High-voltage direct-current grounding electrode line high-resistance fault positioning method
A technology of high-voltage direct current and positioning method, which is applied in the direction of fault location, information technology support system, etc., and can solve problems such as low voltage level of grounding electrode line, low reliability and accuracy of distance measurement, and great influence on safe operation of DC system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
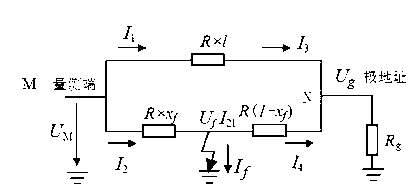
[0037] Example 1: 800kV DC ground electrode line such as figure 1 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 80km, the line impedance is: 0.00756+j0.39999Ω / km, and the pole address resistance is 0.2Ω. The data sampling rate is 6.4kHz. Ground electrode line l 2 A ground fault occurs 50km away from the measurement end, and the transition resistance is 0.2Ω.
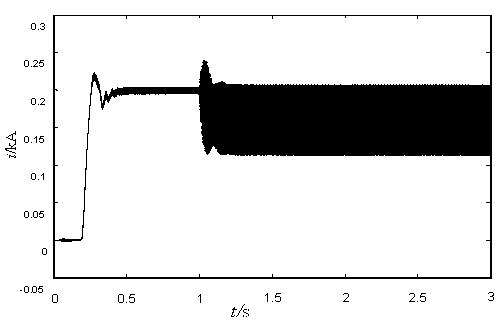
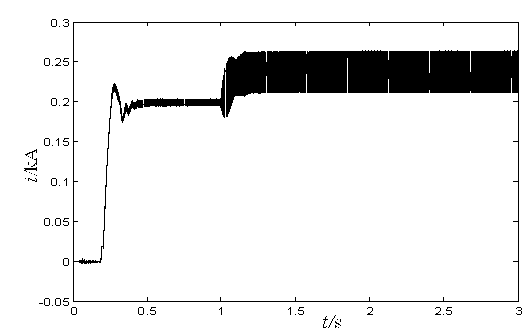
[0038] Measured ground electrode line l 2Measuring terminal current when ground fault occurs i 1 and i 2 like figure 2 , 3 shown, measure the terminal voltage u M like Figure 4 shown.
[0039] According to the specific steps of the fault location method in the foregoing summary of the invention, the fault location data is calculated as follows: Figure 5 shown. According to the obtained fault location data, the fault distance can be obtained x f =50.4km.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: 800kV DC ground electrode line such as figure 1 shown. The line parameters are as follows: the total length of the line is 80km, the line impedance is: 0.00756+j0.39999Ω / km, and the pole address resistance is 0.2Ω. The data sampling rate is 6.4kHz. Ground electrode line l 2 A ground fault occurs 50km away from the measuring end, and the transition resistance is 2Ω.
[0041] Measured ground electrode line l 2 Measuring terminal current when ground fault occurs i 1 and i 2 like Image 6 , 7 shown, measure the terminal voltage u M like Figure 8 shown.
[0042] According to the specific steps of the fault location method in the foregoing summary of the invention, the fault location data is calculated as follows: Figure 9 shown. According to the obtained fault location data, the fault distance can be obtained x f =50.3km.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Transition resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Transition resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com