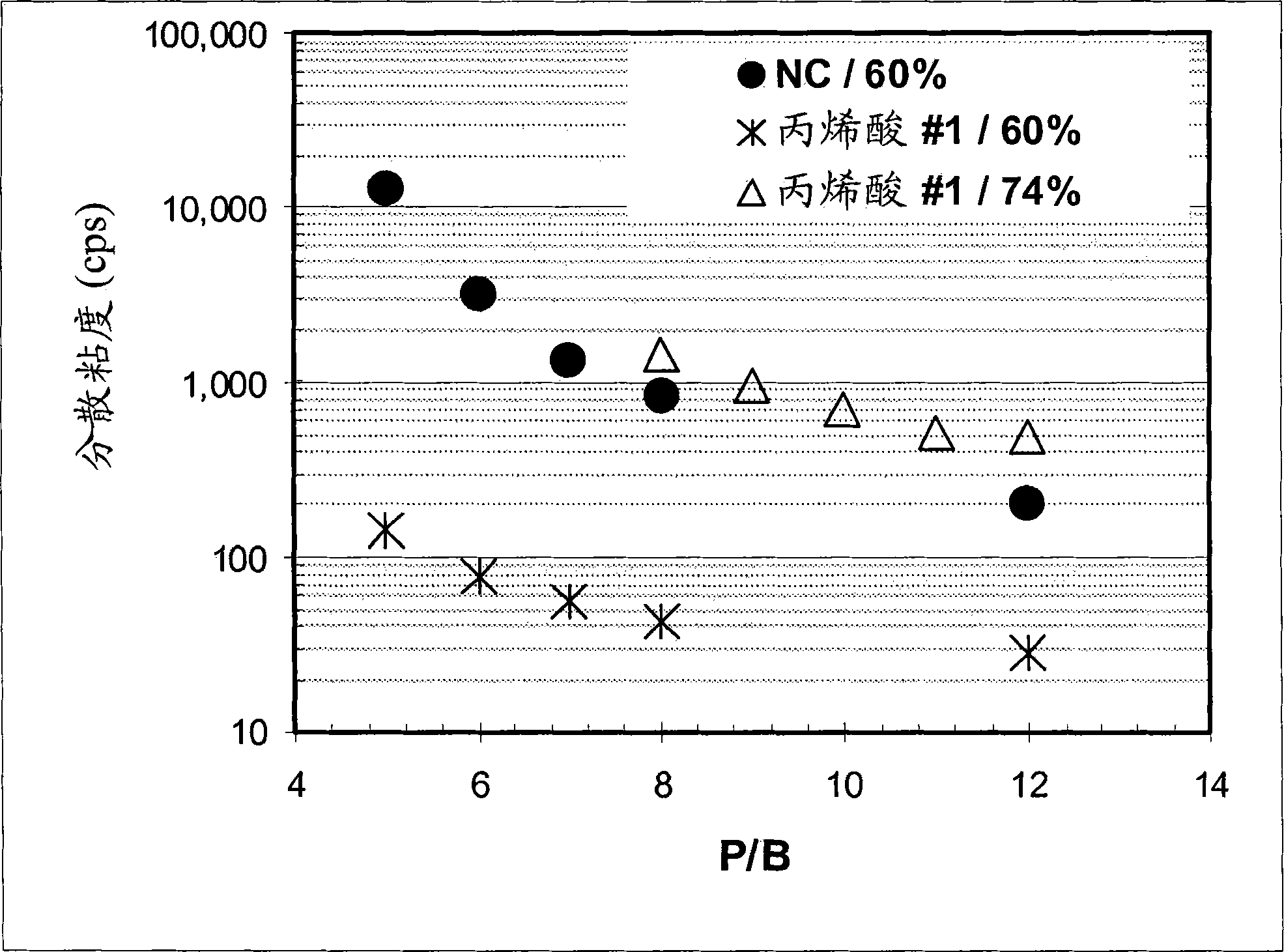
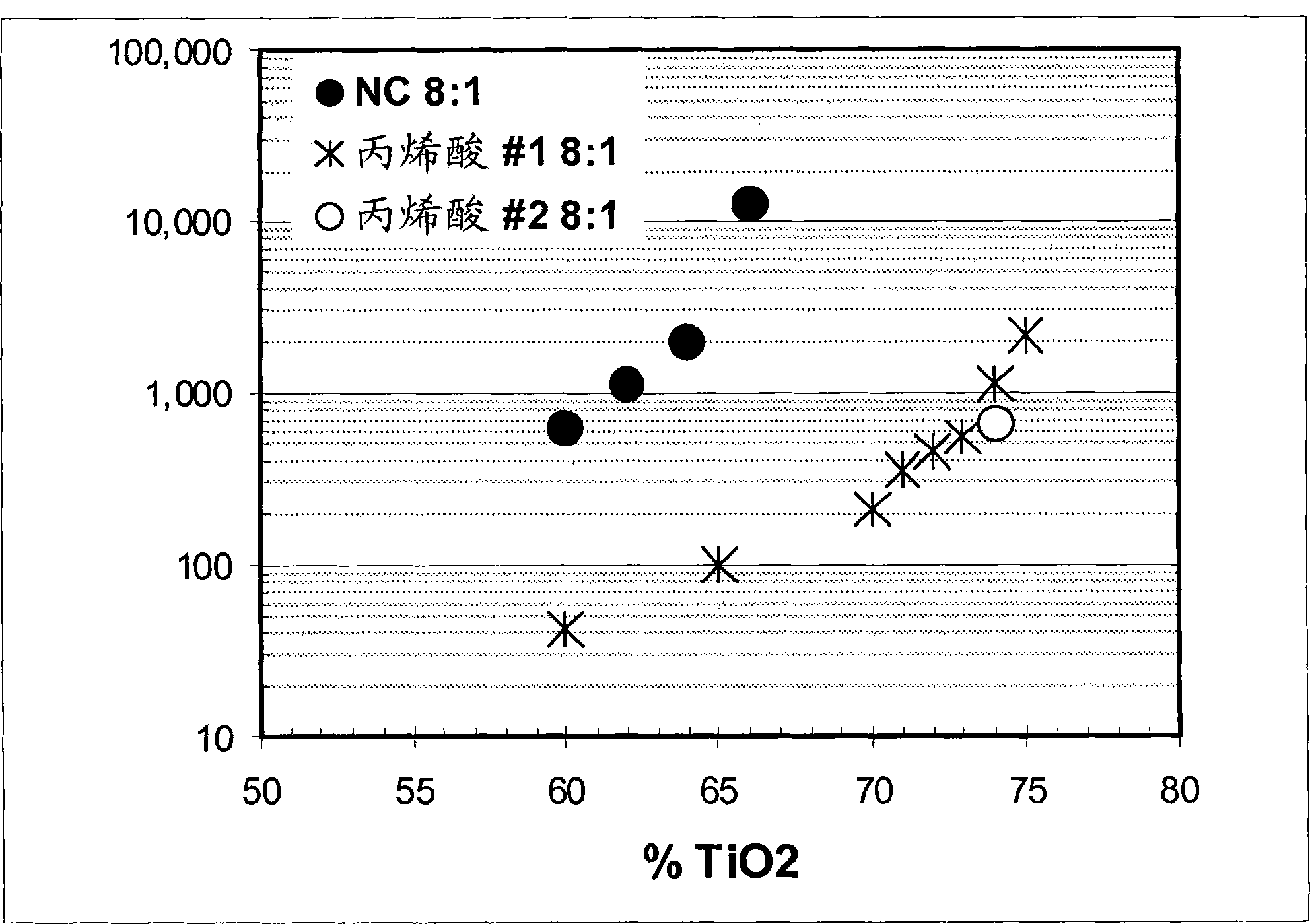
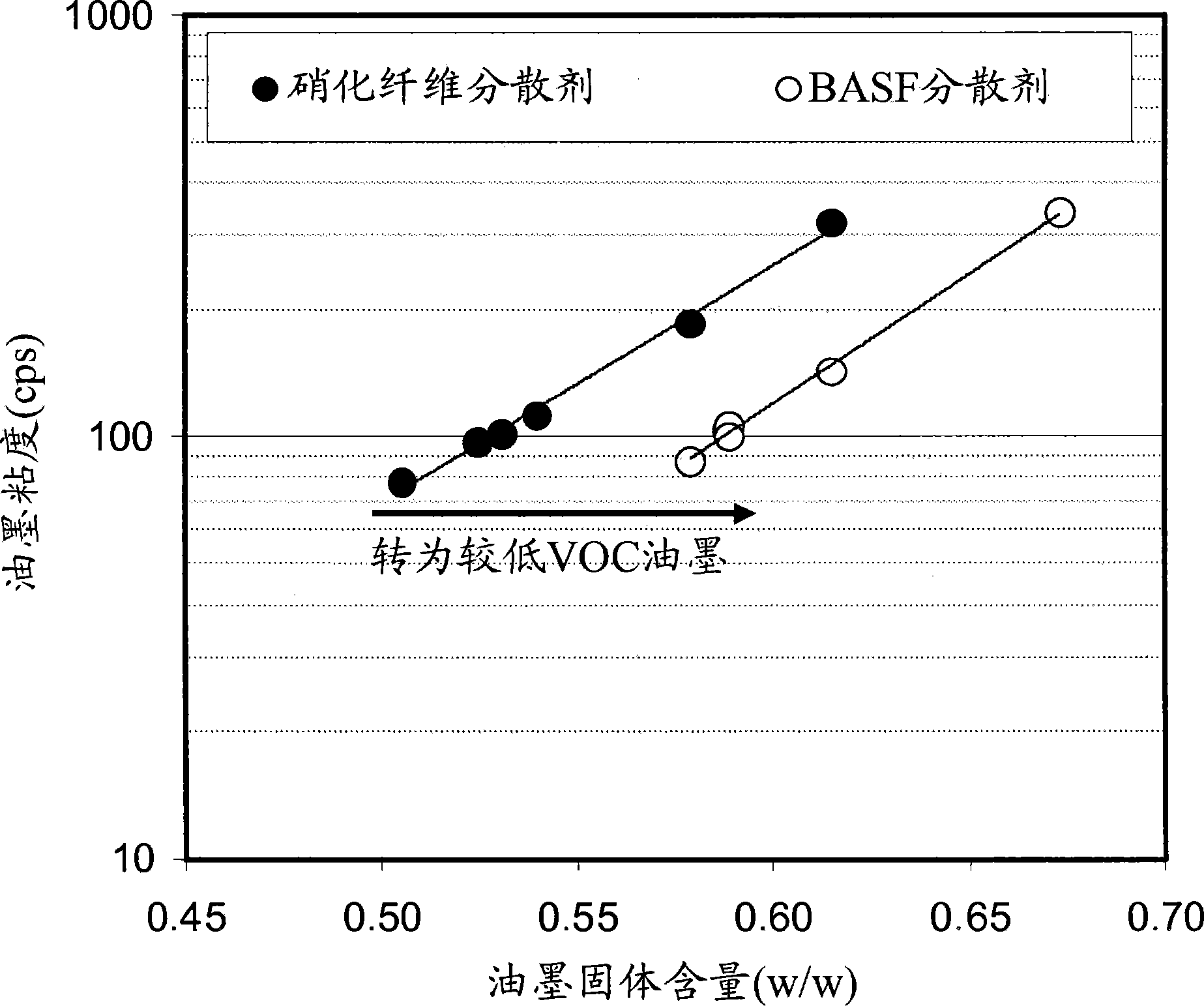
[0059] Example 1 - An ink was prepared by mixing a titanium dioxide dispersion with nitrocellulose, dimer acid derived polyamide or thermoplastic polyurethane and diluting with the appropriate solvent to standard application viscosity (100 cps measured at 25 s from a No. 2 viscosity cup). Titanium dioxide dispersions were prepared using standard nitrocellulose dispersants and various styrene-acrylic dispersants. The ink is then coated onto polyethylene terephthalate, polypropylene, oriented polypropylene or polyethylene film using an automated K-coater equipped with a wire wound rod or anilox proofer, followed by drying in a 50°F drying oven. Dry for 30 to 60 seconds. The physical and optical properties of the inks were then measured, such as tack, water resistance, wrinkle resistance, gloss, color strength and opacity.
[0060] In general, the styrene-acrylic dispersions improved the gloss and color properties of the inks compared to standard inks. Table 1 is a comparison o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| gloss | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com