Method for acquiring thickness change of photoresist and monitoring influence of photoresist thickness on graphic dimension
A technology for pattern size and thickness change, which is applied in microlithography exposure equipment, photolithography process exposure devices, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, etc., can solve the problem that the pattern size cannot be changed obviously, and the influence of pattern size cannot be found in time and other issues to achieve the effect of reducing requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0025] This embodiment provides a method to obtain the change of photoresist thickness, refer to the attached figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
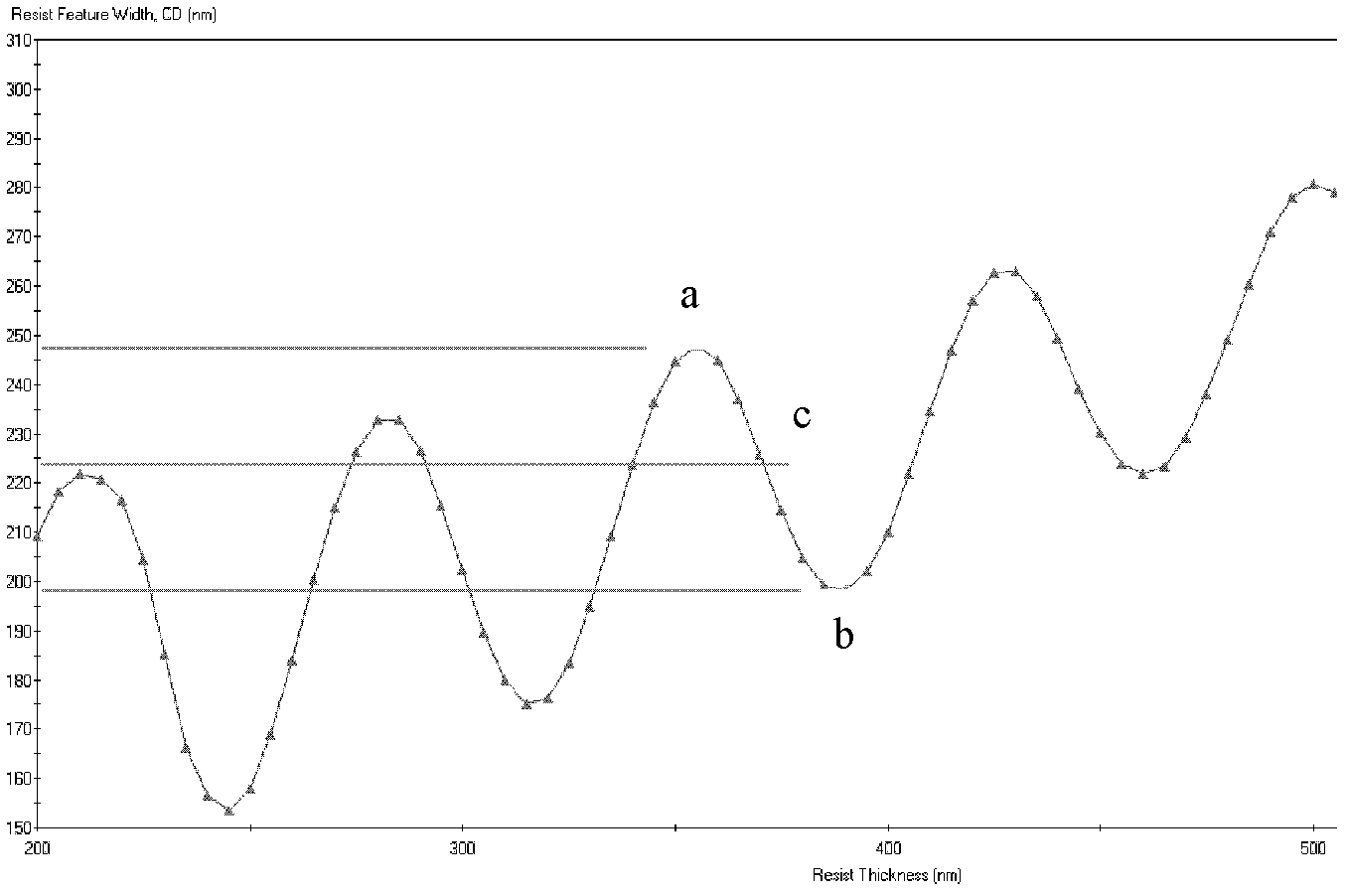
[0026] Step S10, providing a semiconductor substrate, forming a photoresist layer with a certain thickness on the semiconductor substrate, the thickness of the photoresist layer being the thickness of the photoresist corresponding to the middle point of the adjacent peak and trough in the rocking curve;
[0027] Wherein, the semiconductor substrate can be any material such as silicon, silicon germanium, silicon-on-insulator, etc., and the semiconductor substrate can be a blank substrate, or any semiconductor integrated circuit formed with semiconductor devices, interconnection structures, etc. Any intermediate structural state during the production process;
[0028] The photoresist layer of a certain thickness is formed by a conventional spin coating process, and the photoresist thickness selected in advance is the thi...
