Cytomegalovirus GB antigen
A cytomegalovirus and cell technology, applied in the field of immune response compositions, can solve the problems of abnormal development of the central nervous system, poor mental performance and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
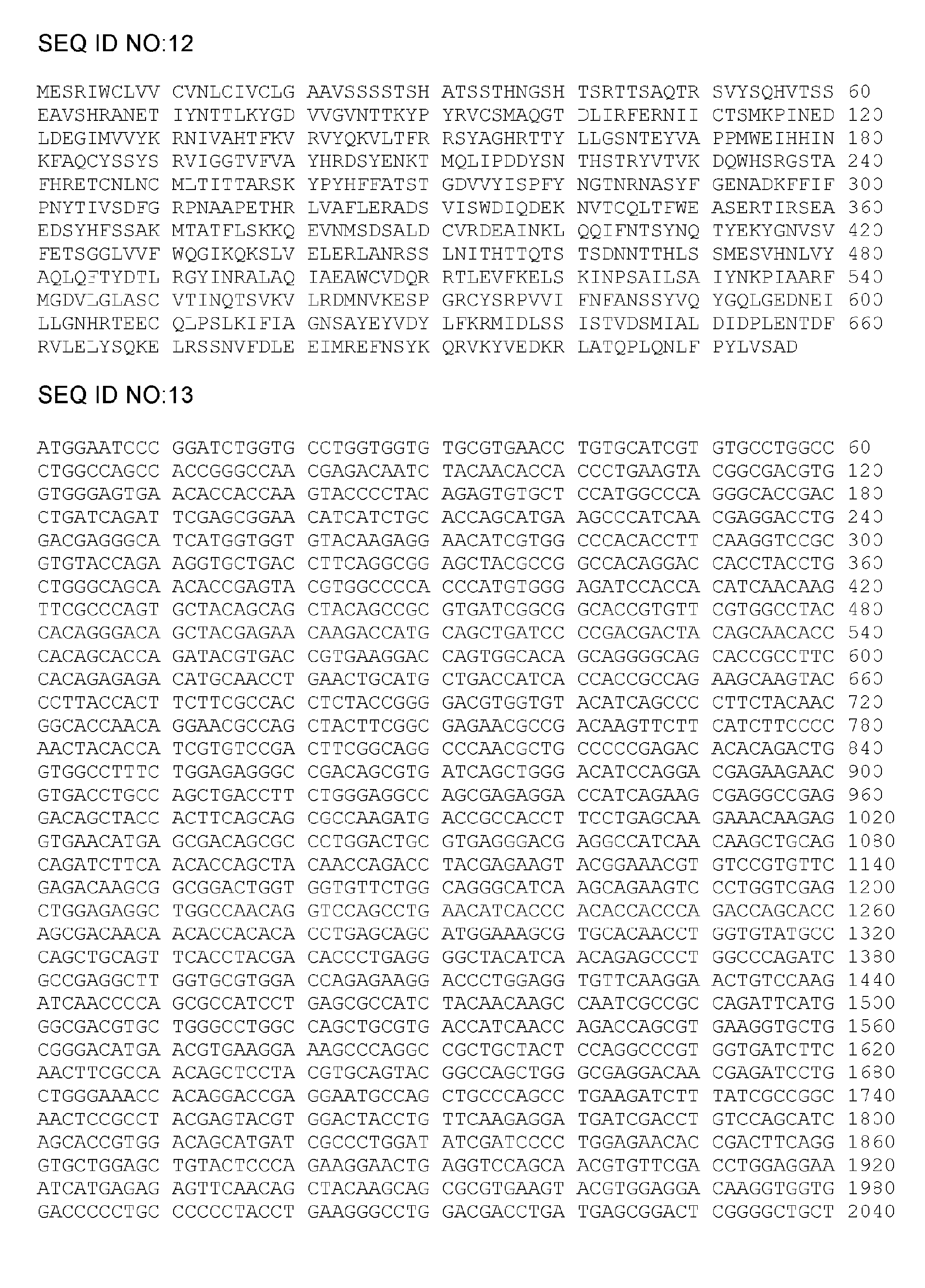
[0133] a) a cytomegalovirus (CMV) gB polypeptide, in the N-terminal to C-terminal direction, comprising: an extracellular domain comprising at least a portion of a fusion loop 1 (FL1) domain and a fusion loop 2 (FL2) domain, either Optionally at least a portion of the transmembrane (TM) domain, and at least a portion of the cytoplasmic domain, wherein at least one amino acid of the FL1 domain is substituted or deleted, and wherein the TM domain or portion thereof, if present, is non-functional.
[0134] b) The CMV gB polypeptide of embodiment a), wherein the TM domain is rendered non-functional by deletion of amino acids at positions 701-775 relative to the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or at corresponding positions in other CMV gB polypeptides .
[0135] c) The CMV gB polypeptide of embodiment a) or b), further comprising at least one amino acid substitution or deletion in the FL2 domain of the fusion loop.
[0136] d) The CMV gB polypeptide of any one of embodiments a) to ...
