Coloring reuse method for micro-polygon ray tracing
A ray tracing and polygonal technology, applied in 3D image processing, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of unavailable high-light reflection, mapping cannot be effectively processed, etc., to reduce the amount of coloring calculation, improve performance, and ensure accuracy sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
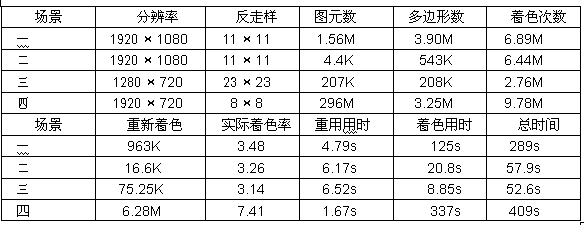
[0030] Embodiment 1. The inventor used the method of the present invention to draw four typical scenes, including a common battle scene in movies (Scene 1), a scene with a reflection / refraction magnifying glass and metal objects with displacement maps (Scene 2) , a scene of a car passing through a tunnel with motion blur (scene three) and a highly complex scene of a waterside castle and woods (scene four), Table 1 is the performance statistics table of the method of the present invention in all scenes. The reuse time is all the additional time for coloring reuse, including the time spent in constructing kd tree, nearest neighbor search and collecting recoloring samples. The actual shading rate is the actual measured average number of shading calculations per pixel, which is generally slightly larger than the user-specified shading rate due to scene layering and shading that needs to be recomputed. As shown in the table, the method of the present invention maintains a controlla...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2. In the above-mentioned scenario 2, the inventor compared the result of not reusing the coloring at all as a reference, the result of this method and the result of the decoupling sampling method. The decoupled sampling method can refer to RAGAN-KELLEY, J., LEHTINEN, J., CHEN, J., DOGGETT, M., AND DURAND, F. 2011. Decoupled sampling for graphics pipelines. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 3 ( May), 17:1–17:17. The result is that the method results are visually in perfect agreement with the reference results. In the decoupled sampling method, the shading value is only reused between samples belonging to the same primitive and these samples have the same hash value under the standard decoupled map, where the sample is calculated by projecting the sample to the image plane. An integer hash of , defocus is not considered during projection. Since this mapping does not account for magnification and deformation caused by ray tracing, this results in blocky artifacts when dr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com