Dynamic electrocardiogram T wave alternate quantitative analysis method based on models
A dynamic electrocardiogram and quantitative analysis technology, applied in the field of biomedical signal processing, can solve problems such as lack of time resolution, difficulty in applying dynamic electrocardiogram TWA quantitative analysis, and difficulty in precise positioning of ECG feature points.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
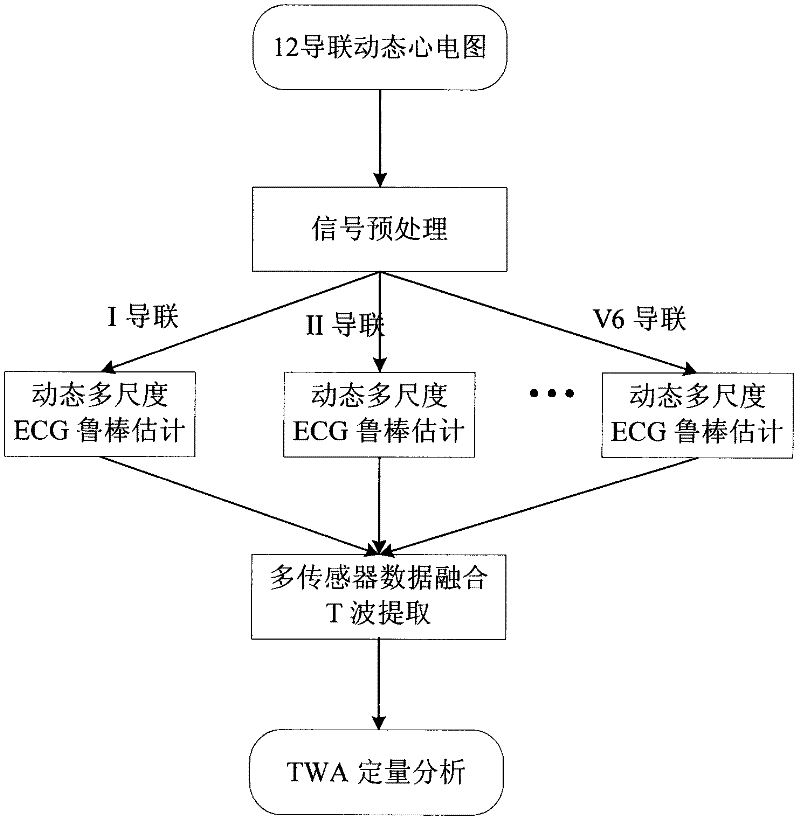
[0052] The invention is attached figure 2 The block diagram shown adopts a combination of theoretical analysis, computer simulation and software design, starting from the theory and method of state estimation of dynamic multi-scale stochastic systems, using multi-sensor data fusion theory to solve the separation of dynamic ECG non-Gaussian noise and the complete extraction of T waves The problem, and then study the time-frequency analysis theory and method of TWA, to realize the quantitative analysis of non-stationary TWA. The analysis process is divided into five stages: dynamic electrocardiogram preprocessing, waveform estimation, T wave extraction and TWA analysis. The technical route adopted is as follows: figure 2 .
[0053] 1. Obtain 12-lead dynamic ECG signals.
[0054] 2. Dynamic ECG preprocessing
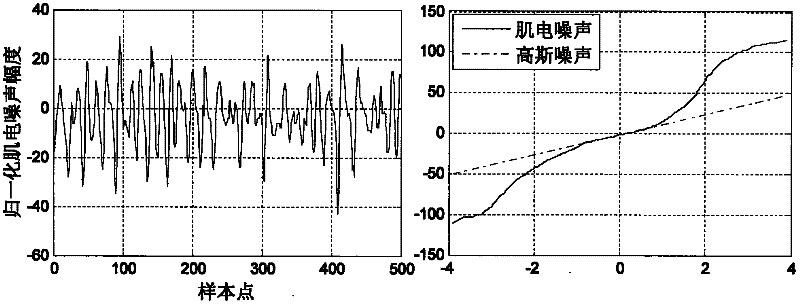
[0055] In the ECG signal preprocessing stage, baseline drift, power frequency interference, and random interference caused by lead movement are mainly removed, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com