Seawater desalination plant system
A technology for factories and seawater, applied in seawater treatment, comprehensive factory control, comprehensive factory control, etc., can solve the problems of high power consumption rate, power waste, large osmotic pressure difference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
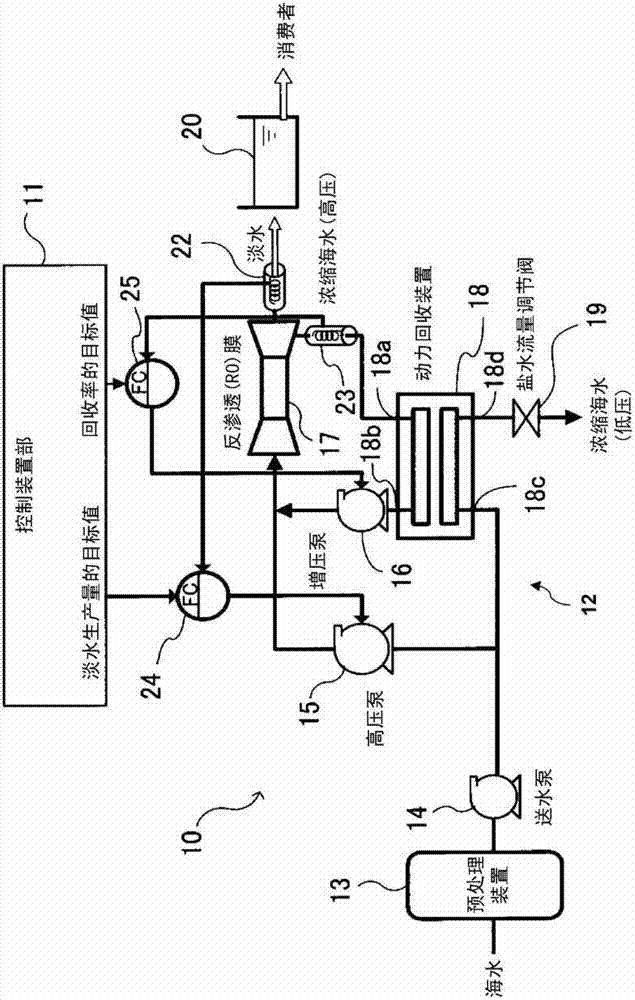
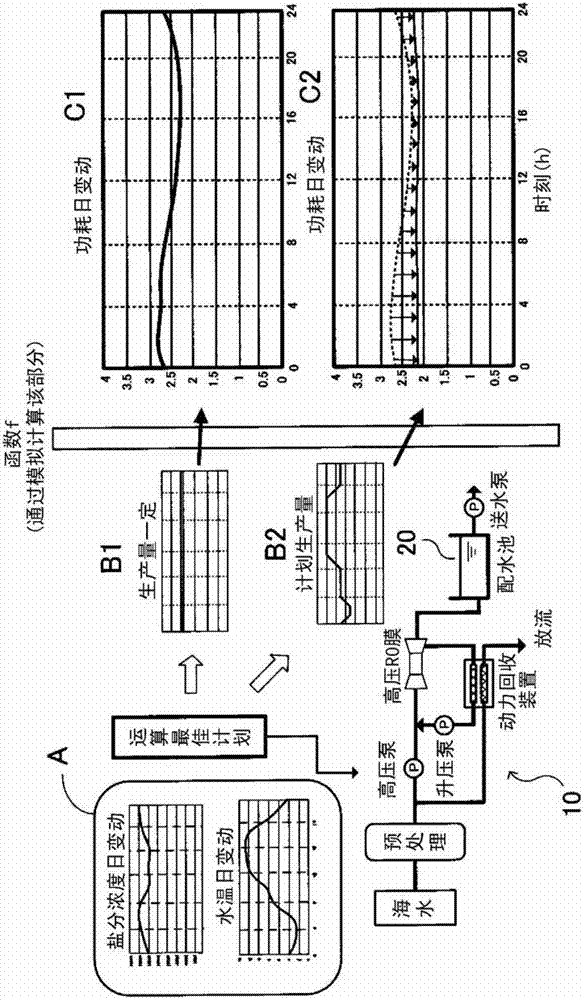
[0021] The seawater desalination plant system involved in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 It includes the factory part 10 , the control device part 11 of the factory part 10 and the water distribution tank 20 shown. The factory section 10 takes in seawater, supplies the taken seawater to a reverse osmosis membrane, produces filtered water filtered by the reverse osmosis membrane as fresh water, and supplies the produced fresh water to consumers via the water distribution tank 20 . The control device unit 11 derives a water production plan for a certain period (for example, 24 hours) that minimizes the electric power consumption rate (electric power consumption rate) per unit of fresh water production, and controls the factory unit 10 based on the derived water production plan. .
