Semiconductor light emitting diode (LED) device and formation method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high consumption of gold materials, high gold prices, and high electromigration, and achieve improved service life, improved thermal stability, and improved resistance to The effect of electromigration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
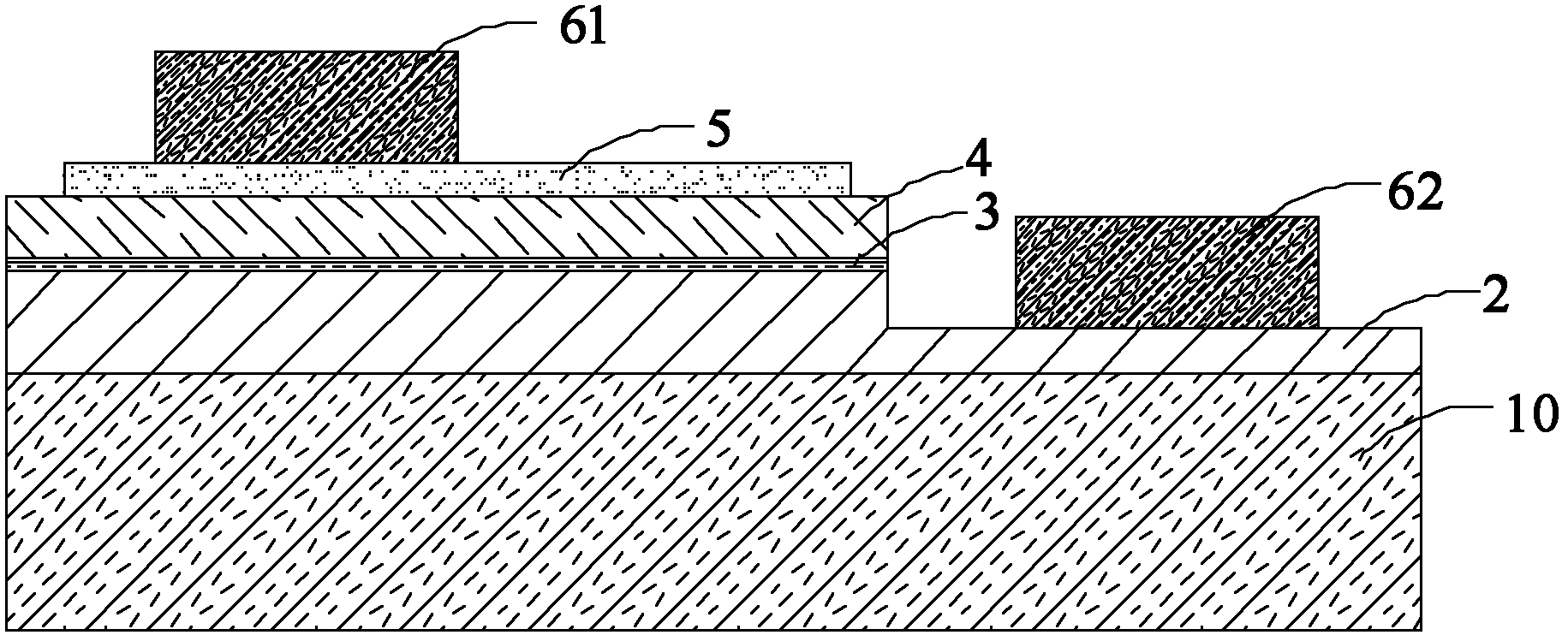
[0082] figure 1 The cross-sectional structure of the semiconductor light emitting diode device of the first embodiment is shown, including: a substrate 10; an N-type semiconductor layer 2, an active layer 3 and a P-type semiconductor layer 4 located on the substrate 10 in sequence; The extended electrode layer 5 on the top; the positive electrode welding layer 61 on the extended electrode layer 5; the trenches located in the P-type semiconductor layer 4, the active layer 3 and the N-type semiconductor layer 2, and the bottom of the trench exposes the N type semiconductor layer 2; the negative electrode welding layer 62 at the bottom of the trench. In this embodiment, the positive electrode welding layer 61 and the negative electrode welding layer 62 are located on the same side of the entire semiconductor light emitting diode device.
