Chemotherapy drug pulse sustained-release implant agent and preparation method thereof
A technology for slow-release implants and chemotherapeutic drugs, applied in drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can solve the problems of re-administration, application restrictions, and drugs can only be released once, so as to avoid side damage and prolong Effect of Effective Drug Concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1, preparation of gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres
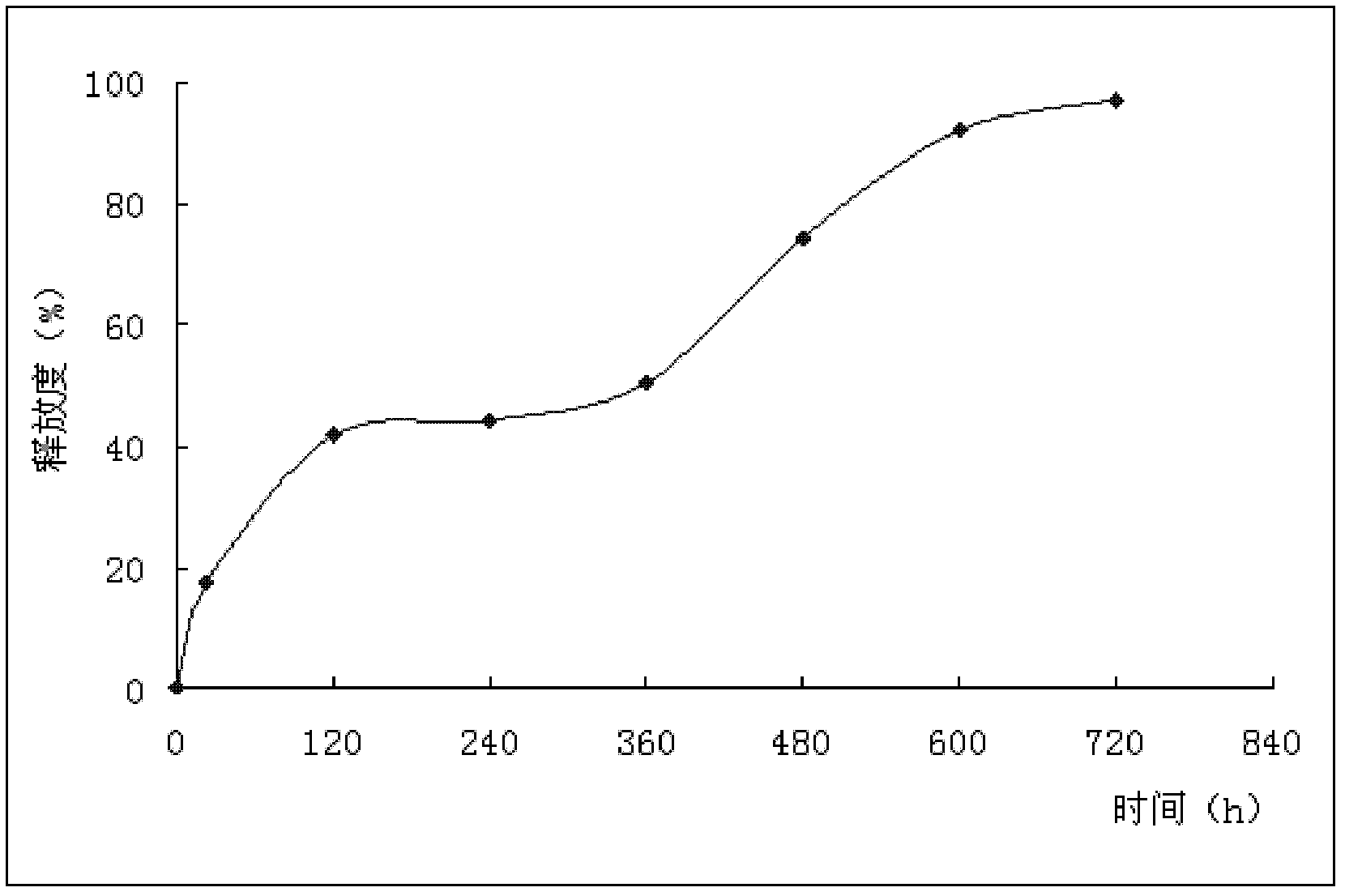
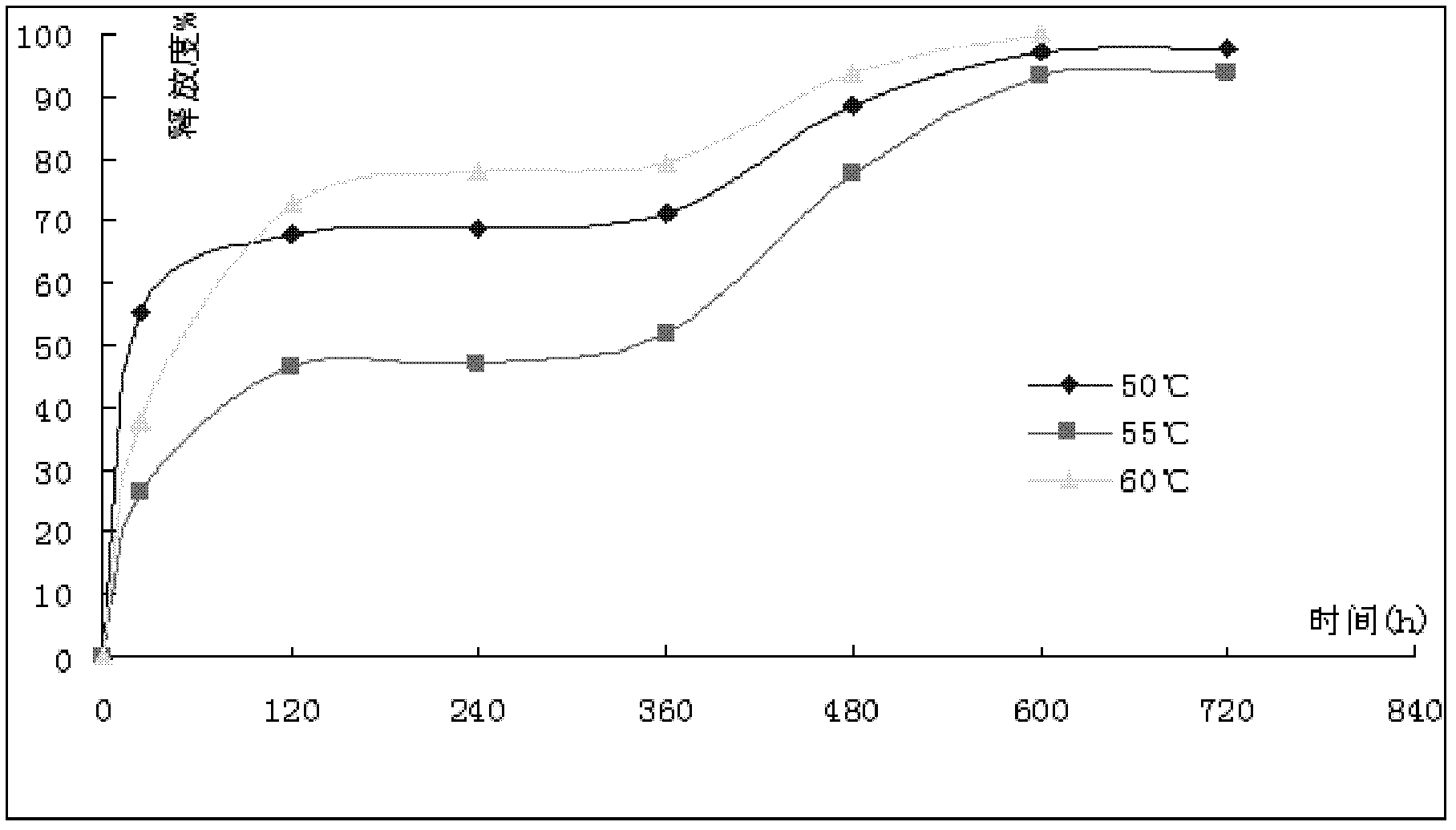
[0026] Pulverize gemcitabine hydrochloride, pass through a 200-mesh sieve, add PLGA (the number average molecular weight is 6000) in dichloromethane solution (the mass-number ratio of gemcitabine hydrochloride and PLGA is 1:9), stir evenly, evaporate the solvent to dryness, and place in a vacuum Dry in a drying oven (-0.1Mpa, 35°C) for 4 hours, take it out and crush it through an 80-mesh sieve, and then dry it for 24 hours, take out the medicinal material, mix it in a melting and mixing equipment with a constant temperature of 120°C, cool it, and crush it. Sieve, take microspheres between 100 mesh and 120 mesh sieves, and process them with a microsphere processor at 55° C. for 10 minutes to obtain gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres, marked as sample A.
[0027] Gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres were prepared according to the same method as above, labeled as sample B and sample C, respectively...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2. Preparation of gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres
[0061] Gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres were prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, except that the melt-kneading temperatures were 110° C. and 130° C., respectively, and the prepared microspheres were marked as sample D and sample E, respectively.
[0062] The stability of gemcitabine hydrochloride during melt kneading at 110 ℃, 120 ℃ and 130 ℃ was investigated, and the detection index was related substances of gemcitabine hydrochloride. The results are shown in Table 4.
[0063] Table 4 Limits of related substances for samples D, A and E
[0064]
[0065] It can be seen from Table 4 that the melt-kneading temperature is 110°C to 130°C, and gemcitabine hydrochloride is stable, and the melt-kneading temperature is preferably 120°C.