Embodiment 1
[0169] Embodiment 1: CMV gB polypeptide
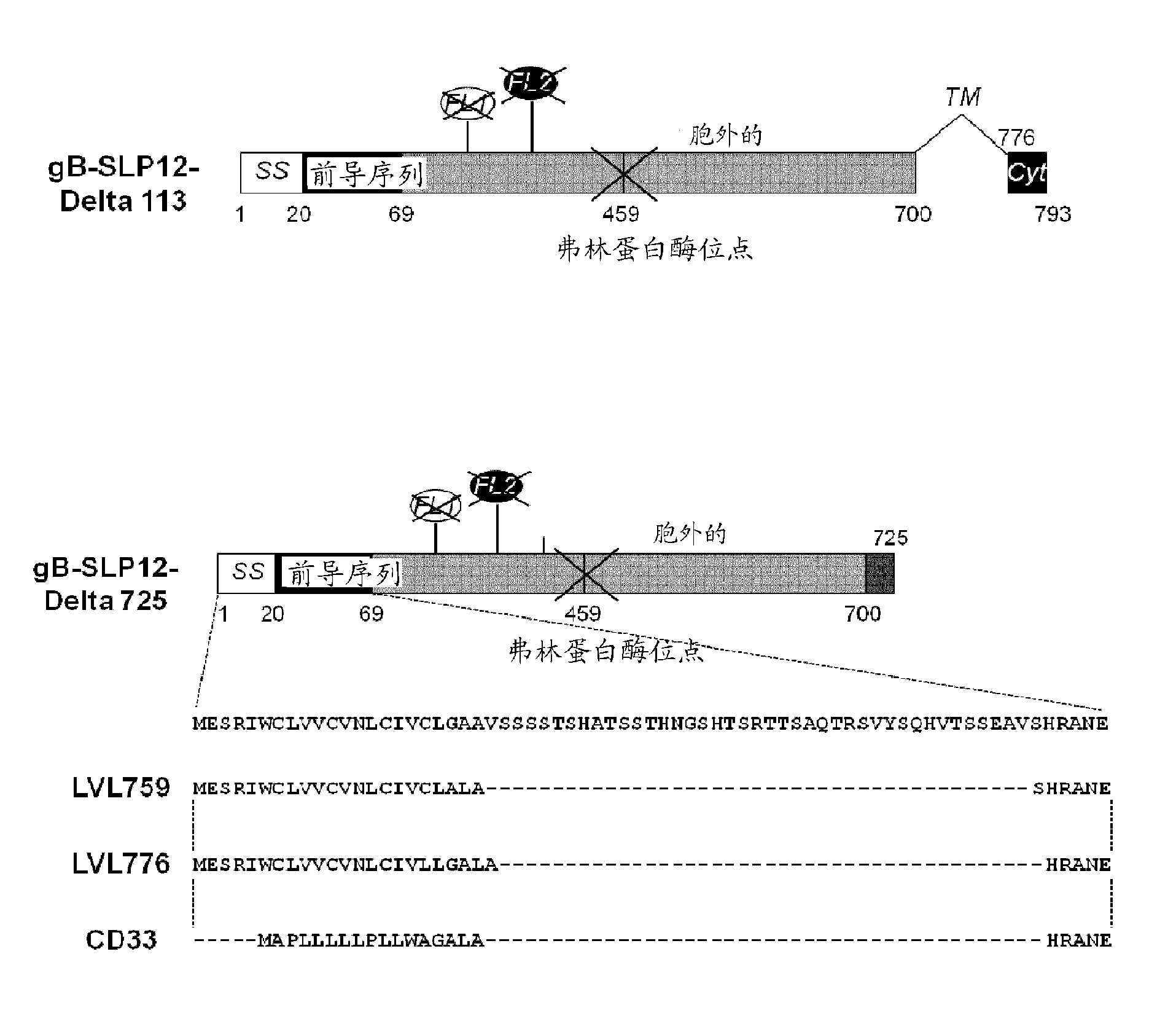
[0170] All gB polypeptide variants specified below (for illustration see figure 1 and figure 2 ) is derived from the amino acid sequence of gB of CMV strain AD169. Accordingly, when specifying mutation positions, the numbering of amino acids is relative to the sequence of AD169 CMV gB set forth in SEQ ID NO:1. In addition, the following constructs (i) all deleted the transmembrane domain (deleted amino acids 701 to 775) and (ii) all contained the following point mutations: replacing amino acid R with amino acid S, in addition to the specific mutations they each contain as described below 50 and R 357 .
[0171] Although the following variants contain a histidine tag at the C-terminus of the polypeptide used for transient transfection, the sequence of the tag is not included in the SEQ ID disclosed therein.
[0172] 1.1 gB-SLP12
[0173] The gB-SLP12 variant contains 2 series of point mutations targeting the putative fusion lo...
Embodiment 2
[0209] Example 2: Expression of CMV gB polypeptides
[0210] Using FreeStyle from Invitrogen TM MAX CHO Expression System The various DNA constructs described above were transiently transfected into CHO (Chinese Hamster Ovary) cells. A construct encoding the polypeptide gB-Delta™ was used as a control. The amino acid sequence of gB-Delta™ is given as SEQ ID NO:2. The expression vector used to express gB-DeltaTM was pMax-AD169. FreeStyle TM MAX CHO uses the CHO-S cell line (the common CHO-K1 cell line is adapted to a separate subclone in suspension) and a synthetic cationic lipid based polymer as a transfection reagent. Plasmid DNA for transfection was isolated using the Qiagen Maxiprep kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Transfection complexes were prepared as recommended by Invitrogen. Briefly, 37.5 μg plasmid and 37.5 μl FreeStyle MAX transfection reagent were diluted in 0.6 ml Opti-Pro TM in SFM medium. Immediately thereafter, add ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com