Parallel three-phase grid-connected inverter adopting mutual reactors and control method for three-phase grid-connected inverter
A technology of a three-phase inverter and control method, applied in the direction of irreversible DC power input conversion to AC power output, electrical components, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problem of large volume and weight, narrow application range, and complex control and other problems to achieve the effect of solving uneven flow, reducing volume and weight, and suppressing zero-sequence circulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
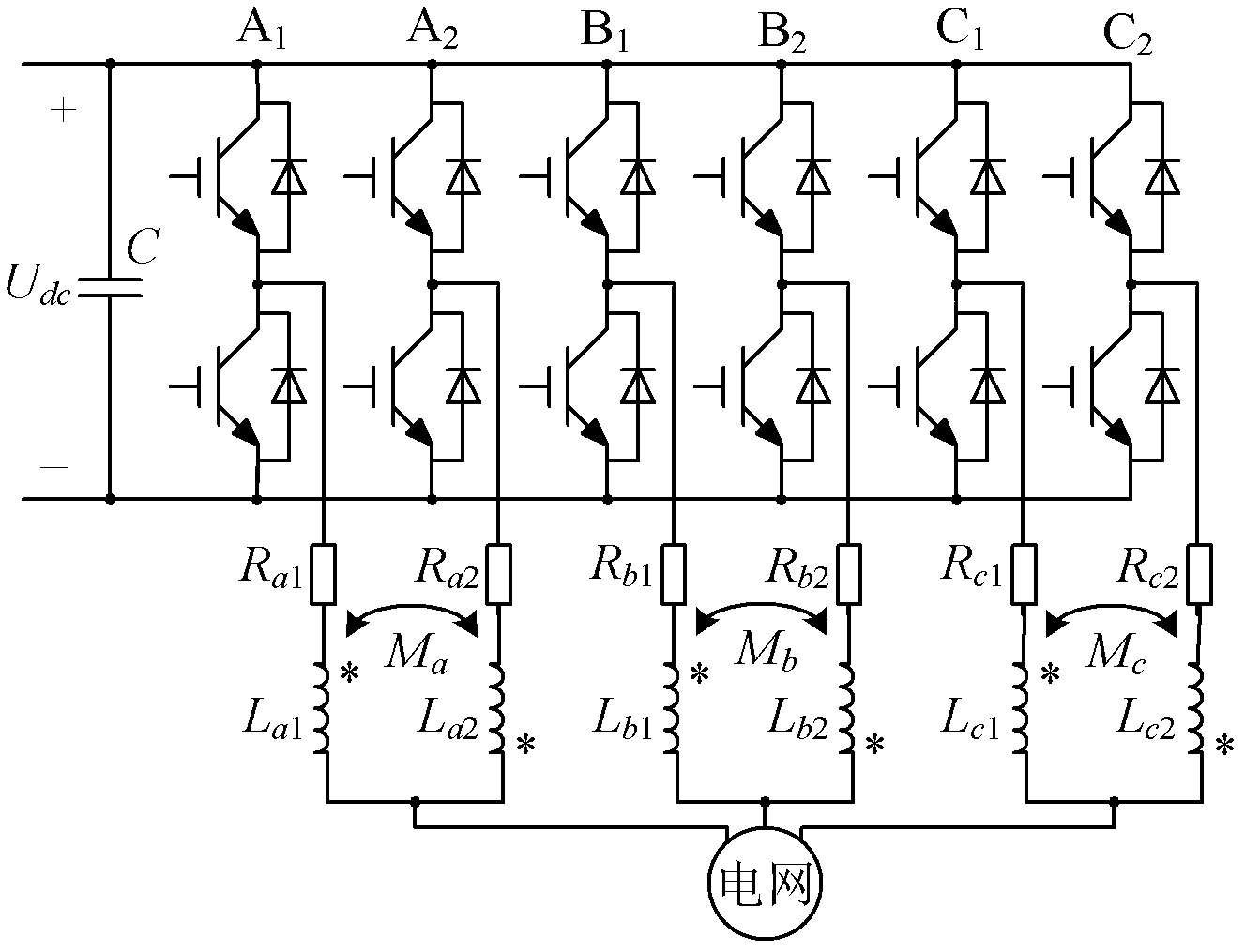
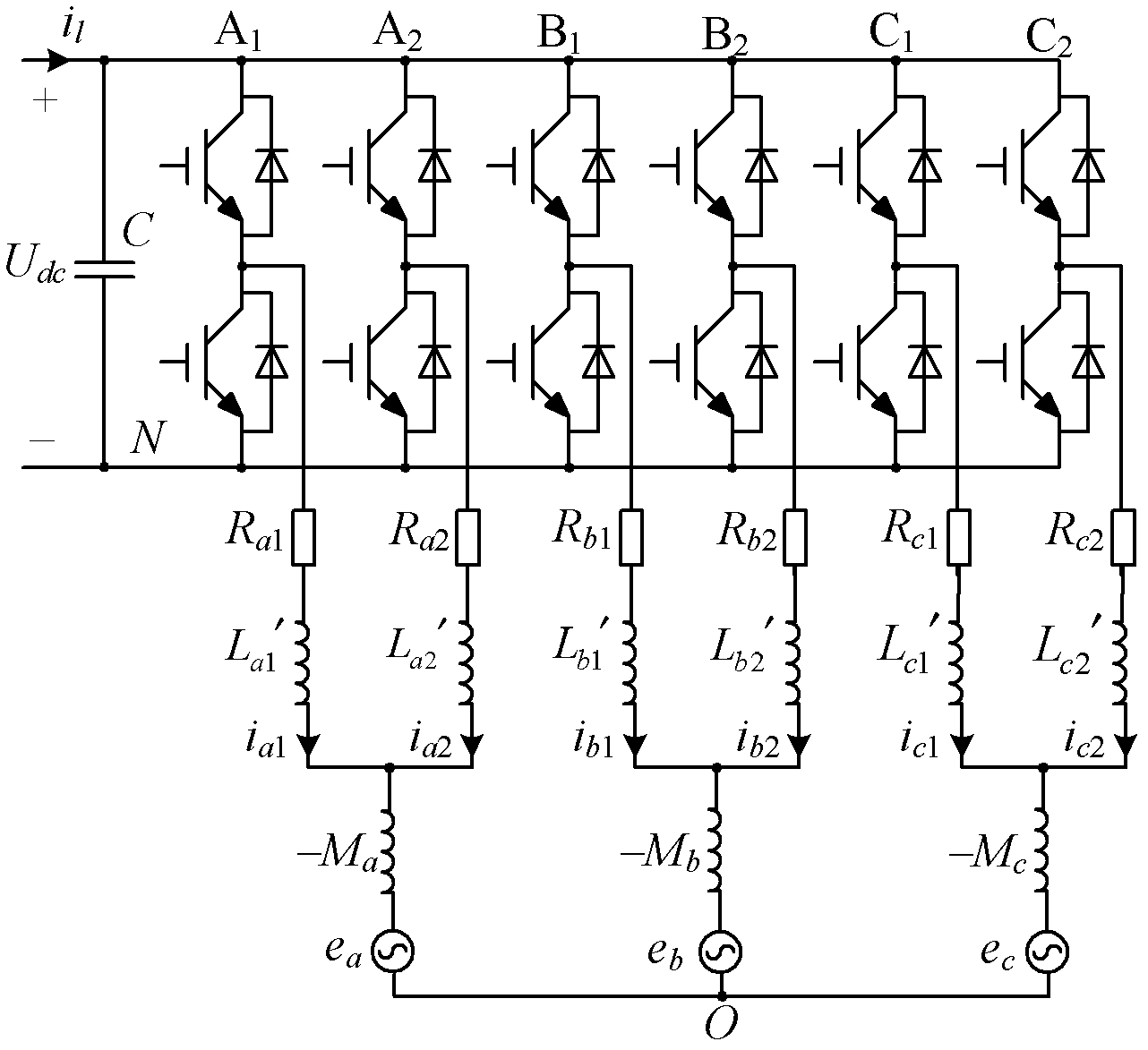
[0027] Specific implementation mode one, see figure 1 , 2 and 3 illustrate this embodiment. The parallel-connected three-phase grid-connected inverter using coupling reactor described in this embodiment is composed of two sets of three-phase grid-connected inverters with the same structure and three sets of coupling reactors. Two sets of three-phase grid-connected inverters with the same structure share a common DC bus, and capacitors are connected in parallel on the DC bus; the two sets of three-phase grid-connected inverters with the same structure are connected in parallel with each other, and the two sets of three-phase grid-connected In the phase grid-connected inverter, the two AC signal output terminals belonging to the same phase are respectively connected together through a set of coupling reactors and connected to the power grid.
