Bioadhesive compositions of local anaesthetics
A technology for local anesthetics and bioadhesion, which is used in anesthetics, drug combinations, active ingredients of heterocyclic compounds, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Example 1. Formulations using a lyotropic phase
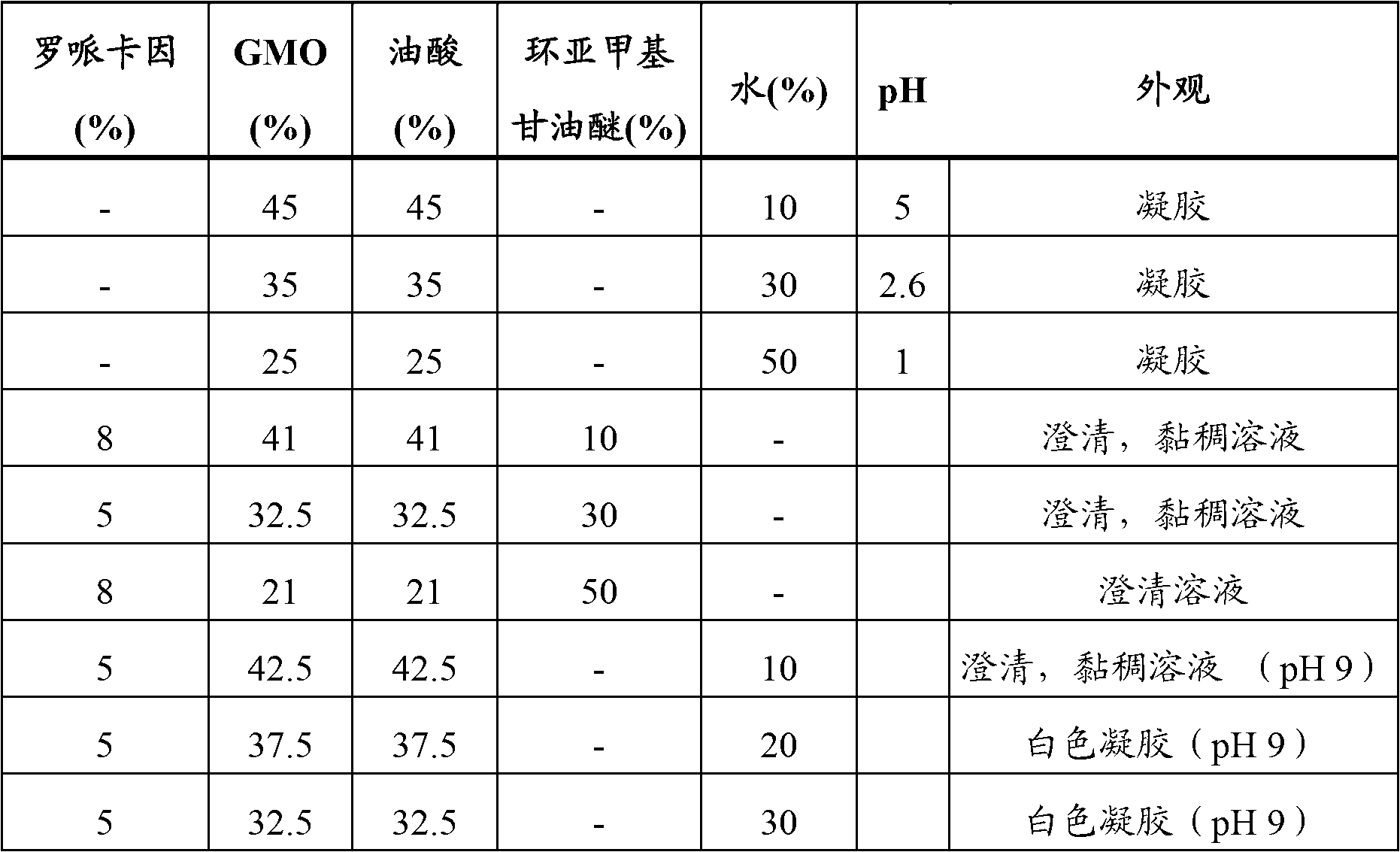
[0096] Preliminary tests were performed on the lyotropic phase system in Table 2 to determine the feasibility of this approach. Research has found that by mixing glyceryl monoolein (GMO), oleic acid and water, a gel (very similar to a cubic phase) is formed. In the prepared formulation, ropivacaine was mixed with GMO, oleic acid and water to form a white gel.
[0097] Table 2. Initial testing of lyotropic phase systems.
[0098] Addition of water refers to the addition of NaOH (aqueous solution) to adjust the pH of the composition containing the local anesthetic to 8.5.