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3. Preparation of gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres
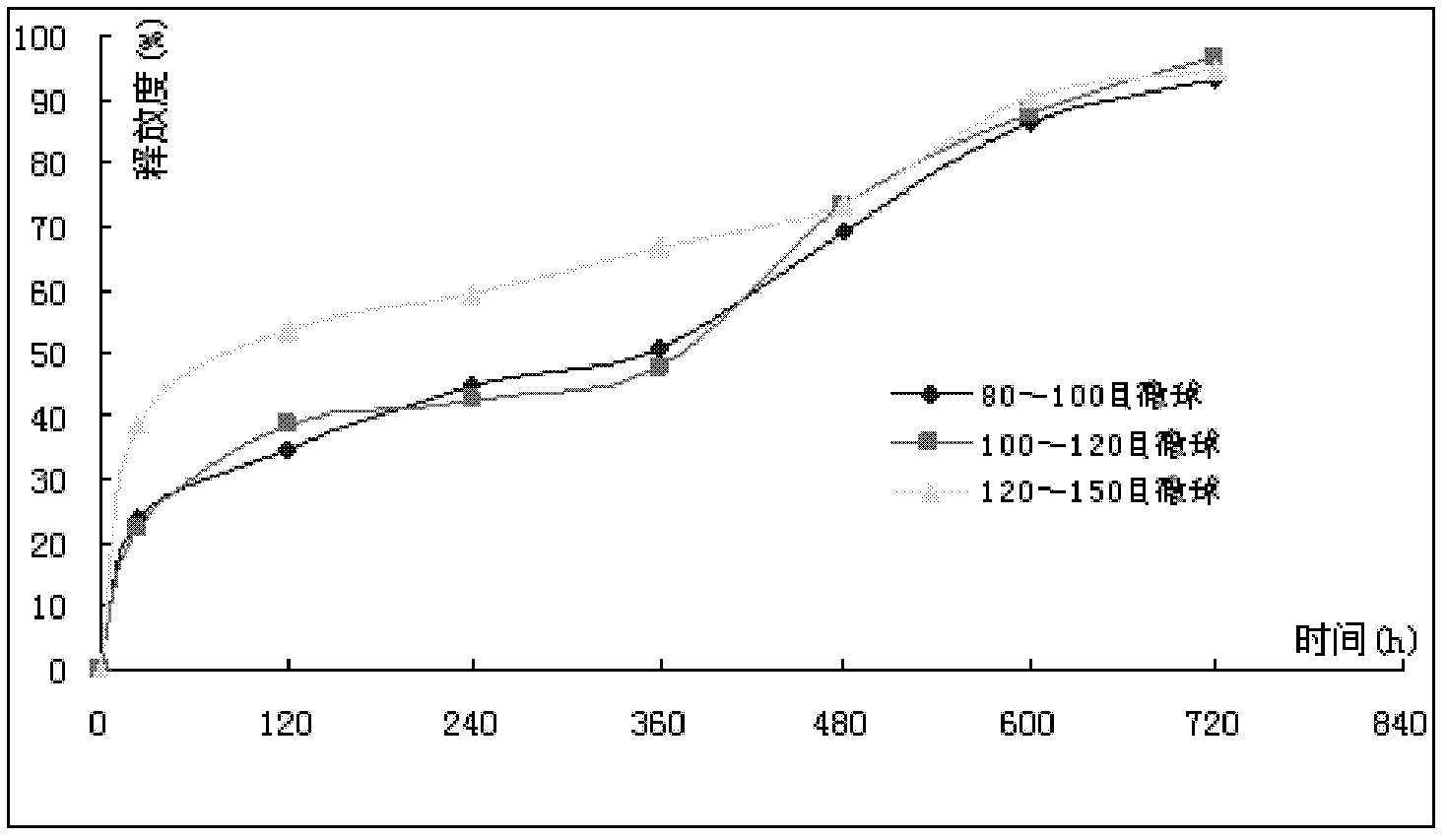
[0067] Gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres were prepared according to the same method as in Example 1, except that the microspheres were passed through 80-100 mesh and 120-150 mesh sieves respectively, and the prepared microspheres were marked as sample F and sample G respectively.
[0068] The in vitro release degrees of samples A, F and G were detected, and the results are shown in Table 5 and figure 2 .
[0069] Table 5 Relationship between in vitro release and time of samples A, F and G
[0070]
[0071] From Table 5 and figure 2 It can be seen that the particle size of the microspheres is between 80-100 mesh sieves and 100-120 mesh sieves, and the in vitro release of gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres can meet the project design requirements. Considering clinical applications, the smaller the particle size, the more convenient, preferably 100-120 mesh microspheres between the sieves. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com