Method for preparing barium plumbate powder by coprecipitation of copper anode mud silver separating residue of circuit board
A copper anode slime and circuit board technology, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
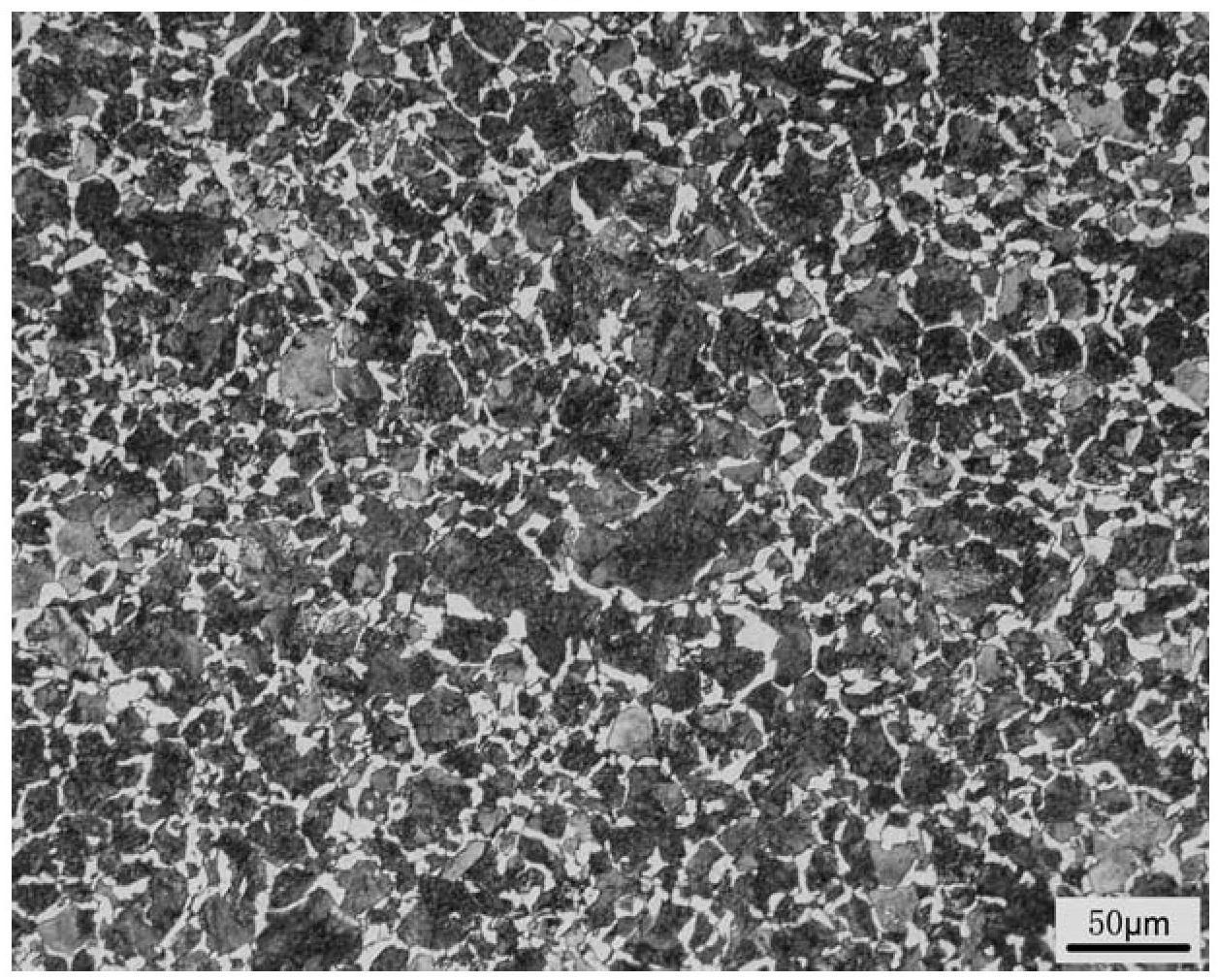
[0017] Preparation process such as figure 1 As shown, put 50kg of circuit board copper anode slime and silver slag (lead content 21.3%) into the stirring tank, add sodium carbonate solution for carbonation reaction. The amount of sodium carbonate added is 3 times the theoretical multiple of carbonation, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:20, the reaction temperature is 60°C, and the reaction time is 120min. The carbonation reaction mixture is filtered to obtain carbonation reaction slag and carbonation reaction liquid. After the carbonation reaction, the liquid is neutralized to neutral with sulfuric acid, and sodium sulfate is recovered by evaporation and crystallization. Put the carbonation reaction slag into the stirring tank, add acetic acid solution to dissolve. The amount of acetic acid added is twice the theoretical multiple of lead carbonate dissolution, the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of the carbonation reaction slag to the acetic acid solution is 1:10, the react...
