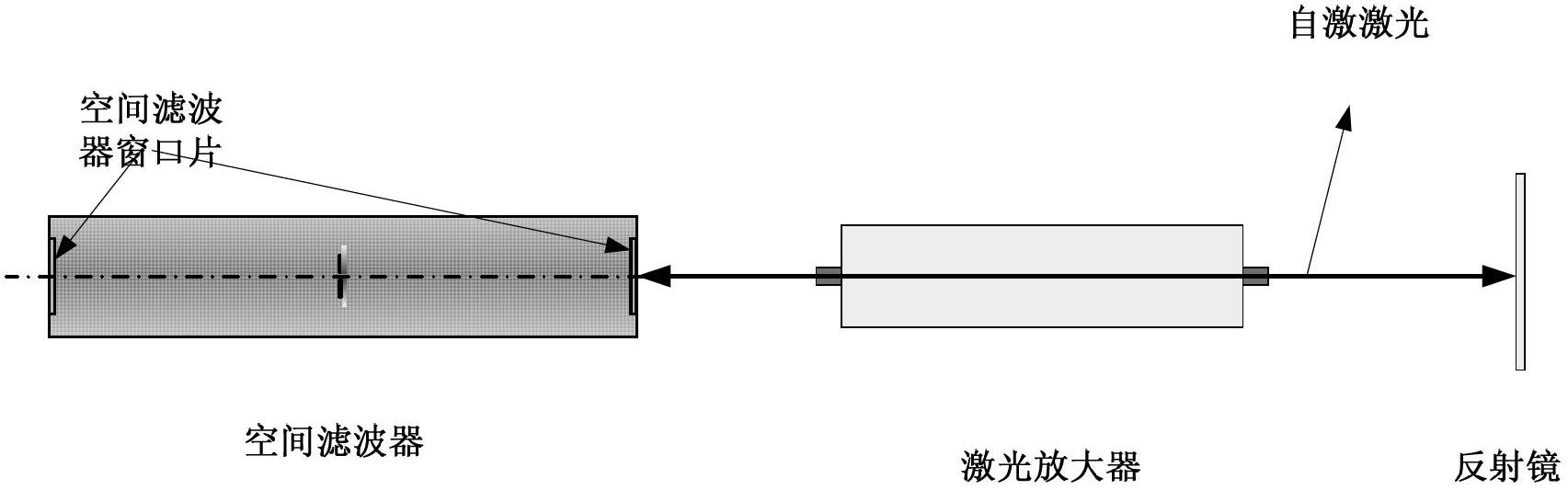
Spatial filter and laser amplification device adopting same
A space filter and laser beam technology, applied in the field of optics, can solve the problems of self-excited oscillation, the transmittance of the window cannot reach 100%, and the damage is large. It is easy to realize, avoid laser self-excited oscillation, and easy to operate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
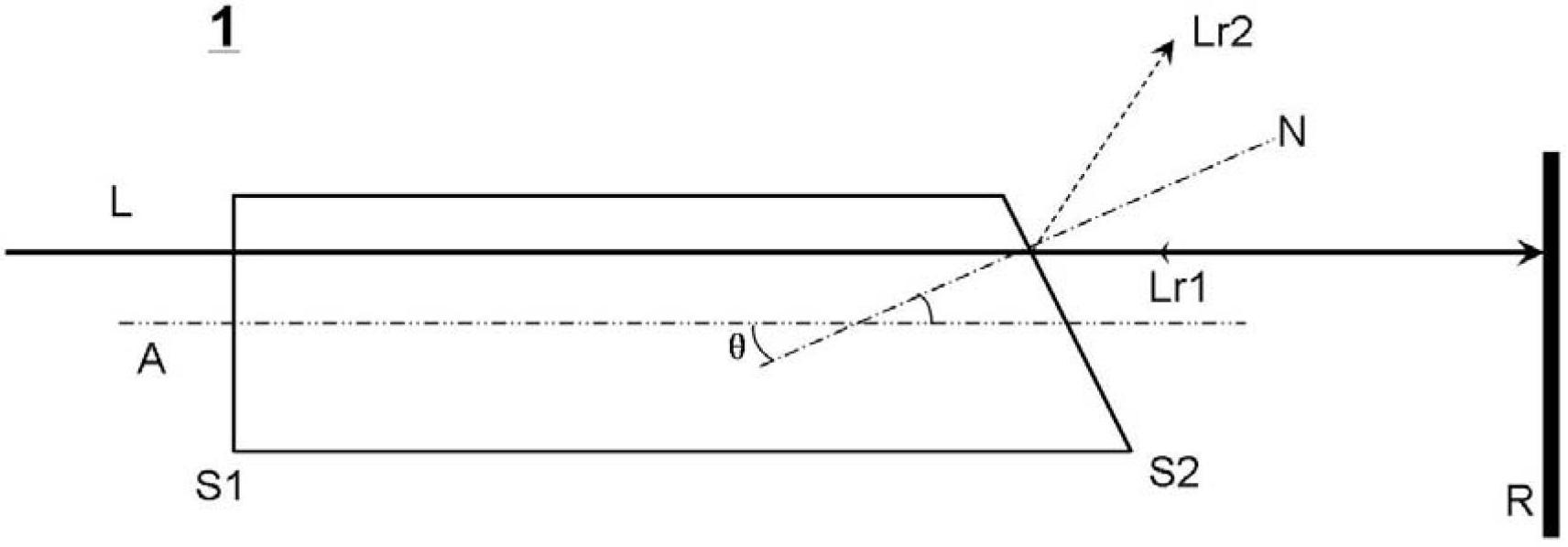
[0025] This embodiment provides a spatial filter 1, the structure of which is as follows figure 2 As shown, the spatial filter 1 is rod-shaped extending along the longitudinal axis A, which has windows S1 (incident window) and S2 (exit window), wherein the window S1 is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis A, that is, the window S1 The normal is parallel to the longitudinal axis A, and the window S2 is not perpendicular to the longitudinal axis A, that is, the normal N of the window S2 and the longitudinal axis A form an angle θ (0° figure 2 It is a schematic cross-sectional view obtained by cutting the spatial filter 1 along the plane where the normal N of the window S2 and the longitudinal axis A lie.
