Data transmission method and system
A data transmission method and data packet technology, which are applied in digital transmission systems, transmission systems, encoding, etc., can solve the problems of continuous propagation of decoding errors, etc., to overcome error propagation, reduce decoding overhead, and reduce encoding and decoding complexity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
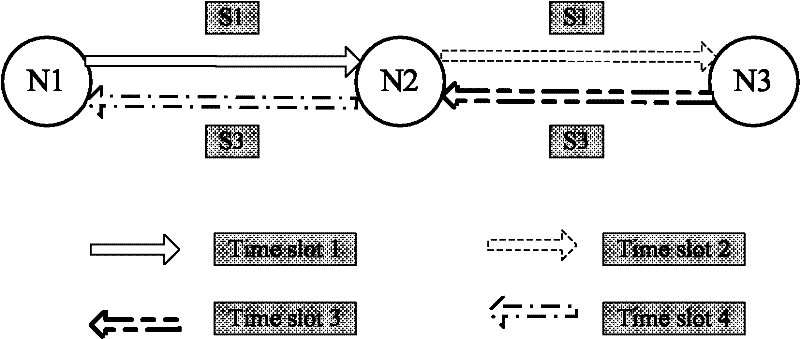
[0044] User A uses Raptor code to send N1≥K data packets to the base station (or relay), where K is the number of original data packets, and N1 is the number of actually sent data packets encoded by Raptor code; when the base station correctly decodes K After the original data packet, the base station sends an ACK confirmation message to user A; when user A receives the ACK message from the base station, it stops sending data packets.
[0045] User B uses Raptor codes to send N2≥K data packets to the base station or relay, where K is the number of original data packets, and N2 is the number of actually sent data packets encoded by Raptor codes; when the base station correctly decodes K original data packets After the data packet, the base station sends an ACK confirmation message to user B; when user B receives the ACK message from the base station, it stops sending data packets;
[0046] The base station (or relay) performs network coding on the original data packets sent by ...
Embodiment 2
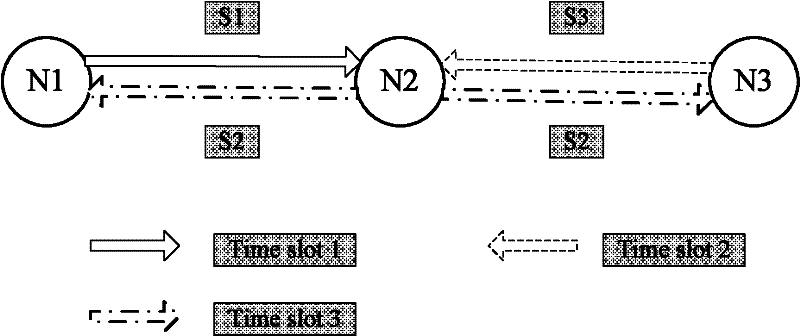
[0063] User A uses Raptor code to send N1≥K data packets to the base station (or relay), where K is the number of original data packets, and N1 is the number of actually sent data packets encoded by Raptor code; when the base station correctly decodes K After the original data packet, the base station sends an ACK confirmation message to user A; when user A receives the ACK message from the base station, it stops sending data packets.
[0064] User B uses Raptor codes to send N2≥K data packets to the base station or relay, where K is the number of original data packets, and N2 is the number of actually sent data packets encoded by Raptor codes; when the base station correctly decodes K original data packets After the data packet, the base station sends an ACK confirmation message to user B; when user B receives the ACK message from the base station, it stops sending data packets;
[0065] The base station (or relay) performs network coding on the original data packets sent by ...
Embodiment 3
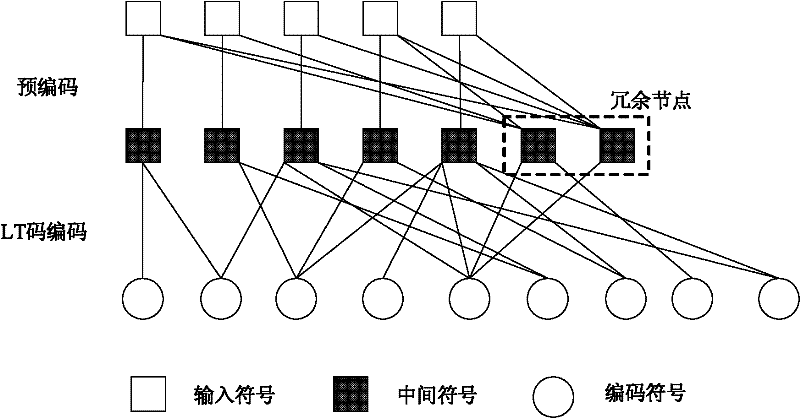
[0078] User A uses fountain codes to send N1≥K data packets to the base station (or relay), where K is the number of original data packets, and N1 is the number of actually sent data packets encoded by fountain codes; when the base station correctly decodes K After the original data packet, the base station sends an ACK confirmation message to user A; when user A receives the ACK message from the base station, it stops sending data packets.
[0079] User B uses fountain codes to send N2≥K data packets to the base station or relay, where K is the number of original data packets, and N2 is the number of actually sent data packets encoded by fountain codes; when the base station correctly decodes K original data packets After the data packet, the base station sends an ACK confirmation message to user B; when user B receives the ACK message from the base station, it stops sending data packets;
[0080] The base station (or relay) performs network coding on the original data packet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com