Method of achieving interphase short circuit fault distance measurement of line by means of single-end electric quantities
A technology of phase-to-phase short circuit and fault location, which is applied in the direction of fault location, etc., can solve the problems of high application cost, influence of ranging accuracy transition resistance, high sampling rate requirements, etc., to overcome the influence of measurement accuracy, easy program implementation, and measurement Effects from simple principles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described in detail according to the accompanying drawings.
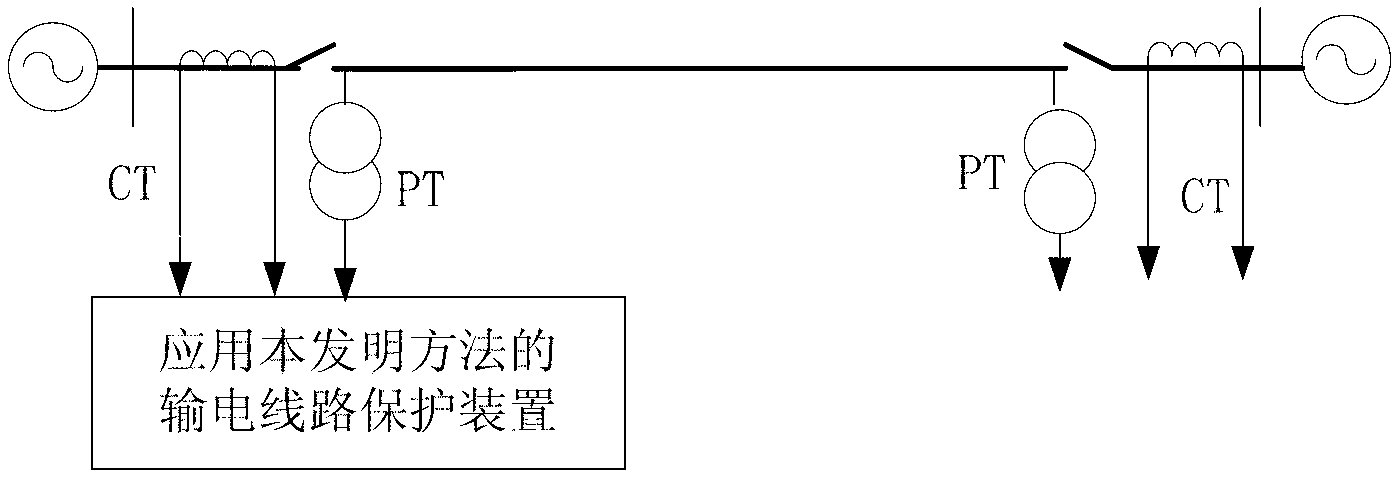
[0014] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the line transmission system applying the present invention. figure 1 Among them, PT is a voltage transformer, and CT is a current transformer. The protection device samples the voltage waveform of the voltage transformer PT and the current waveform of the current transformer CT at the installation place of the transmission line protection to obtain the instantaneous value of the voltage and current, and calculates the instantaneous value of the voltage and current obtained by sampling using the Fourier algorithm Fault phase-to-phase voltage at transmission line protection installation , fault current between phases and negative sequence current between fault phases , as the input quantity; among them, φφ=AB, BC, CA phase.
[0015] The protection device calculates the fault phase-to-phase volta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com