[0026] From figure 2 It can be seen that when the incident laser beam L enters the spatial filter perpendicular to the window S1, the incident laser beam L propagates along the direction of the longitudinal axis A and exits from the window S2, and finally enters the mirror...
Embodiment 2
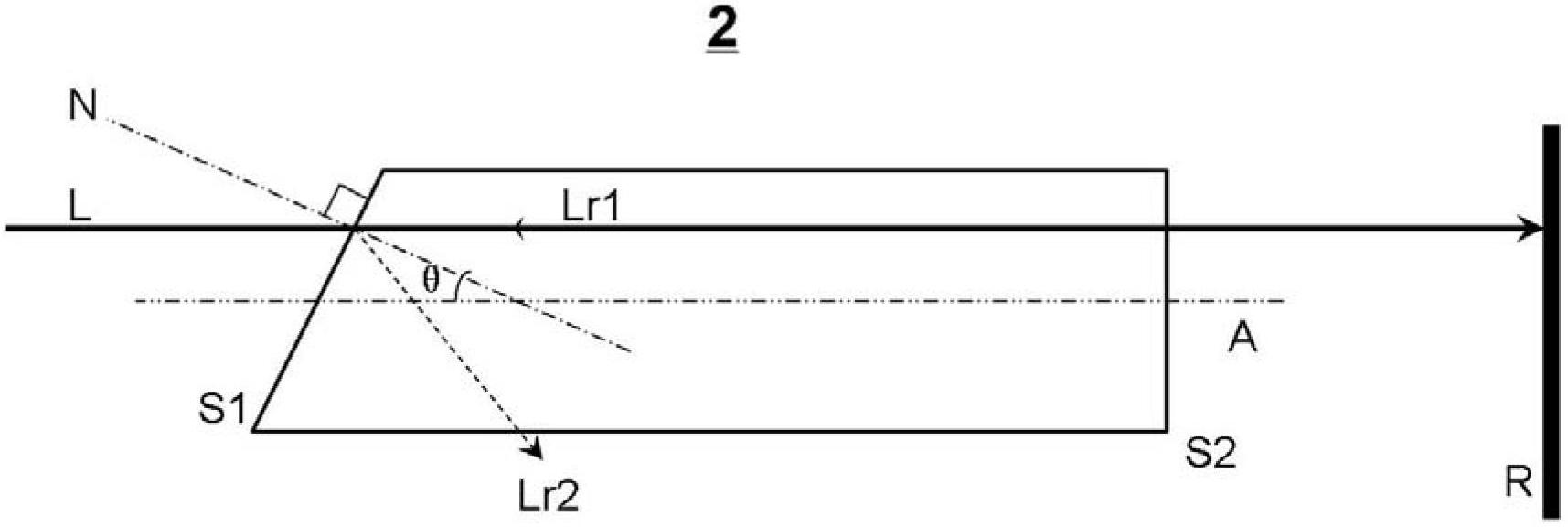
[0028] This embodiment provides a spatial filter 2, its structure is as follows image 3 As shown, the spatial filter 2 is rod-shaped extending along the longitudinal axis A, which has windows S1 (incident window) and S2 (exit window), wherein the window S2 is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis A, that is, the window S2 The normal line is parallel to the longitudinal axis A, and the window S1 is not perpendicular to the longitudinal axis A, that is, the normal N of the window S1 and the longitudinal axis A form an angle θ (0° image 3 It is a schematic cross-sectional view obtained by cutting the spatial filter 2 along the plane where the normal N of the window S1 and the longitudinal axis A lie.
[0029] From image 3 It can be seen that when the incident laser beam L is incident into the spatial filter parallel to the longitudinal axis A, the incident laser beam L propagates along the direction of the longitudinal axis A and exits from the window S2, and finally enters th...
Embodiment 3
[0031] This embodiment provides a spatial filter 3, its structure is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the spatial filter 3 is rod-shaped extending along the longitudinal axis A, and has windows S1 (incident window) and S2 (exit window), wherein both the windows S1 and S1 are non-perpendicular to the longitudinal axis A, and the window The normal N1 of the sheet S1 forms an included angle θ with the longitudinal axis A (0° Figure 4 It is a schematic cross-sectional view obtained by cutting the spatial filter 3 along the plane where the normal N1, the normal N2, and the longitudinal axis A are located.
[0032] From Figure 4 It can be seen that when the incident laser beam L is incident into the spatial filter parallel to the longitudinal axis A, the incident laser beam L propagates along the direction of the longitudinal axis A and exits from the window S2, and finally enters the mirror perpendicular to the longitudinal axis A On R, before it is incident on the mirror R, it als...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com