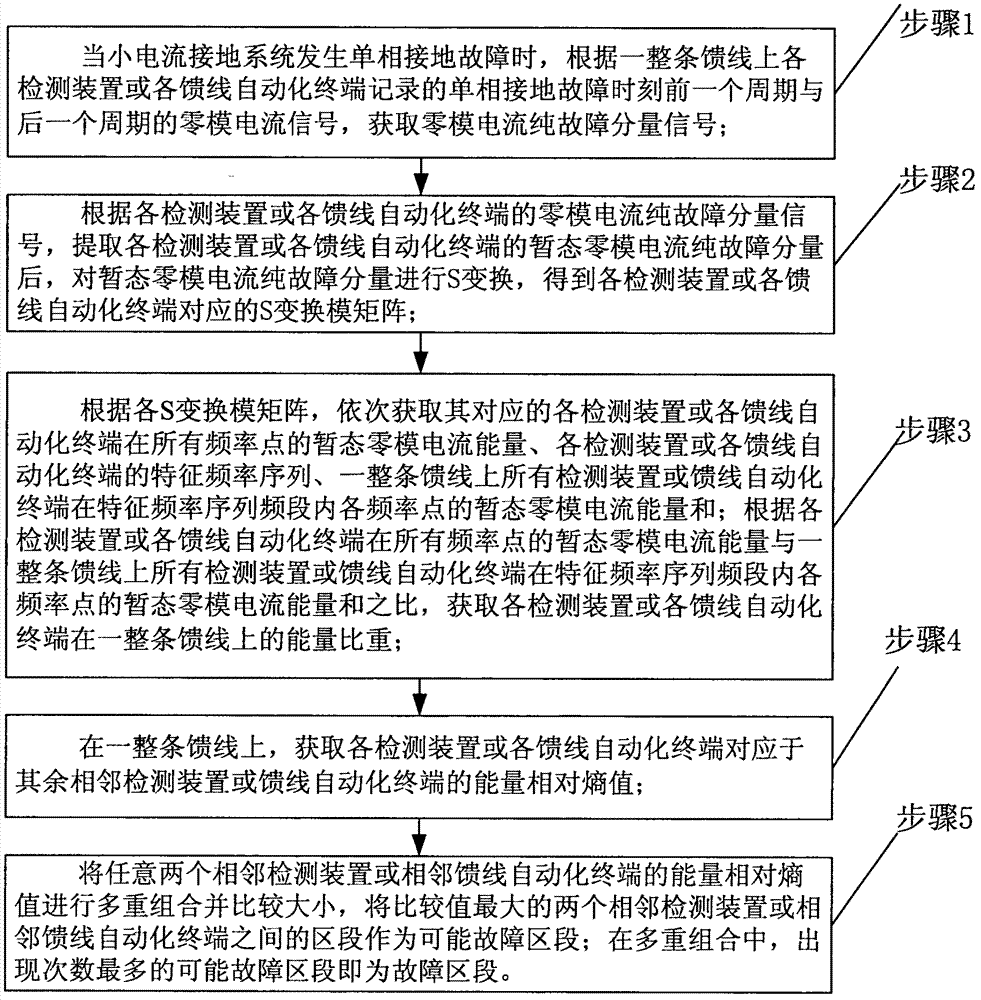
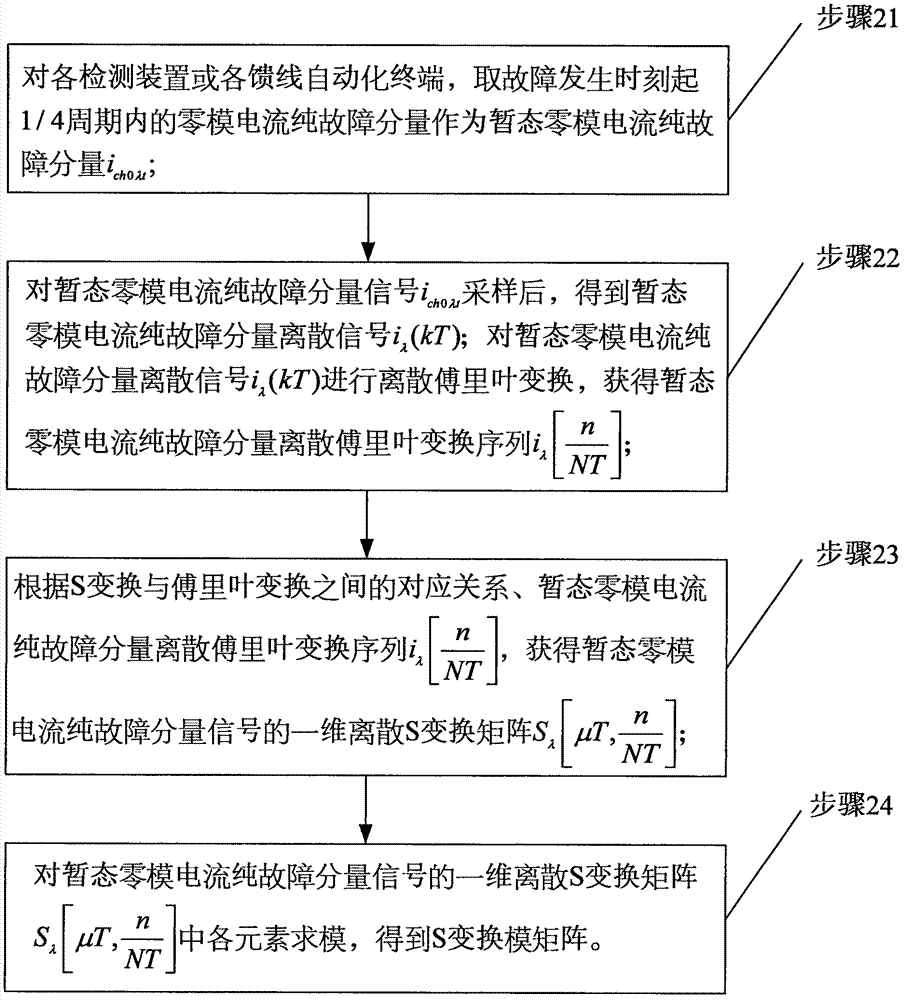
Single-phase ground fault section positioning method for low-current grounding system
A single-phase grounding fault, small current grounding technology, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve the problem of low detection accuracy, and achieve the effect of high detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0066] Figure 5 It is the overhead line transmission model of the small current grounding system described in the embodiment of the present invention. Such as Figure 5 As shown, four detection devices A, B, C, and D are installed along a feeder line, assuming that the single-phase ground fault occurs in the BC section.
[0067] In this embodiment, the line parameters are: positive sequence impedance Z 1 =0.17+j0.38Ω / km, positive sequence ground admittance b 1 =j3.045us / km, zero sequence impedance Z 0 =0.23+j1.72Ω / km, zero sequence ground admittance b 0 = j1.884us / km, l 1 = 20km, l 2 = 15km, l 3 = 24km, l 4 = 8km, l 5 = 16km, l 6 = 30km. The parameters of the transformer are: Δ / Y connection, the primary side voltage is 220KV, the secondary side voltage is 35KV, and the leakage impedance of the primary winding is Z 1δ =0.4+j12.2Ω, the leakage impedance of the secondary winding is Z 2δ =0.006+j0.183Ω, the steady-state excitation current is 0.672A, the main magnetic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com