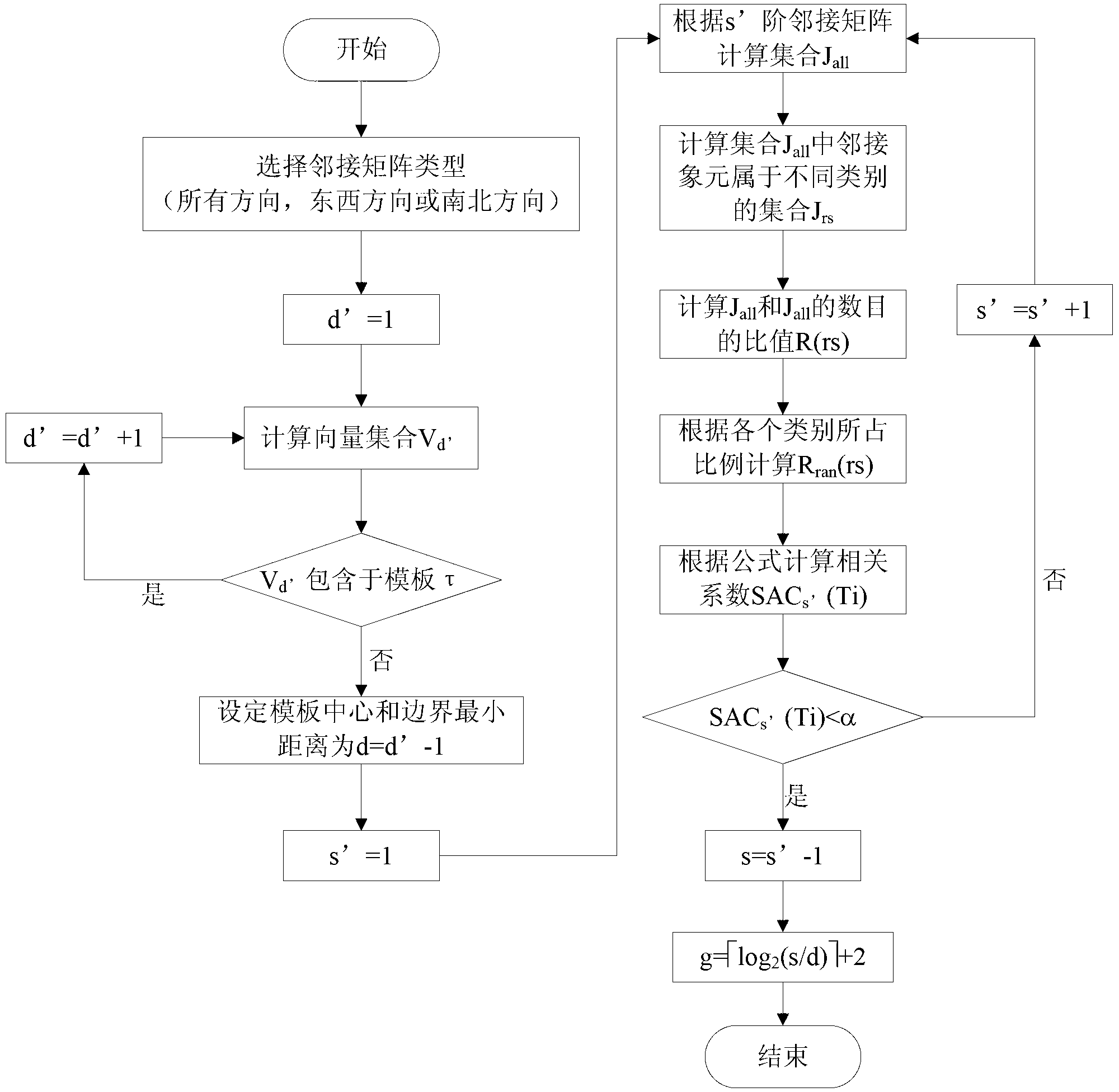Method for geography phenomenon multi-point simulation spatial scale selection
A space-scale, multi-point simulation technology, applied in the field of spatial information, to improve simulation efficiency and avoid uncertainty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
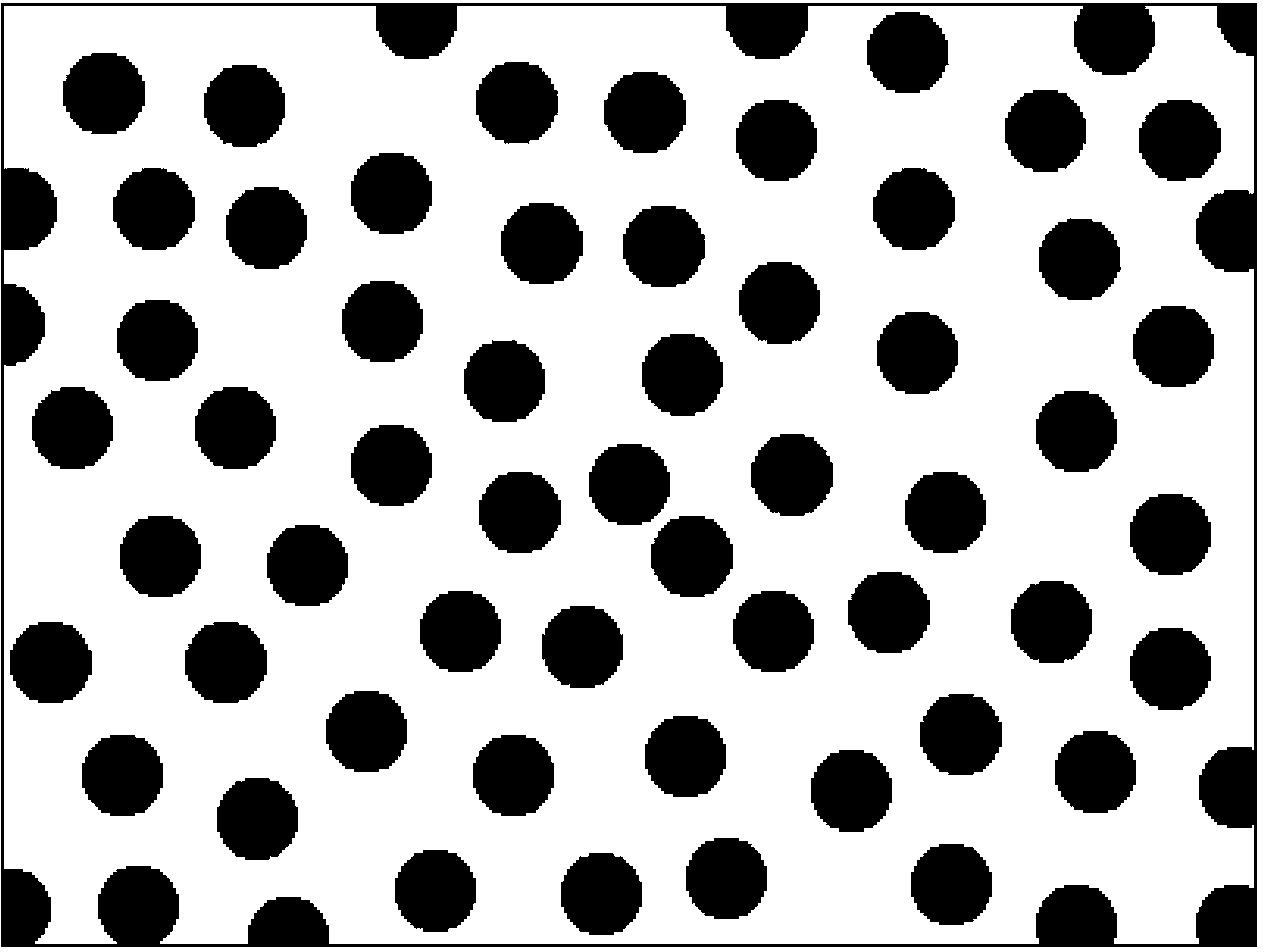
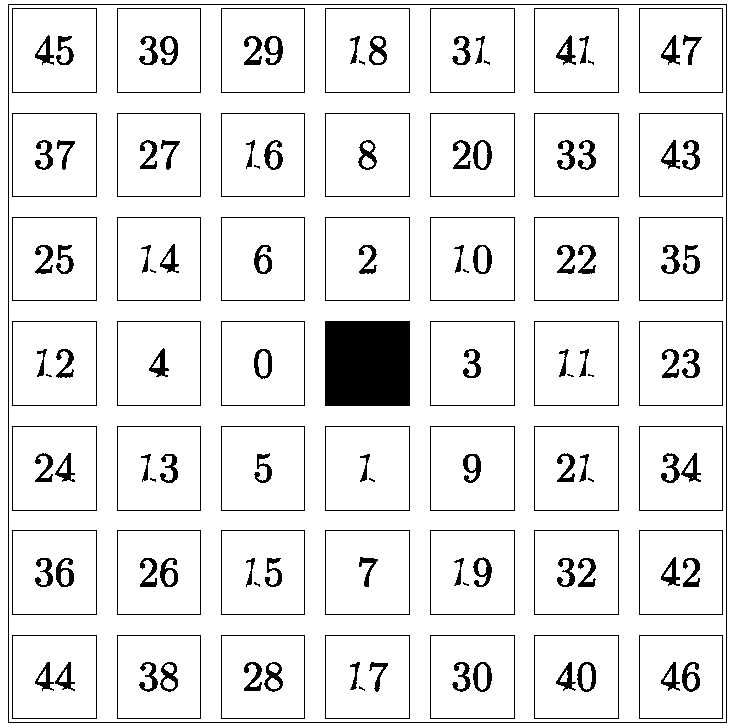
[0044] The first example simulates typical isotropic ground objects. The target ground objects used here are assumed to be circular. Here, the two types of ground objects are simply named white and black ground objects according to their colors. figure 2 is the training image required for multi-point simulation, the size is 400×300, image 3 It is a template required for multipoint simulation.
[0045] The whole implementation process can be divided into four steps:
[0046] (1) Choose an adjacency matrix.
[0047] The target object in this example is a circle, which is a typical isotropic object, so it is necessary to comprehensively consider the spatial scales in all directions. Therefore, the adjacency matrix where if|i x -j x |+|i y -j y |=k, then w k dis ( i , j ) = 1 , otherwise w ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] The first example simulates typical anisotropic objects. The target objects used here are assumed to have striped features. Here, the two types of objects are simply named as white objects and black objects according to their colors. . Figure 5 is the training image required for multi-point simulation, with a size of 250×250. image 3 It is a template required for multipoint simulation.
[0057] The entire implementation process is also divided into four steps:
[0058] (1) Choose an adjacency matrix.
[0059] The target objects in this example have typical east-west striping characteristics, so only the spatial scale in the east-west direction needs to be considered. Therefore, the adjacency matrix where if|i x -j x |=0 and |i y -j y |=k, then w k ES ( i , j ) = 1 , otherwise w ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com