Method for transmitting data packet in mobile communication system
A mobile communication system and data packet technology, which is applied in the field of data packet transmission in mobile communication systems, can solve the problems of reduced data transmission efficiency and complex processing, and achieve the effect of occupying less physical transmission resources and improving data transmission efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be further described below through specific embodiments.
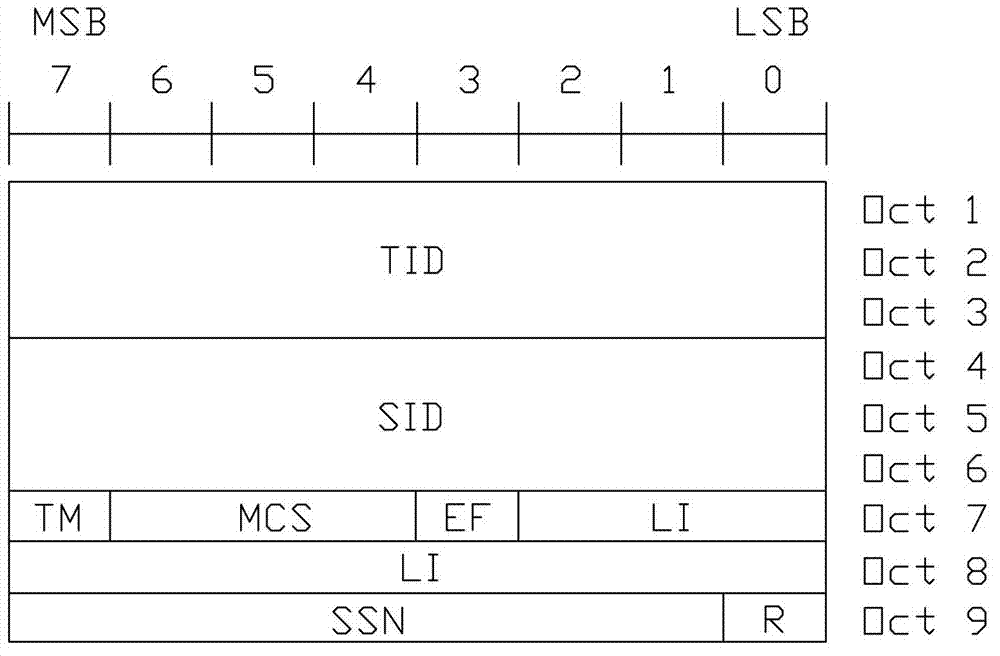
[0029] refer to image 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 , a method for sending data packets in a mobile communication system, segmenting a service data unit SDU and processing it to generate one or more protocol data units PDUs, and then dividing the PDUs into byte-aligned segments that can be allocated in just one wireless frame One or multiple transmission blocks of the same length transmitted by physical channel resources, when the data payload of the last segment is not enough to fill the entire segment, add padding bits at the end of the segment, so that the length of the segment is the same as The other segments are the same, and a unified data packet header is used to indicate the transmission format of these transmission blocks. Specifically include the following steps:
[0030] ① Segment the service data unit SDU;
[0031] ② Add CRC to SDU segment to generate PDU;
[0032] ③ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com