[0083] Wherein, the substrate 10 can be a sapphire substrate, the N-type semiconductor layer 2 can be an N-type doped III-V compound semicondu...
no. 2 example
[0095] The structure and forming method of the semiconductor light emitting diode device of the second embodiment are the same as those of the first embodiment, except that the thickness of the positive electrode welding layer 61 and the negative electrode welding layer 62 is 4 μm, and the material is an aluminum alloy of Al-1wt% Cu , the planar area of the active layer 3 is 2025 square milliinches, and the forward voltage is 3.3V when working at 350mA.
no. 3 example
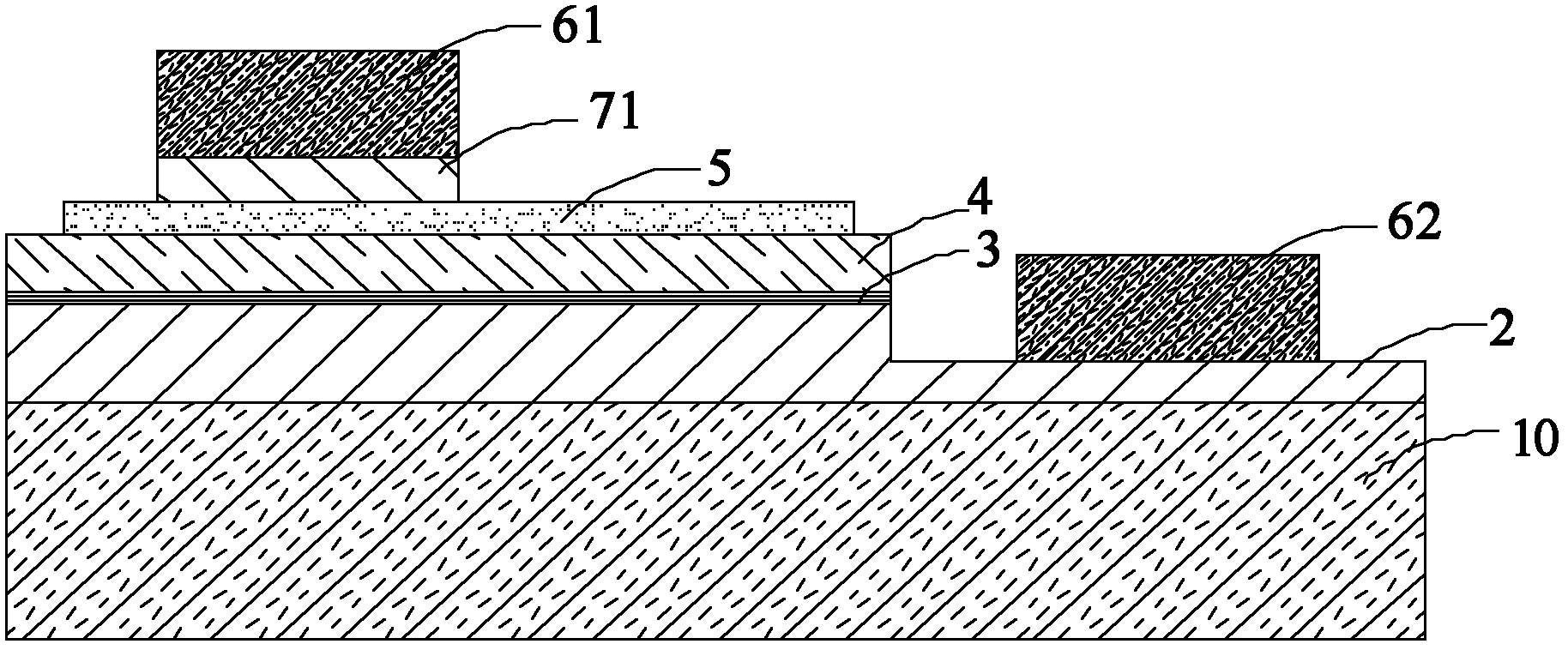
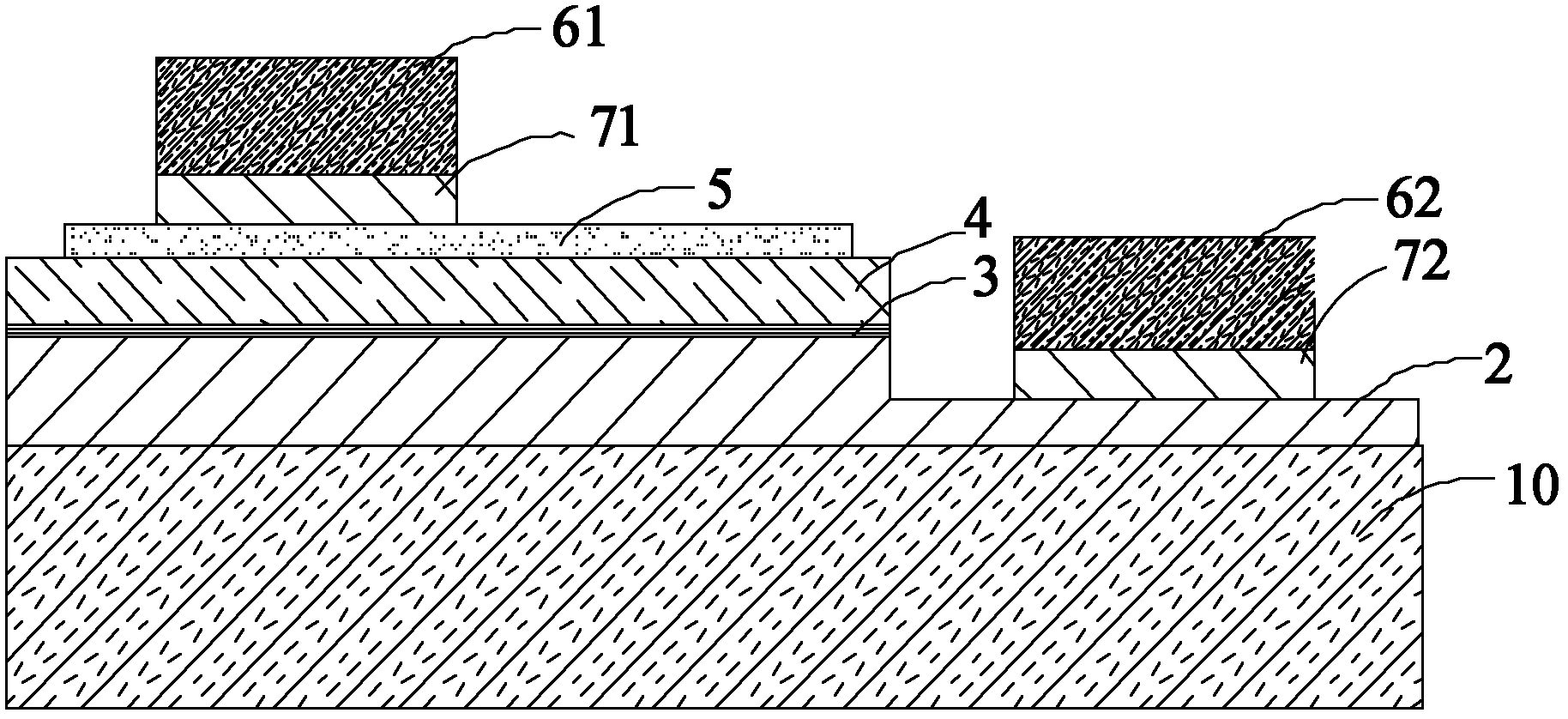
[0097] figure 2 The cross-sectional structure of the semiconductor light emitting diode device of the third embodiment is shown, and its structure and formation method are basically similar to those of the device in the first embodiment, except that a positive electrode contact layer 71 is formed on the extended electrode layer 5, and the positive electrode contact layer 71 is formed on the positive electrode layer 5. The electrode welding layer 61 is formed on the positive electrode contact layer 71 capable of reducing ohmic contact. In addition, a positive electrode transition layer (not shown in the figure) can also be formed between the positive electrode contact layer 71 and the positive electrode welding layer 61, and the positive electrode transition layer can be used to prevent the positive electrode welding layer 61 from contacting the extended electrode layer 5. Interdiffusion reaction, optional materials can be Ti, Pt, Ni, W, TiW, etc.
[0098]In the third embodim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com