Method for building a water maze spatial learning and memory model for tree shrews
A technology of learning memory and establishing methods, which is applied in the field of building tree shrew models of water maze space learning and memory, and can solve problems such as restrictive effects and limited data reference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] 1. Screening of animals before the experiment:
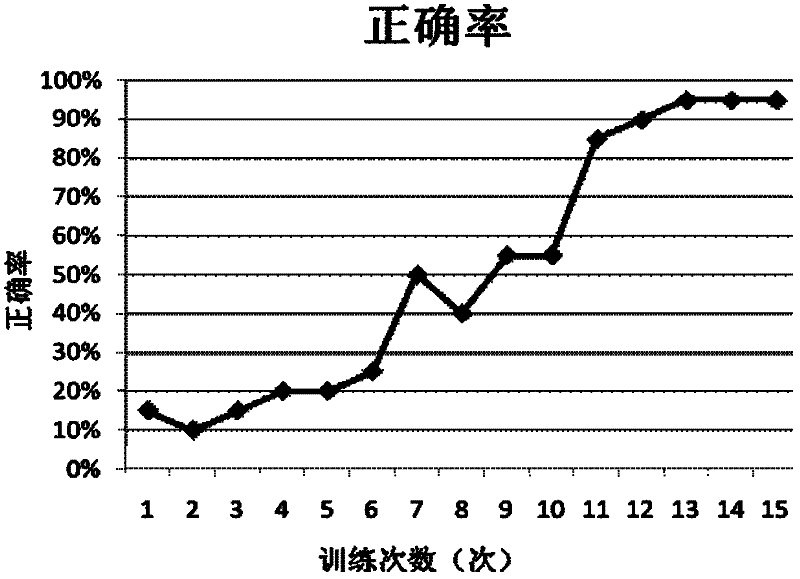
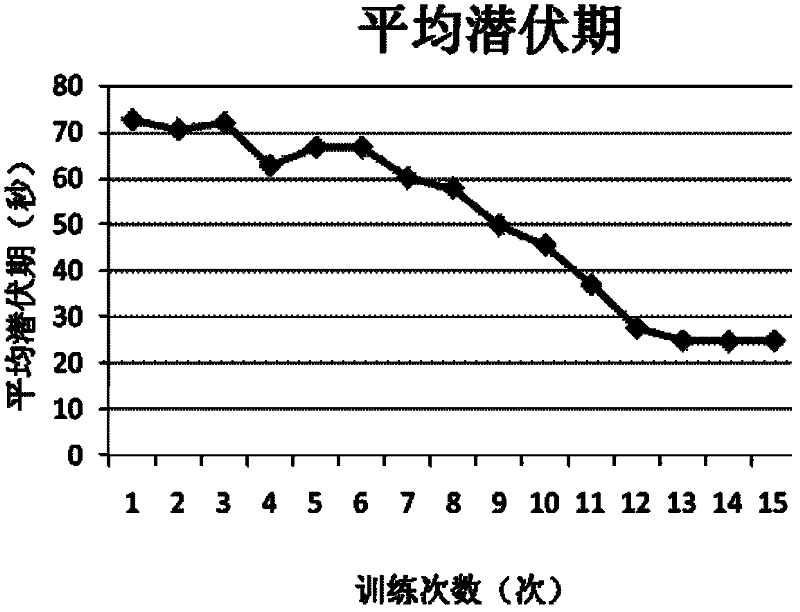
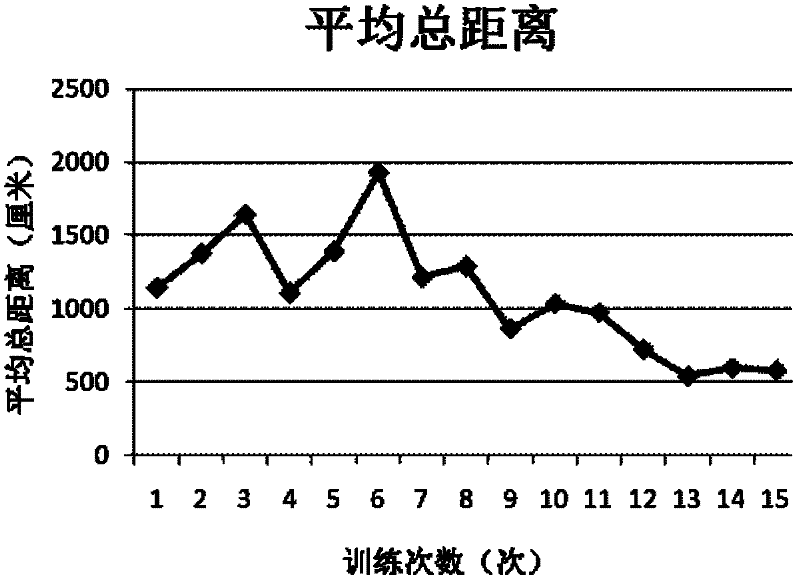
[0034] The tree shrew used in the experiment is the first generation of Chinese Burmese tree shrew self-propagating in the laboratory. It is 12 months old and weighs 110g-120g. Before the experiment, the tree shrew has been kept in a quiet environment with normal light rhythm. Pretreatment with pick and place. From 13 male tree shrews, 10 tree shrews that started to swim within 10 seconds, with a swimming speed ≥ 15cm / s were selected, and the offspring tree shrews with a total swimming time of 30 seconds were selected; selected from 15 female tree shrews 10 tree shrews with a swimming speed ≥ 15cm / s that started to swim within 10s after being placed in the water maze experimental pool were screened for the first generation of tree shrews whose swimming time was 30s.
[0035] 2. Experimental device preparation
[0036] The water maze experiment was a circular pool with a diameter of 160 cm and a height of 50 cm as requir...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com