[0028] The power switches in the two sets of three-phase grid-connected inverters with the same structure described in this embodiment c...
specific Embodiment approach 2
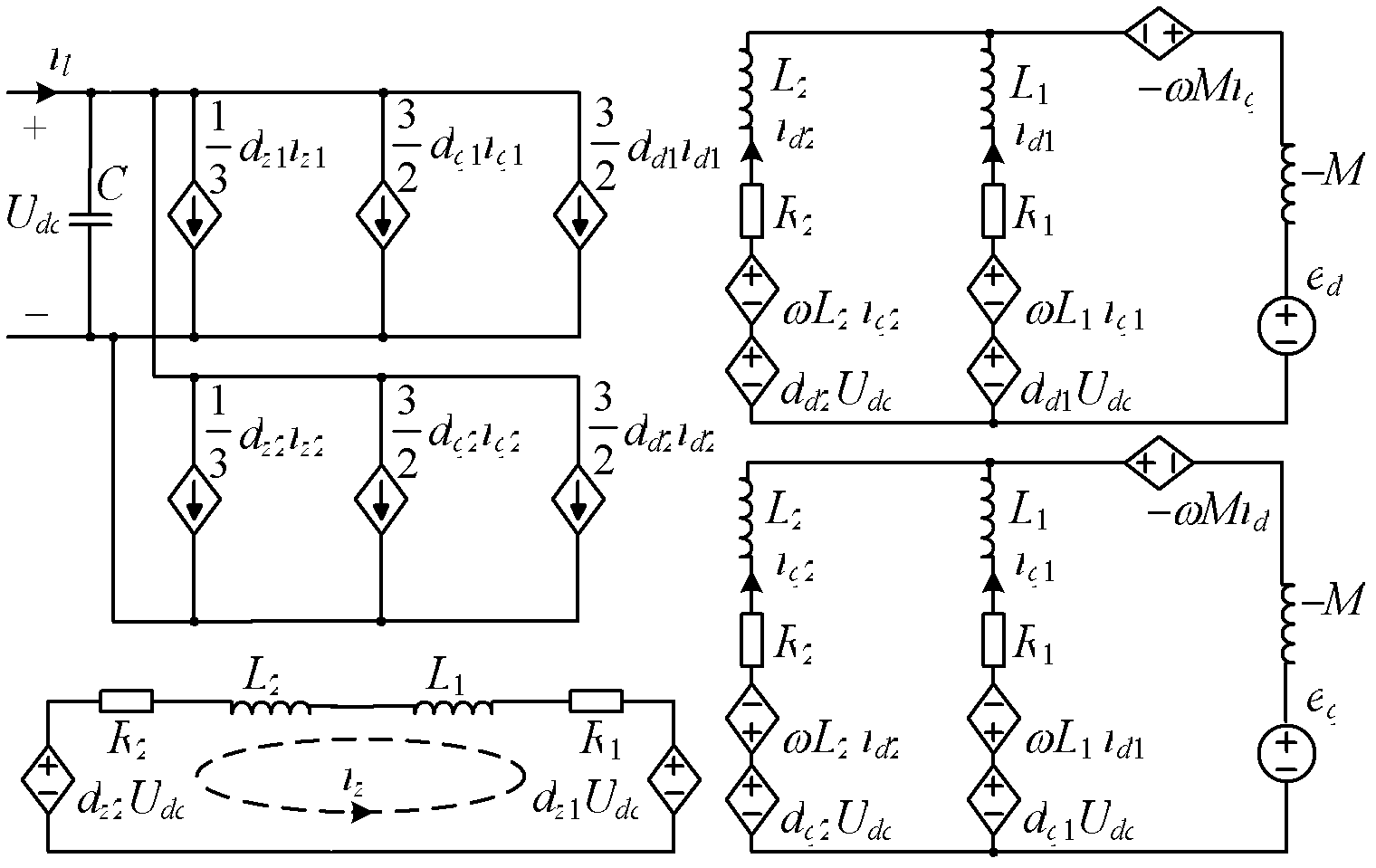
[0040] Specific implementation mode two, see Figure 4 This embodiment will be described. This embodiment describes the control method for the parallel-connected three-phase grid-connected inverter using coupling reactors described in the first embodiment, the control method is: using the DC bus voltage signal obtained by voltage sensor measurement as The DC voltage feedback value Udc, the difference between the DC bus voltage reference value Udcref and the DC voltage feedback value Udc are input to the voltage loop PI controller, and the idref is obtained after being processed by the voltage loop PI controller, and the idref is obtained after weight distribution. Two current given values id1ref, id2ref, the two current given values id1ref, id2ref respectively serve as the current given values of the d-axis current loop controllers of two sets of grid-connected three-phase inverters;
[0041] At the same time, current sensors are used to measure the three-phase current ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0045]Specific Embodiment 3. This embodiment is a further limitation of the control method described in Specific Embodiment 2. In this embodiment, the process of weight distribution is: perform current weighting according to the power capacity of two sets of three-phase inverters Allocation, if the power capacity of the two sets of three-phase inverters is equal, the equivalent allocation is carried out, that is, i d1ref = i d2ref =0.5i dref ; If the power capacities of the two sets of three-phase inverters are not equal, they will be distributed in proportion according to the power capacity, that is, i d1ref =j·i dref , i d2ref =(1-j)i dref , j is the power capacity ratio of two sets of three-phase inverters.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com