Planting method for increasing peanut yield
A planting method and peanut production technology, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems affecting the ventilation and light transmission of the canopy, the uneven distribution of plant stems and branches on the ridge, and the uniform distribution of unfavorable groups, so as to improve the light transmittance and gas exchange, and the canopy The effect of increasing the photosynthetic intensity and increasing the photosynthetic efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Embodiment 1 Spring sowing large peanut field test
[0014] Sowing on April 28, sowing method:
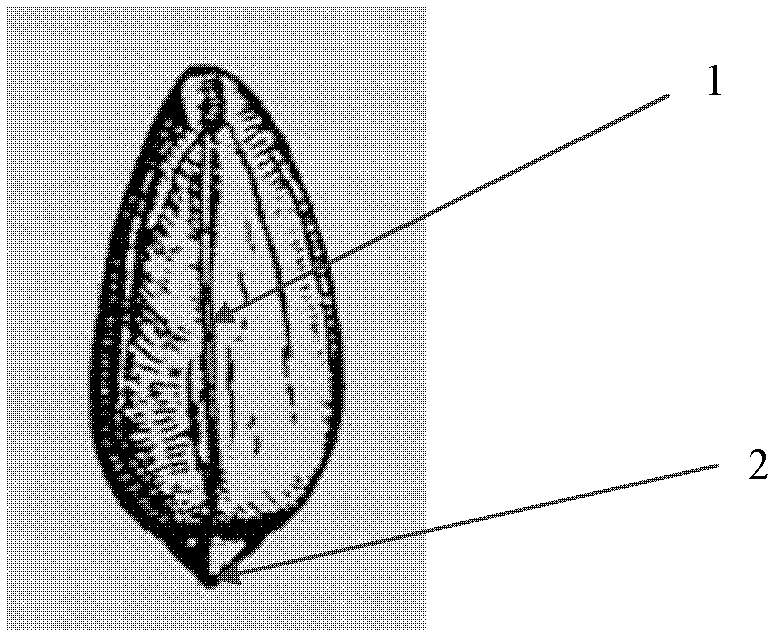
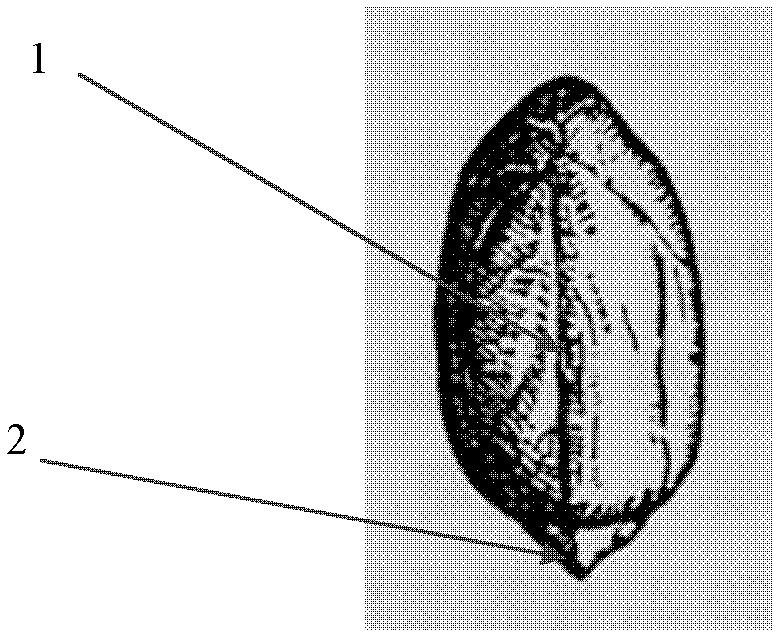
[0015] Experimental group: when sowing, put two seeds side by side in the sowing ditch upright, with the radicle 2 facing down, and make the joint 1 of the two cotyledons parallel to the ridge (such as figure 1 , figure 2 shown), the two holes on the ridge are staggered sowing peanuts (such as image 3 shown).
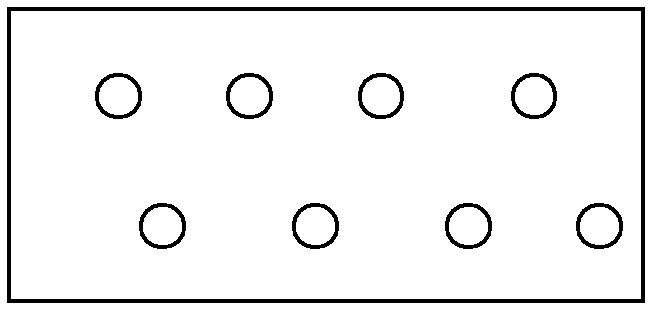
[0016] Control group: the traditional sowing method was adopted, two seeds were randomly placed flat in the sowing ditch, and the positions of the peanuts in the two holes on the ridge were opposite (such as Figure 4 shown).
[0017] The remaining conditions of the experimental group were the same as those of the control group. The ridge distance of the test field was 85 cm, the width of the ridge surface was 55 cm, two rows of peanuts were sown on the ridge, the distance between the holes was 30 cm, and the hole distance was 16.5 cm. Two seeds were planted in ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2 field test of small peanuts sown in spring
[0022] Sowing on May 2, sowing method:
[0023] Experimental group: When sowing, put two seeds side by side in the sowing ditch, with the radicle facing down, and make the joints of the two cotyledons parallel to the ridge direction, and sow peanuts in two holes on the ridge.
[0024] Control group: the traditional sowing method was adopted, two seeds were randomly placed flat in the sowing ditch, and the peanuts in the two holes on the ridge were opposite to each other.
[0025] The remaining conditions of the experimental group were the same as those of the control group. The ridge distance in the test field was 85 cm, the ridge width was 55 cm, two rows of peanuts were sown on the ridge, 30 cm apart, and the hole distance was 16 cm. Two seeds were planted in each hole. The variety is the pearl bean-shaped peanut Huayu No. 20.
[0026] Results: Comparing the date of emergence and CO at the base of plants on t...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3 Summer direct seeding small peanut field test
[0030] Sowing on May 5, sowing method:
[0031] Experimental group: When sowing, put two seeds side by side in the sowing ditch, with the radicle facing down, and make the joints of the two cotyledons parallel to the ridge direction, and sow peanuts in two holes on the ridge.
[0032] Control group: the traditional sowing method was adopted, two seeds were randomly placed flat in the sowing ditch, and the peanuts in the two holes on the ridge were opposite to each other.
[0033] The remaining conditions of the experimental group were the same as those of the control group. The ridge distance in the test field was 85 cm, the ridge width was 55 cm, two rows of peanuts were sown on the ridge, 30 cm apart, and the hole distance was 16 cm. Two seeds were planted in each hole. The variety is the pearl bean-shaped peanut Huayu No. 20.
[0034] Results: Comparing the date of emergence and CO at the base of plants on t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com