[0099]
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2. Formulations containing GMOs and oleic acid
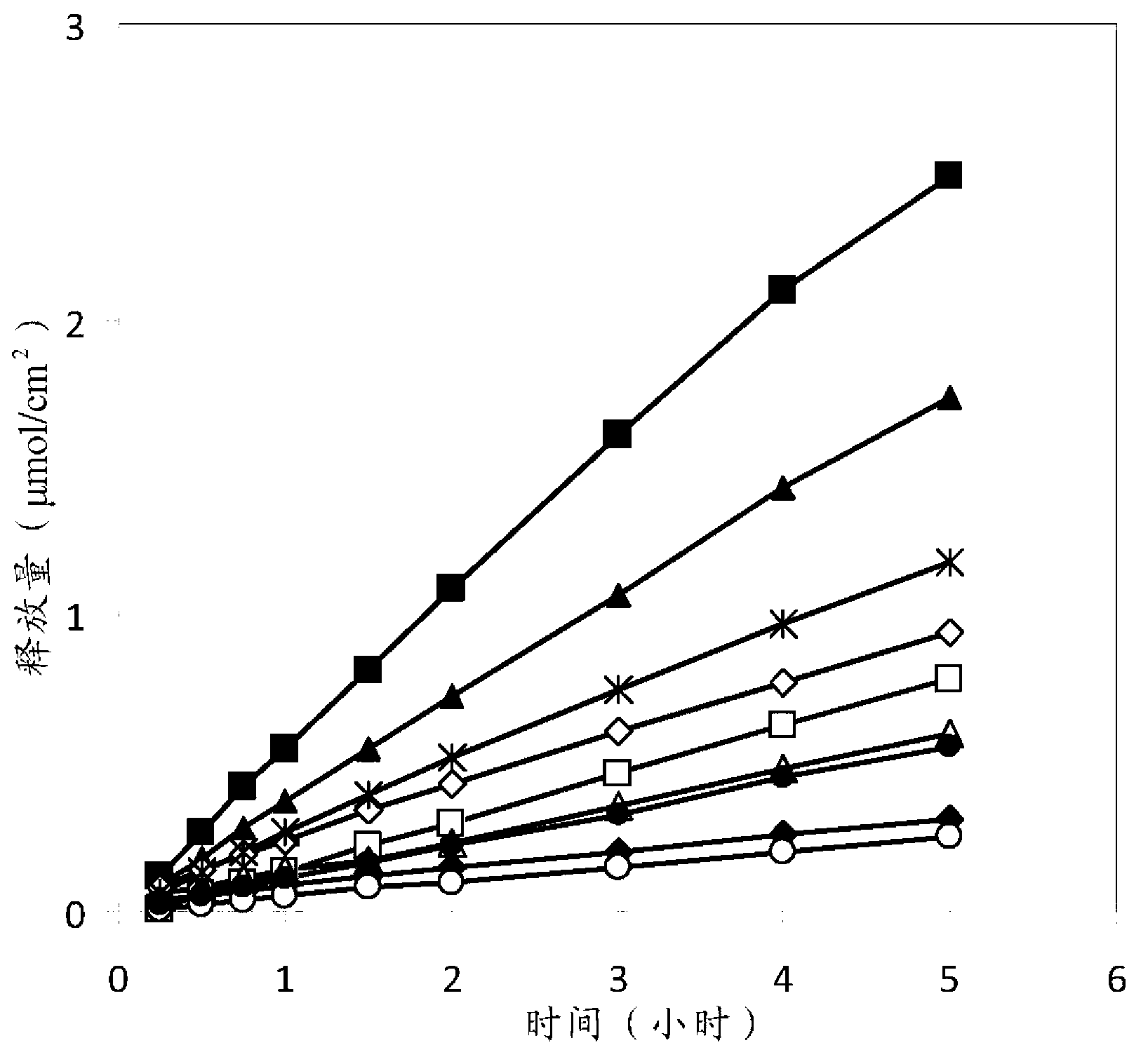
[0101] The different excipients in the composition are related to the amount of ropivacaine in the formulation. In Table 3, formulations containing different concentrations of ropivacaine are listed. The table is categorized by the concentration of increased ropivacaine in the formulation. The different combinations of these components result in a gel-like formulation in which ropivacaine is dissolved. The phase properties of the formulations were investigated using crossed-polarizers to distinguish between lamellar and cubic phases in colloidal formulations.