no. 2 example
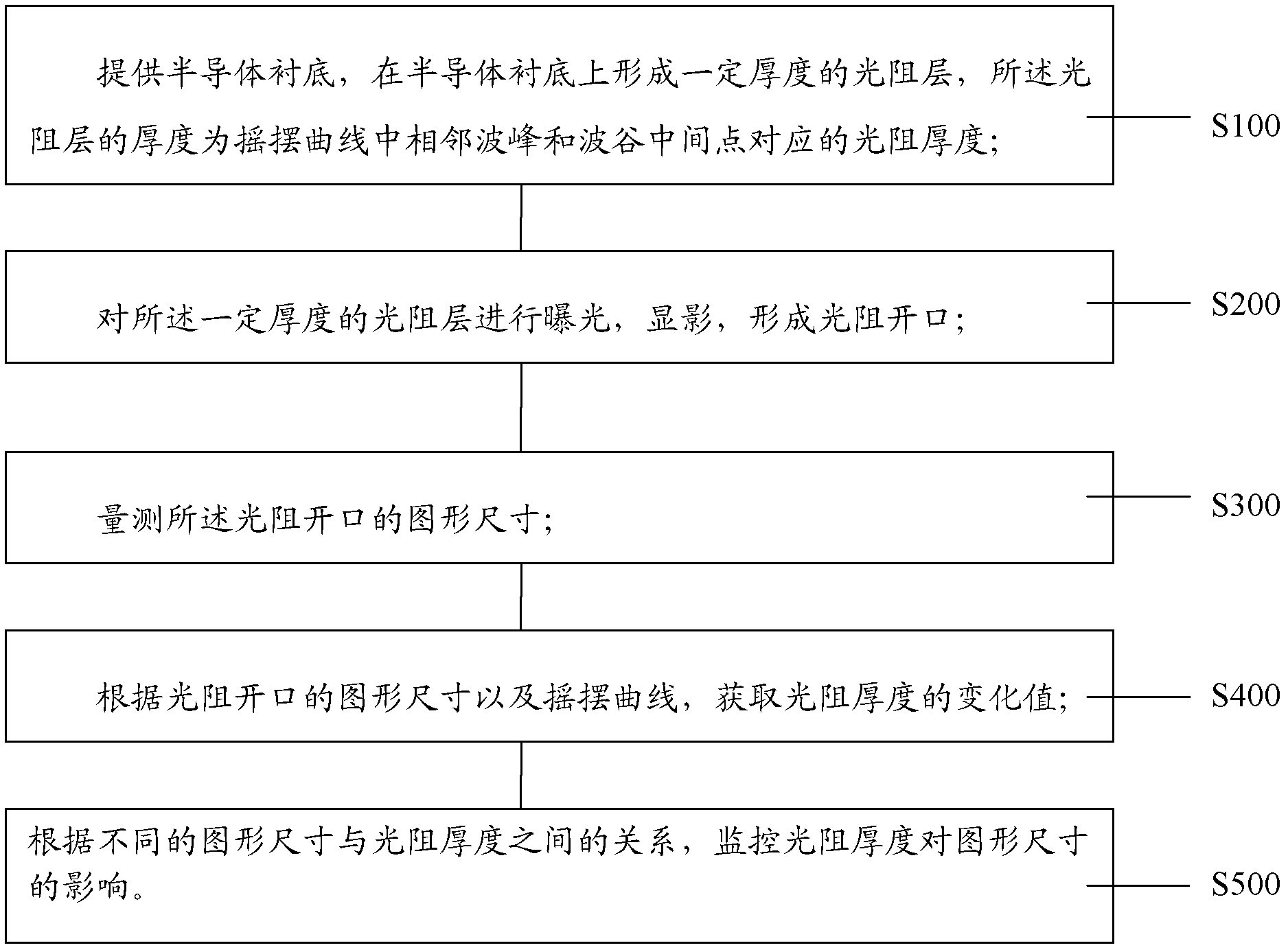
[0035] This embodiment provides a method for monitoring the influence of photoresist thickness on pattern size, refer to the attached image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0036] Step S100, provide a semiconductor substrate, and form a photoresist layer with a certain thickness on the semiconductor substrate, the thickness of the photoresist layer is the thickness of the photoresist corresponding to the middle point of the adjacent peak and trough in the rocking curve;
[0037] Wherein, the semiconductor substrate can be any material such as silicon, silicon germanium, silicon-on-insulator, etc., and the semiconductor substrate can be a blank substrate, or any semiconductor integrated circuit formed with semiconductor devices, interconnection structures, etc. Any intermediate structural state during the production process;
[0038] The photoresist layer of a certain thickness is formed by a conventional spin coating process, and the photoresist thickness selected i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com