Embodiment 2
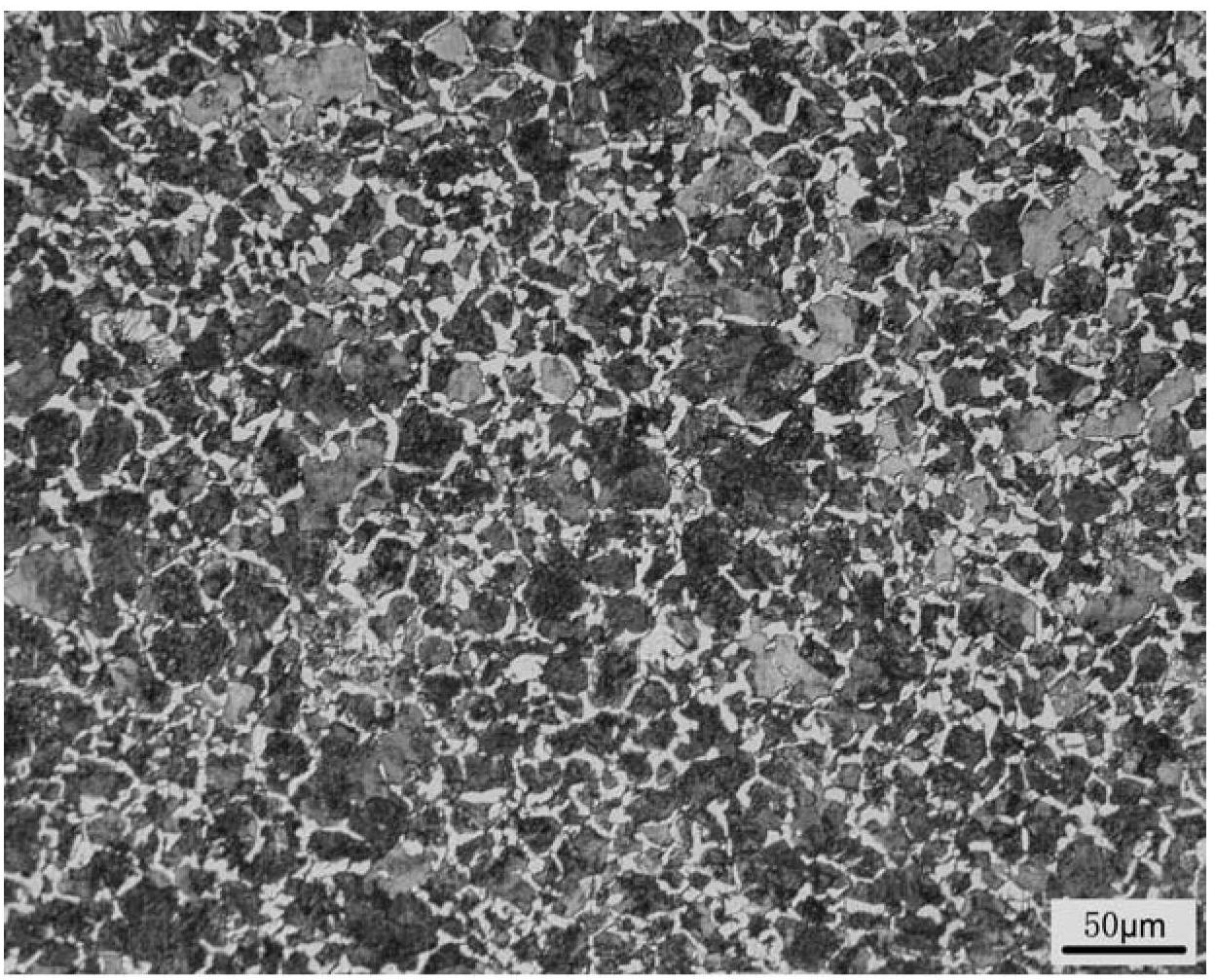
[0019] Put 50kg of circuit board copper anode slime and silver slag (lead content 18.3%) into the stirring tank, add sodium carbonate solution for carbonation reaction. The amount of sodium carbonate added is twice the theoretical multiple of carbonation, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:10, the reaction temperature is 70°C, and the reaction time is 60 minutes. The carbonation reaction mixture is filtered to obtain carbonation reaction slag and carbonation reaction liquid. After the carbonation reaction, the liquid is neutralized to neutral with sulfuric acid, and sodium sulfate is recovered by evaporation and crystallization. Put the carbonation reaction slag into the stirring tank, add acetic acid solution to dissolve. The amount of acetic acid added is 5 times the theoretical multiple of lead carbonate dissolution, the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of the carbonation reaction slag to the acetic acid solution is 1:7, the reaction temperature is room temperature, and the ...
