Graph theory based multi-cell two-layer network spectrum allocation method
A spectrum allocation and multi-cell technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as unfavorable throughput, interference between macro base stations and home base stations, achieve simple channel allocation, maximize total throughput, and ensure the effect of signal-to-interference-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
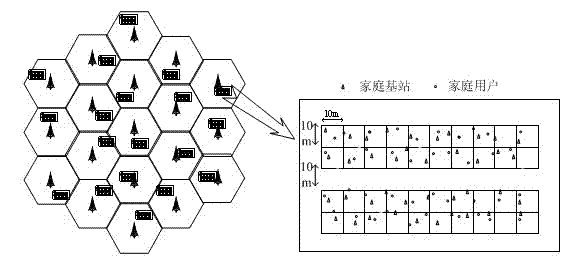
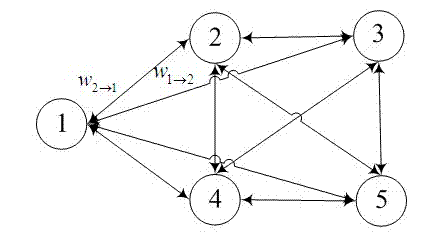
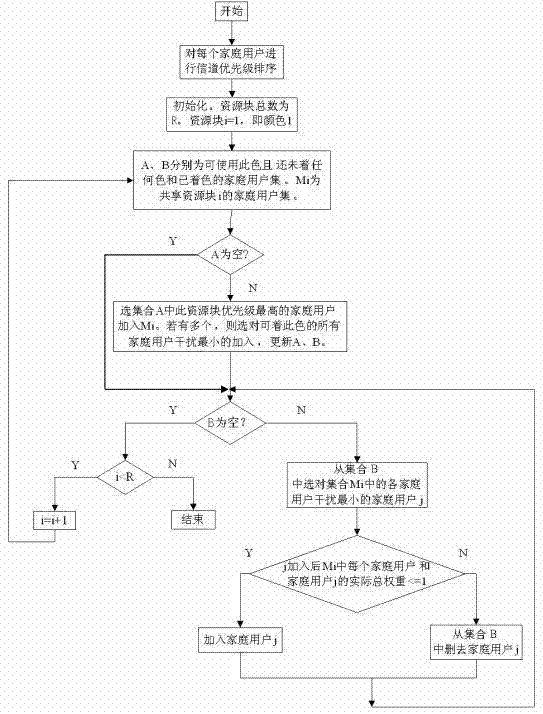
[0034] What the present invention is aimed at is the downlink OFDM system two-layer network model, as attached figure 1 shown. A multi-cell OFDM downlink system composed of L macro cells, where macro cells and home cells coexist. The macro base station is located in the center of the cell, and M macro users are randomly distributed in each macro cell. The home cell adopts the Dual stripe model, and a home cell block is randomly distributed in each macro cell, and a home base station and a home user are randomly distributed in each home cell.
[0035] The activation probability ρ is expressed as the proportion of activated home cells, and the higher the ρ, the more active home base stations. The basic spectrum resource unit in LTE is a resource block, and each downlink resource block is composed of 12 subcarriers with a bandwidth Δf=15kHz in the frequency domain, and corresponds to 0.5ms in the time domain. In this paper, resource blocks are used as the minimum allocation un...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com