[0102] Table 3A. Ropivacaine, Lipids – GMO, Organic Acids – Oleic Acid
[0103] Studying formulations that gel in situ
[0104]
[0105]
[0106] It should be noted that pH has a significant effect on the viscosity of the formulation, with higher pH closer to pH 9 increasing the viscosity. Both the pH of the formulation and the amount of wate...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Example 3. Formulations in which GMOs were replaced with other lipids
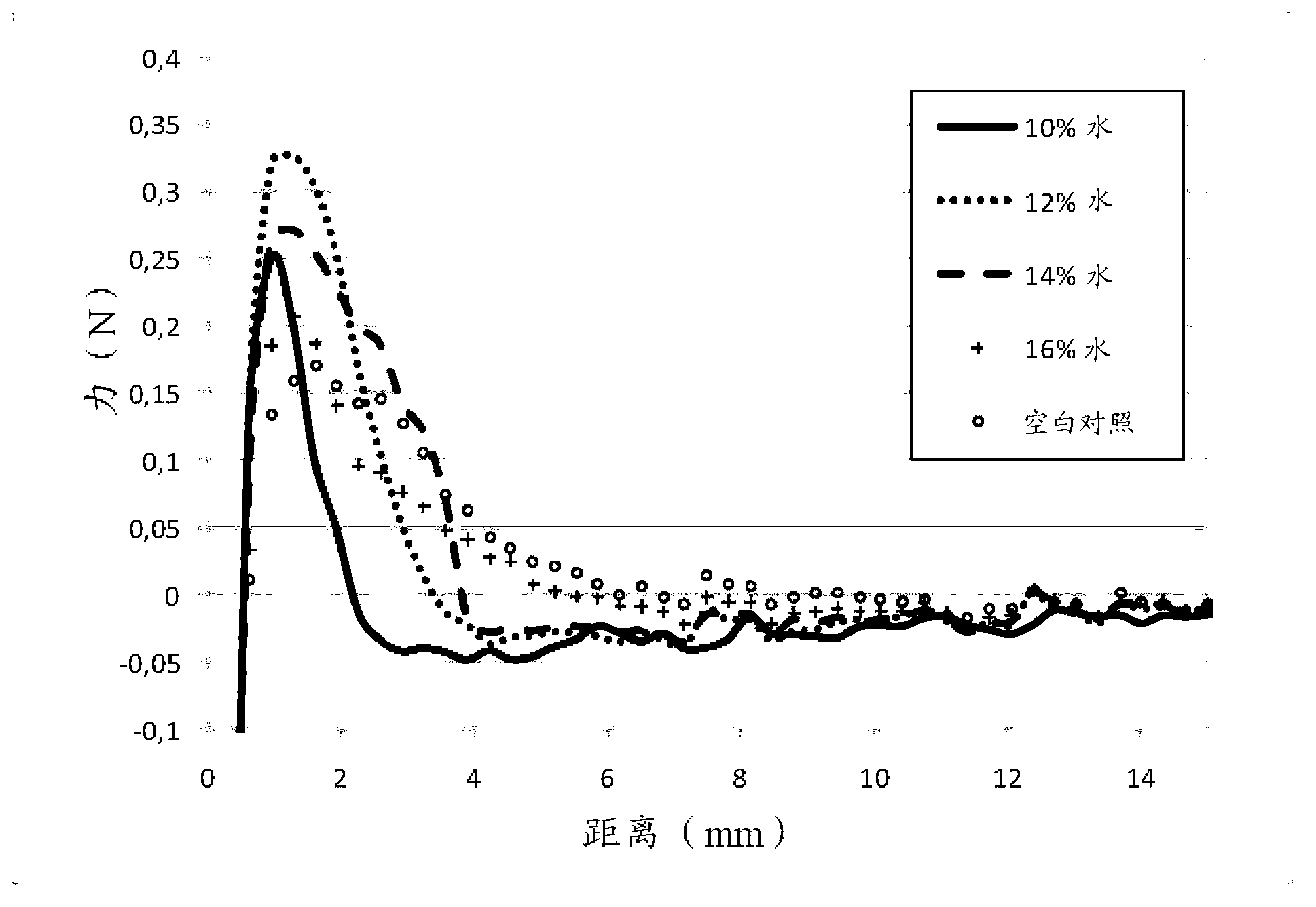
[0111] The GMOs in the prepared formulations were replaced by technical grade GMOs and other lipids as listed below. The different excipients in the composition are related to the amount of ropivacaine in the formulation. The contents of the prepared formulations are listed in Tables 4-6. All investigated lipids could form gel formulations with lamellar and cubic phase structures. Since all lipids used in this study can form gels, this allows flexibility in the choice of components used in the formulation.
[0112] Table 4. Ropivacaine, lipids – technical grade GMO, organic acid – oleic acid
[0113] Studying formulations that gel in situ
[0114]
[0115] GDOs are co-used with different brands of GMOs in Tables 5 and 6:
[0116] GMO-Monoolein (Rylo MG19, min 96% monoglycerides, max 4% diglycerides)
[0117] GDO-Glyceryl Dioleate (Rylo MG19Pharma, min 94% diglycerides, max 1% monoglycerid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com