Method for dynamically partitioning shared cache in multi-core environment
A shared cache, dynamic technology, applied in the direction of memory address/allocation/relocation, resource allocation, memory system, etc., can solve problems such as inability to apply and adjust program cache, achieve the effect of low overhead and improve overall performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
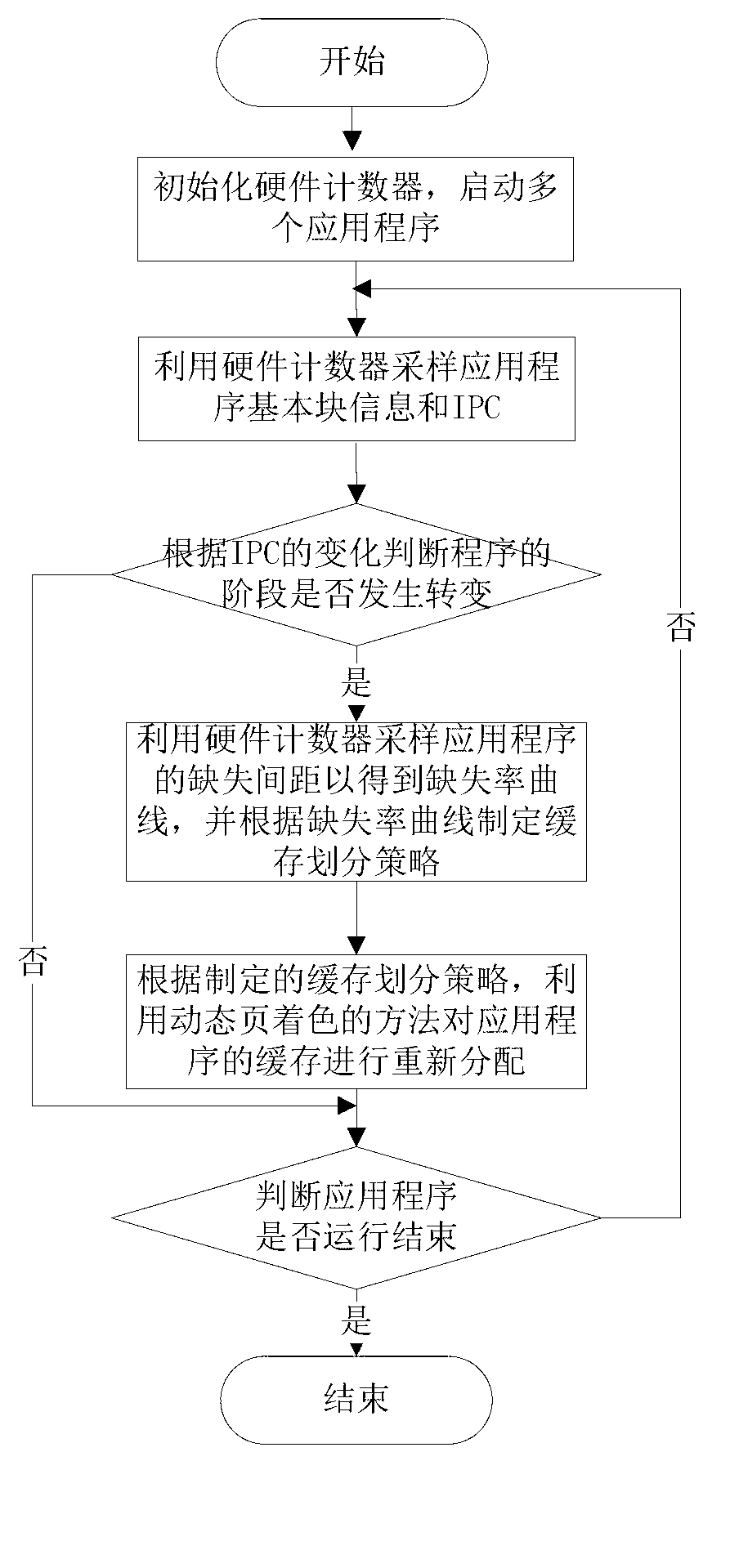
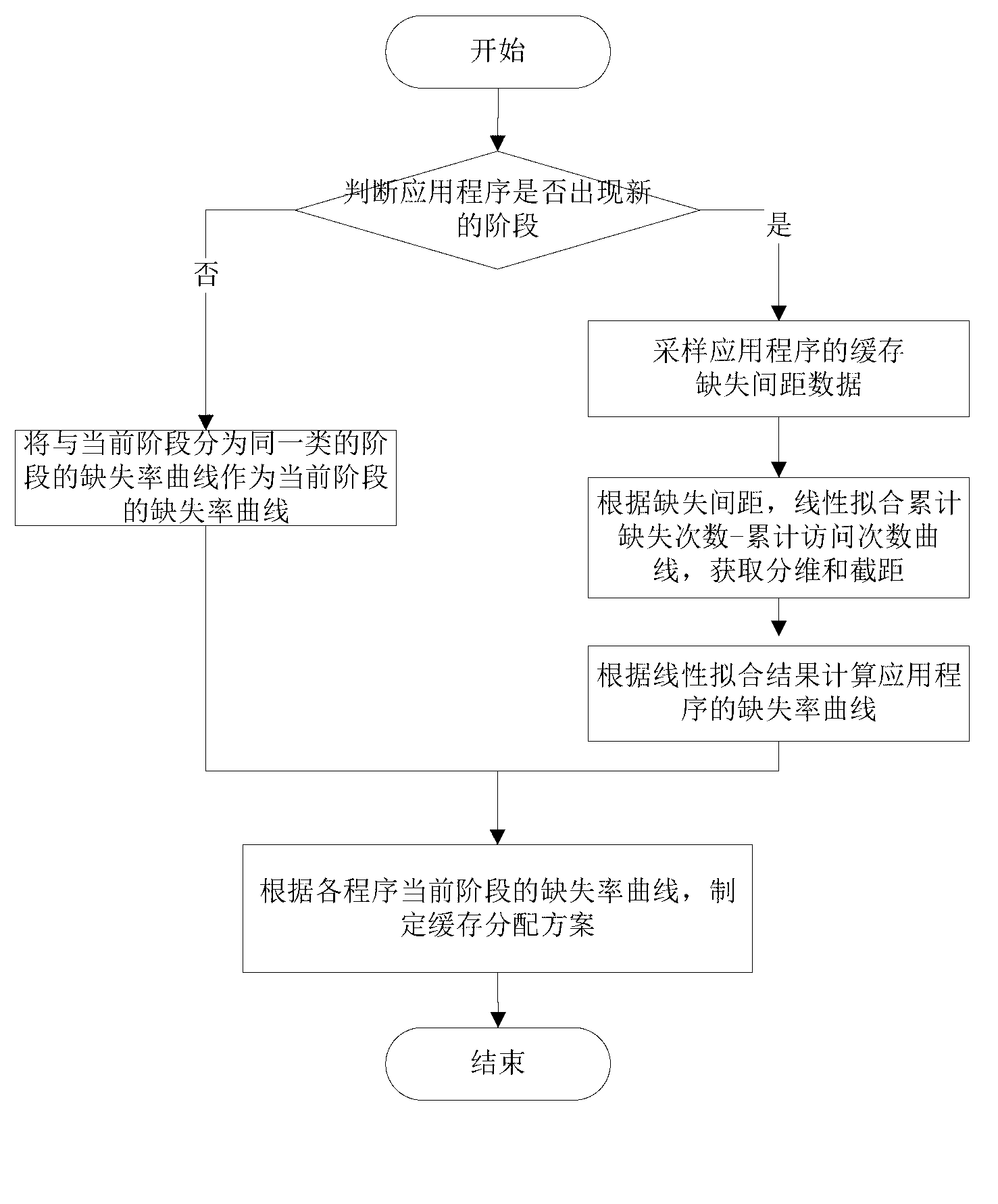
[0050] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
[0051] At first the technical terms in the present invention are explained and defined:
[0052] Sparse Basic Block Vector: SBBV (Sparse Basic Block Vector, referred to as SBBV) in English, the feature vector used in the behavior analysis of the program stage, including the address of the conditional branch instruction and the number of instructions executed between the conditional branch instructions.
[0053] Cache Missing Interval: When the cache is invalidated each time, the total number of cache accesses recorded between two invalidations;
[0054] Miss Rate Curve: It is expressed in English ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com