Intradermal positioning device for lumbar vertebra minimally invasive surgery
A minimally invasive surgery and positioning device technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as inaccuracy and increase operation time, and achieve the effects of reducing radiation, shortening operation time, and accurate positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
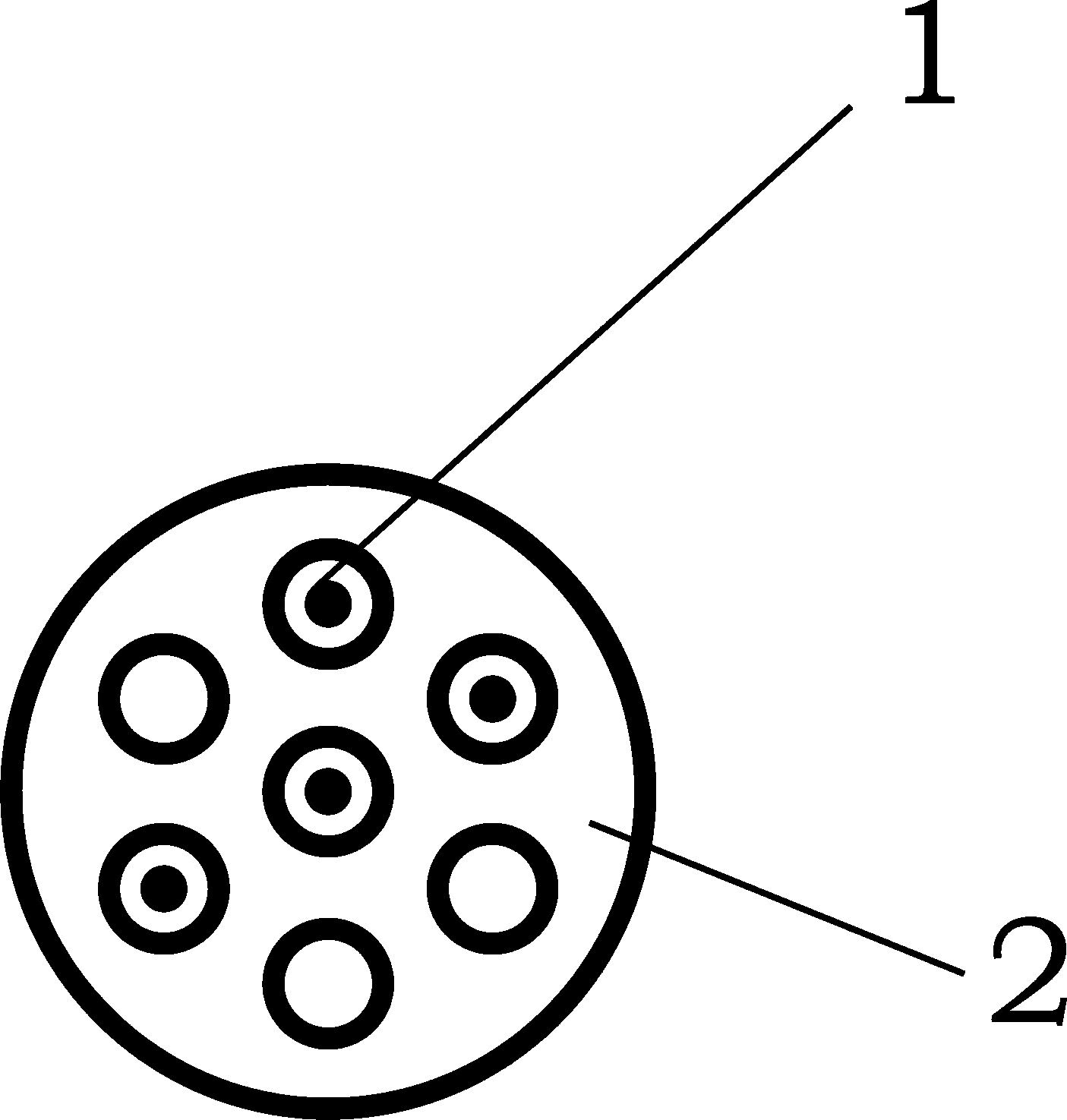
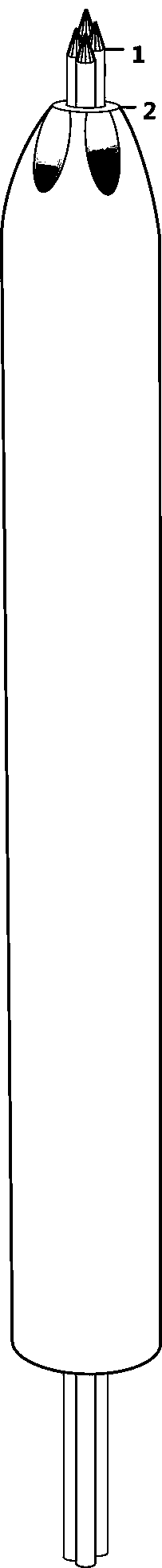
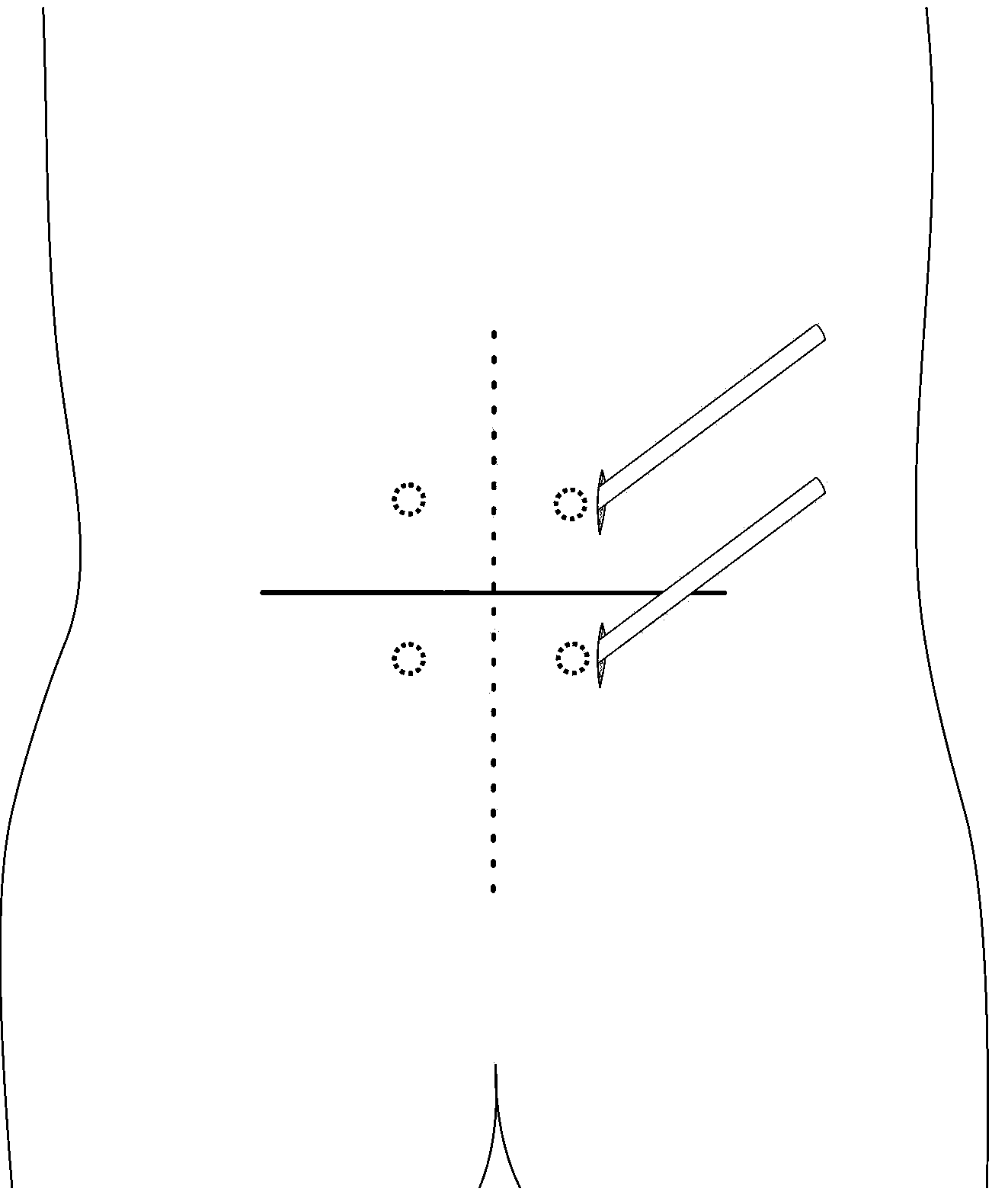
[0020] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-2 As shown in the figure, the locator 1 has a pointed tip inside the skin and a flat tip outside the skin, and several hollow channels for the insertion of the Kirschner wire 2 for intraoperative positioning. like Figure 3-Figure 8 As shown, (this part is better described in conjunction with the figure) according to the position of the pedicle marked on the body surface, the patient's fat and thin, and the head tilt angle of the vertebral body, open 1-1.5cm beside the marked position of the pedicle screw on the body surface Make a skin incision of about 1cm on the left and right (such as image 3 ), inserted into the intradermal positioning device after step-by-step expansion ( Figure 4 ), and then inject 3-4 pieces of Kirschner wires from each intradermal positioning device, carry out positive and lateral X-ray fluoroscopy, and select the appropriate Kirschner wires for puncture positioning ( Figure 5 ), remove the remaining Kirschner w...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: The inventor has done relevant clinical research on the locator. In 121 patients with lumbar disc herniation combined with lumbar instability and thoracolumbar fractures, the traditional method was compared with the new method. The positioning time was 15.12±4.69min, and the positioning times were 6.47 times. However, the positioning time of the new method using the locator is 5.51±1.32min, and the number of positioning is 2.45 times.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com