[0022] exist figure 1 Among them, the factory unit 10 of this embodiment includes a pretreatment device 13 , a water supply pump 14 , a high pressure pump 15 , a booster pump 16 , a reverse...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
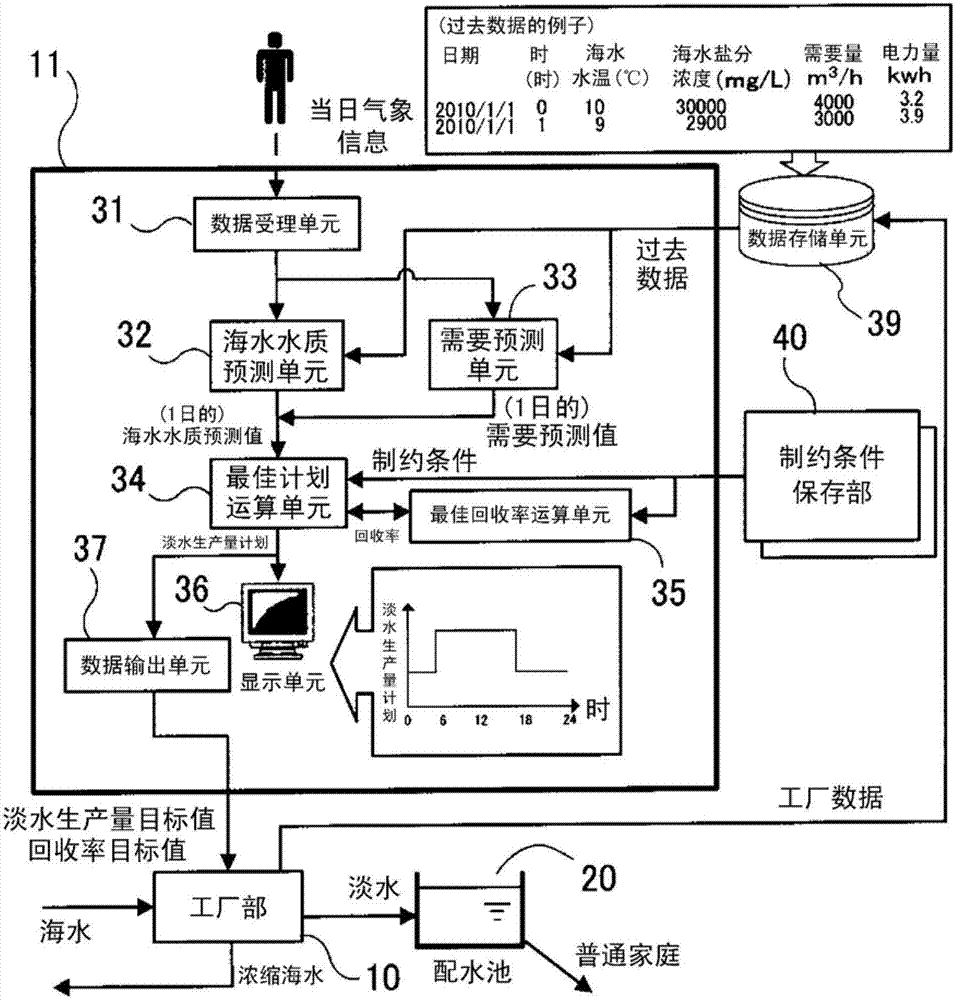
[0097] exist Image 6 In the controller unit 11 of the second embodiment shown, the figure 2 The controller unit 11 of the illustrated embodiment has a distribution tank water level monitoring unit 42 and a plan modification unit 43 added as functions. The actual measured water level of the distribution tank 20 measured by the water level measuring unit 44 is input to the distribution tank water level monitoring unit 42 .
[0098] The distribution tank water level monitoring unit 42 calculates the difference between the fresh water production volume per predetermined time of the optimal fresh water production volume plan obtained by the optimal plan calculation unit 34 and the demand per predetermined time predicted by the demand prediction unit 33. The predicted water level of the distribution tank 20 every predetermined time. The water level of the distribution tank 20 can be predicted by dividing the difference between the fresh water production and demand by the area of...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0103] Figure 7 The third embodiment shown does not have figure 2 The optimal plan calculation unit 34 and the optimal recovery rate calculation unit 35 in the first embodiment are shown. In the third embodiment, the operator determines the fresh water production amount plan and the recovery rate plan, and inputs the fresh water production amount plan to the data receiving unit 31 . In the present embodiment, the operator prepares in advance a plurality of daily fresh water production volume plans in which the daily fresh water production volume is allocated to every hour based on past empirical rules. Then, the operator selects the optimal freshwater production plan based on the day of the day, weather information, etc., and inputs the selected freshwater production plan to the data receiving unit 31 . In order to grasp whether the input fresh water production plan is good or not, the control device part 11 has a calculation unit 46 instead of the optimal plan calculation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com