AP (access point) transmitting power optimization method based on energy conservation and interference avoidance in green WLAN (wireless local area network)
A transmission power and optimization method technology, which is applied in power management, energy-saving ICT, and energy consumption reduction. The effect of frequency interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
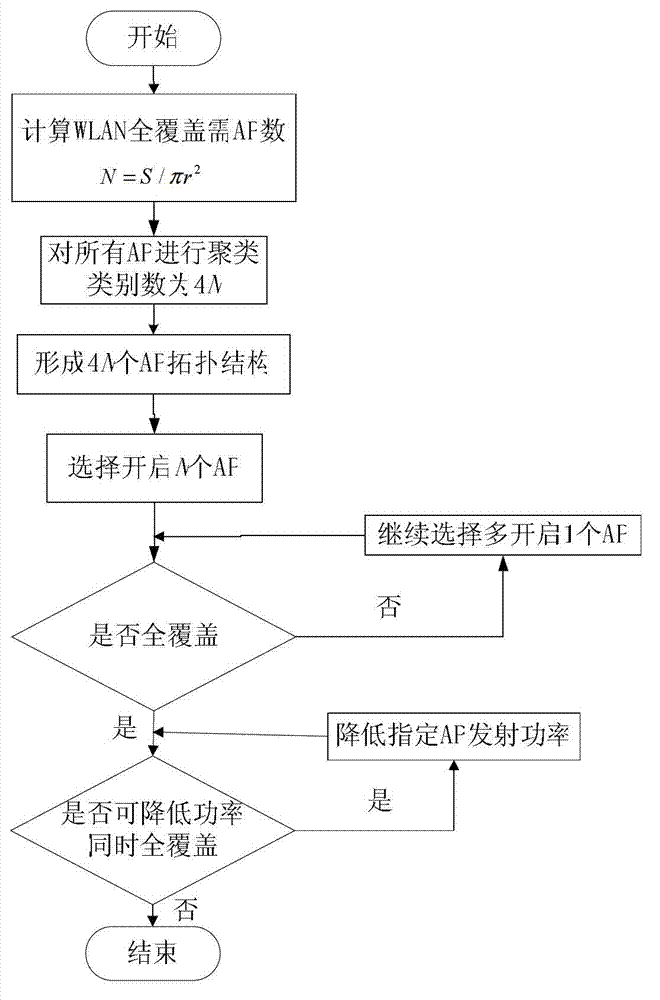
[0038] Specific implementation manner one: such as figure 1 As shown, the AP transmit power optimization method based on energy saving and interference avoidance in the green WLAN described in this embodiment is performed for APs that have been densely deployed in the WLAN, and it includes the following steps:
[0039] 1. Determine the number N of APs required for full WLAN coverage, that is, divide the total area of the WLAN area by the individual coverage area of each AP, and round up to get an integer N; this is an ideal value, in fact there will be a lot of overlapping coverage between APs In order to ensure full coverage, set the required number of APs to 4N, and then consider appropriately reducing the number of open APs;
[0040] 2. Establish a two-dimensional rectangular coordinate system, and cluster the densely deployed APs in the WLAN according to their geographical locations through a clustering algorithm. The target is 4N categories; then in each category, select t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
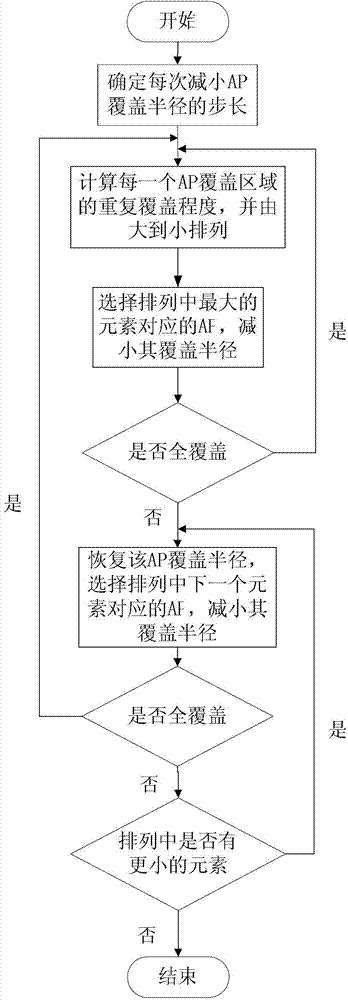
[0044] Specific implementation manner two: such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is a further limitation on specific embodiment 1:
