Method for separating non-wood lignocellulosic biomass lignin with composite solvents
A technology of lignin and extraction method, applied in continuous pulping process, pulping with inorganic alkali, etc., can solve the problems of crude lignin yield not higher than 65%, degradation of lignin molecular structure, low purity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Separation process:
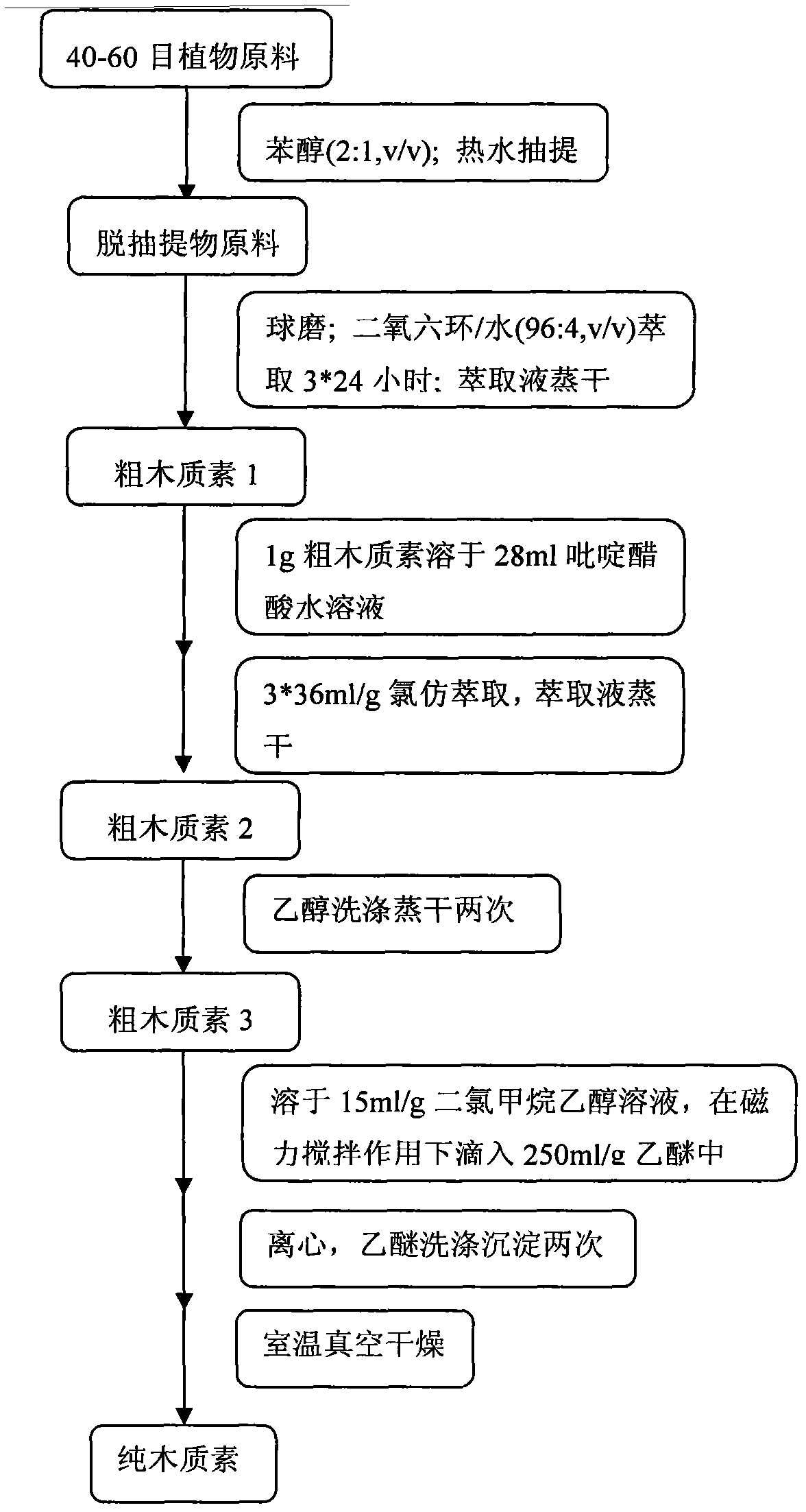
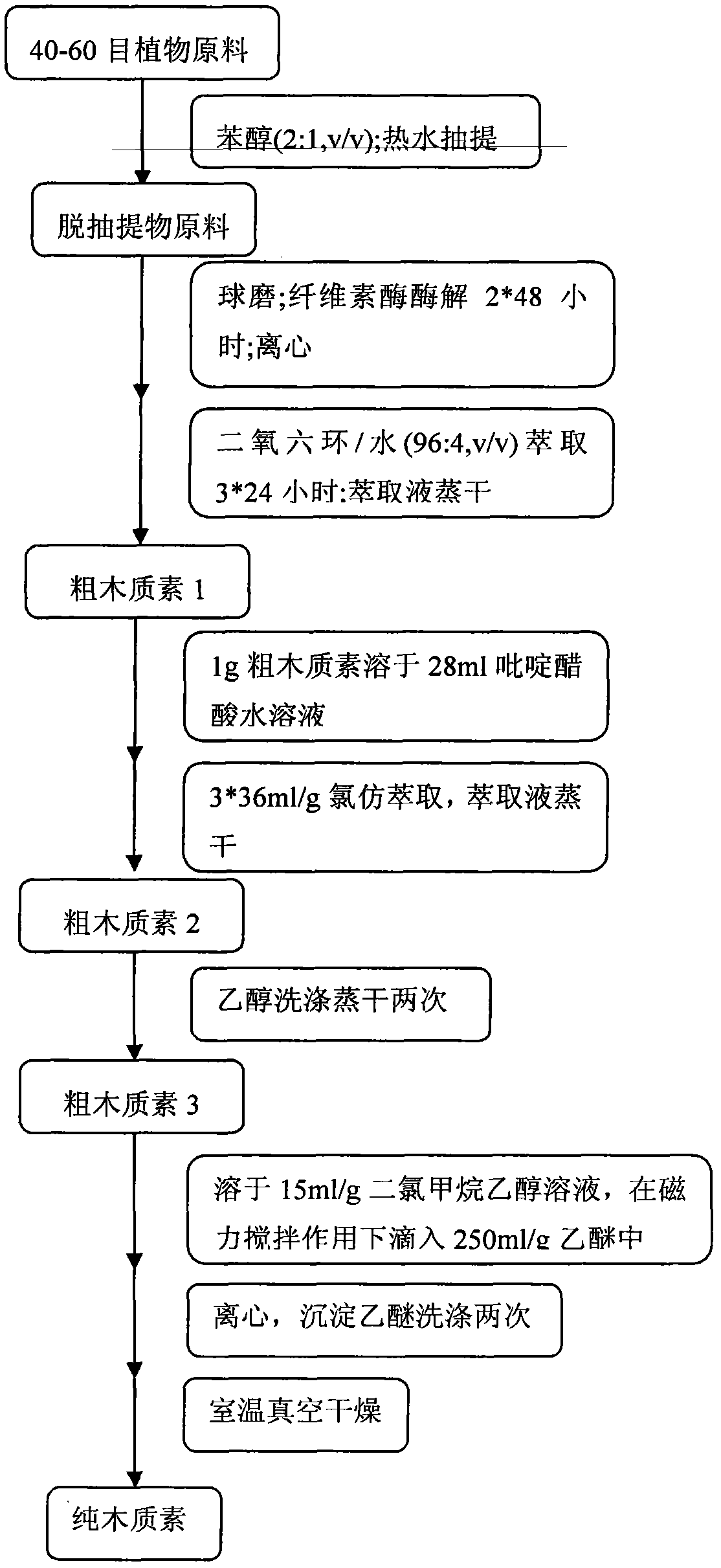
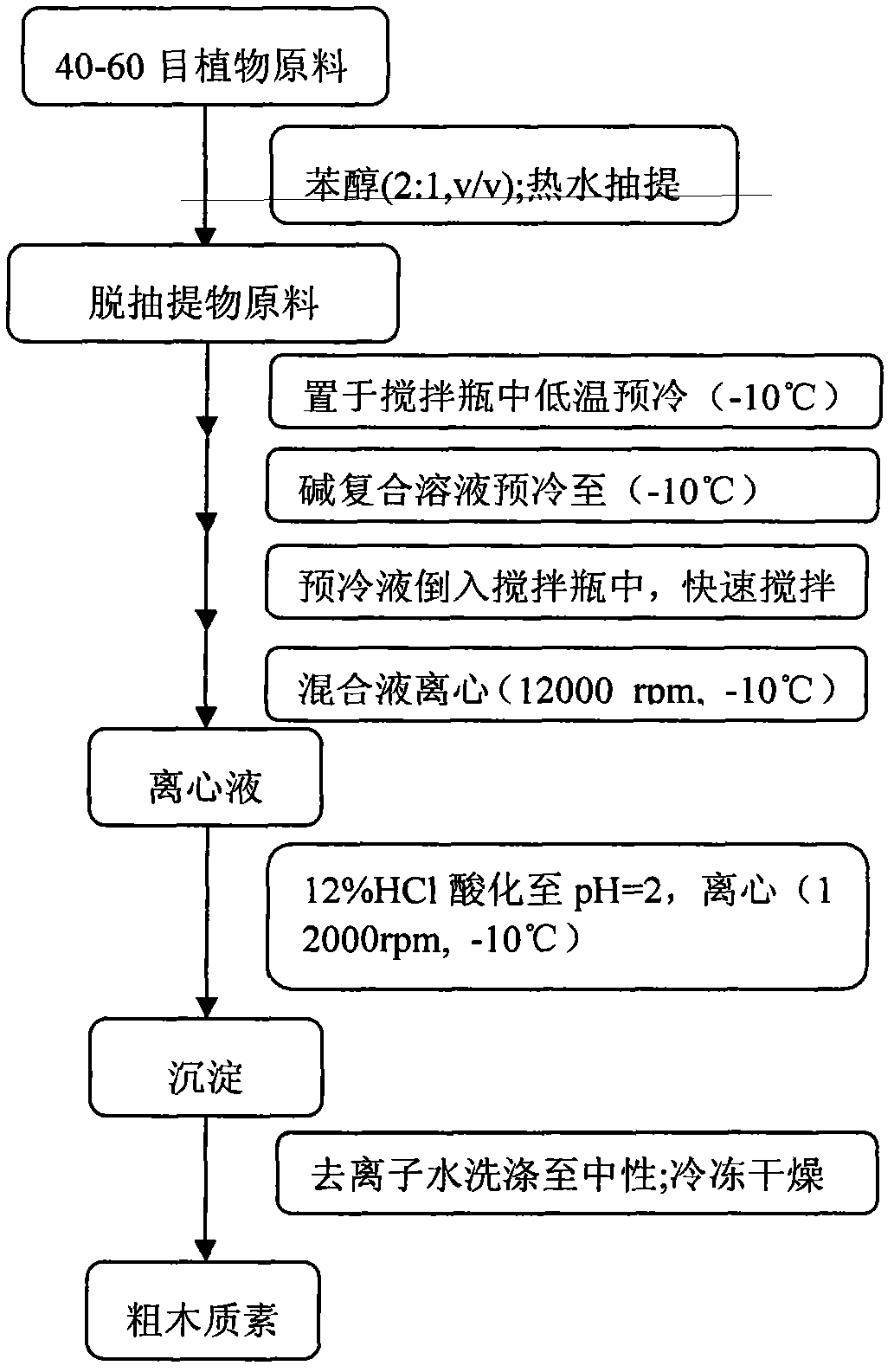
[0020] Below through specific embodiment and in conjunction with appendix image 3 Explain the separation process: remove the leaves, ears, sheaths and nodes of wheat grass, grind 40-60 mesh grass powder through a plant grinder, and then extract with benzene alcohol (benzene and ethanol, the volume ratio is 2:1) and hot water extraction , air-dried for later use. Weigh 6g of absolute dry grass powder into a 500ml polyethylene bottle, stir, and pre-cool at -10°C for 3 hours, weigh 10g, 8g, 6.5g and 69.5g of sodium hydroxide, urea, thiourea and deionized water g mixed and poured into a 500ml polyethylene bottle, mixed and pre-cooled at -10°C for 3 hours.
[0021] After pre-cooling, quickly pour the alkali compound solution into a stirring bottle containing grass powder, stir at 8000rpm for 3 minutes, then transfer to a 500ml centrifuge bottle, and centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10 minutes at -10°C. The centrate and residue were collected separately....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com