Embodiment 3
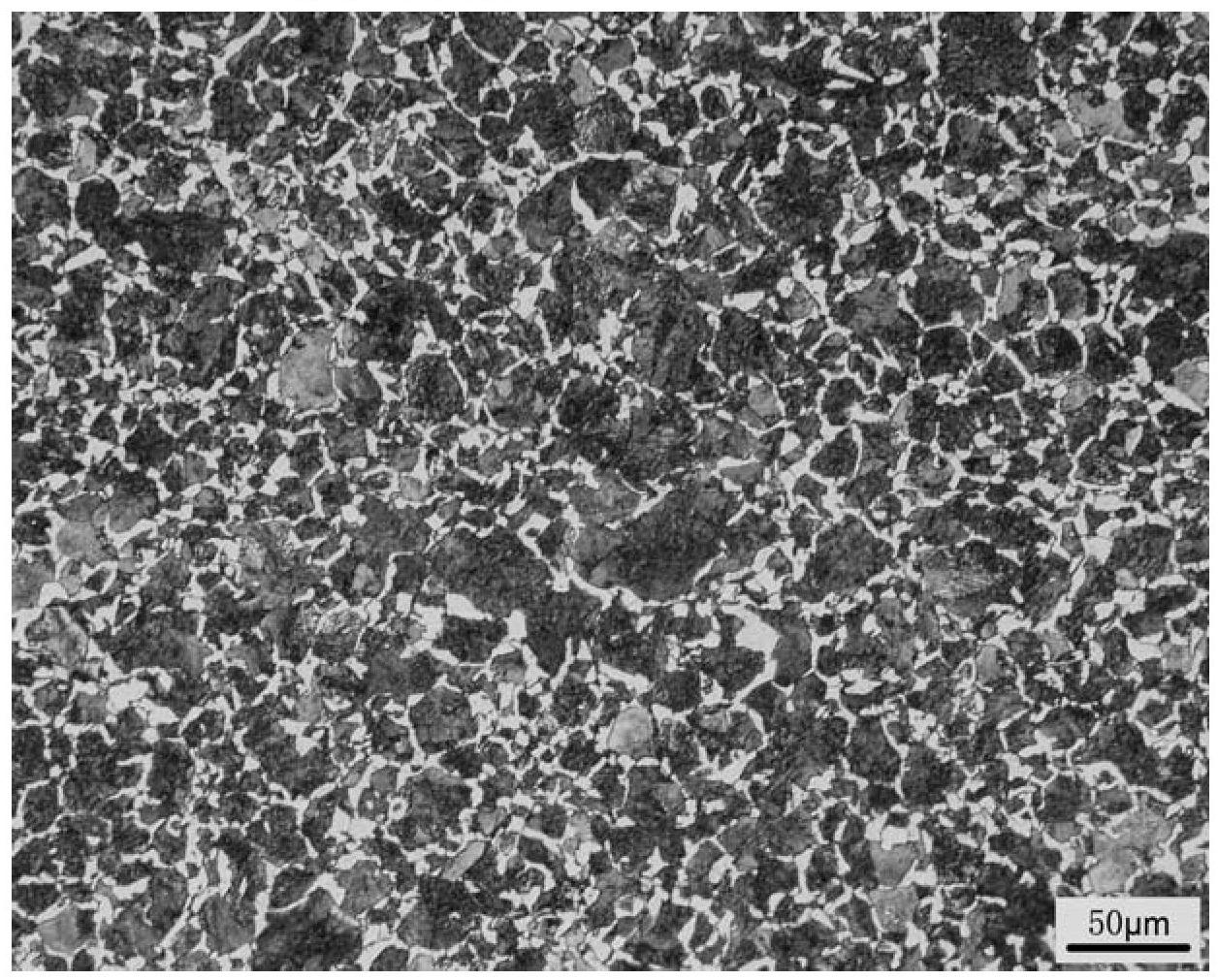
[0021] Put 50kg of circuit board copper anode slime and silver slag (lead content 20.6%) into the stirring tank, add sodium carbonate solution for carbonation reaction. The amount of sodium carbonate added is 5 times the theoretical multiple of carbonation, the mass ratio of solid to liquid is 1:15, the reaction temperature is 20°C, and the reaction time is 120min. The carbonation reaction mixture is filtered to obtain carbonation reaction slag and carbonation reaction liquid. After the carbonation reaction, the liquid is neutralized to neutral with sulfuric acid, and sodium sulfate is recovered by evaporation and crystallization. Put the carbonation reaction slag into the stirring tank, add acetic acid solution to dissolve. The amount of acetic acid added is 3 times the theoretical multiple of lead carbonate dissolution, the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of the carbonation reaction slag to the acetic acid solution is 1:5, the reaction temperature is room temperature, and the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com