[0045] Implementation process of AP transmit power optimization method: This process performs transmit power optimization control based on energy saving and interference avoidance for APs whose positions and numbers in the WLAN have been fixed. The present invention assumes that the AP generation power is continuously controllable. The following briefly describes the AP transmit power Relationship with coverage radius:
[0046] The channel transmission loss satisfies formula (1):
[0047] L(d)=|d| -n S(d)R(d)(1)
[0048] In formula (1), d is the transmission distance, |d| -n Is the path loss, n is a constant from 3 to 6, S(d) represents shadow fading, and R(d) represents multipath fading. It can be seen that the longer the transmission distance, the greater the fading;
[0049] The received power satisfies formula (2):
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0073] Here is an example for analysis:
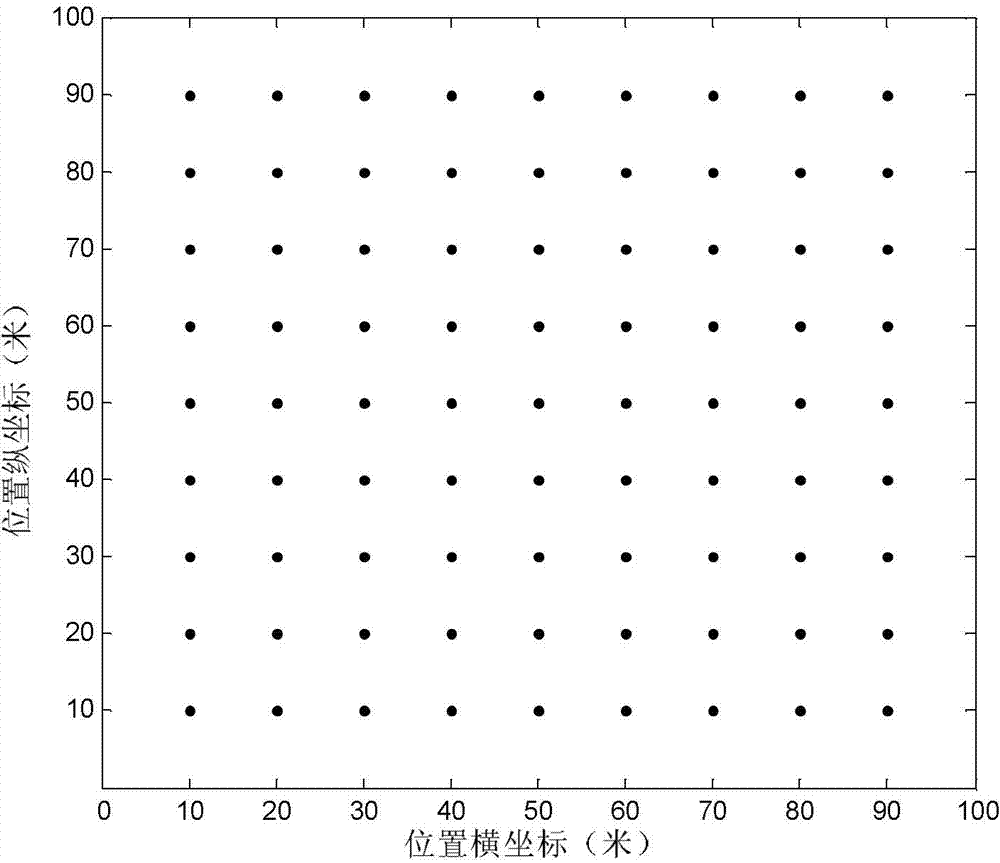
[0074] The schematic diagram of WLAN environment is as image 3 As shown, the wireless coverage area is 100m×100m, and 81 APs are evenly distributed inside. Take the initial coverage radius of the AP as: r=30m.
[0075] When each AP is turned on separately, the coverage area is: S cover =πr 2
[0076] Total coverage area of WLAN experimental scene: S total =100×100=10000m 2
[0077] In theory, the number of APs required to complete full coverage:
[0078] In order to ensure full coverage, the number of APs in the cluster center is initially selected as 4N=16.
[0079] The 81 APs are clustered according to their geographic locations through the fuzzy K-means clustering algorithm, and 4N results and corresponding central node AP coordinates are obtained. According to the "Minimum Maximum Principle", when the number of APs selected to be turned on is 9, the full coverage is satisfied, and the following Figure 4 The shown schematic diagram o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com